Difference between revisions of "Control Activities"
m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == What | + | == What are Control Activities? == |
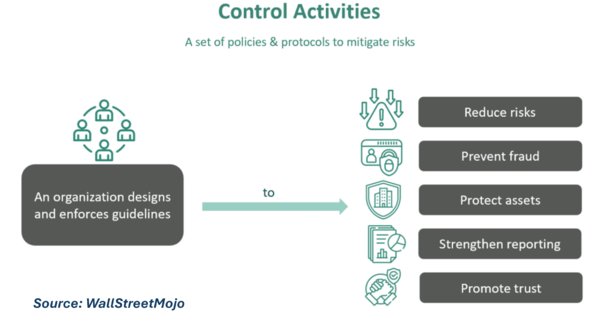
| + | '''Control Activities''' are the policies, procedures, and mechanisms an organization implements to ensure that management's directives to mitigate risks to achieving objectives are carried out. They form a fundamental part of internal control systems designed to address operational effectiveness and efficiency, reliable financial reporting, and compliance with laws and regulations. Control activities can be preventive or detective in nature and are implemented across all levels of the organization. | ||
| − | |||
| + | [[File:Control Activities.png|600px|Control Activities]] | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | == Role and Purpose of Control Activities == | ||
| + | The primary role of control activities is to prevent errors or fraud and to detect and correct them if they occur. The purposes include: | ||
| + | *Ensuring Compliance: Helping organizations comply with relevant laws, regulations, and policies. | ||
| + | *Safeguarding Assets: Protecting physical and intangible assets from loss due to fraud, waste, unauthorized use, or accidents. | ||
| + | *Promoting Operational Efficiency: Improving the efficiency and effectiveness of operations by ensuring that resources are used appropriately. | ||
| + | == Usage of Control Activities == | ||
| + | Control activities are used in various aspects of organizational operations: | ||
| + | *Authorization of Transactions: Ensuring that all transactions are authorized by personnel within predefined limits. | ||
| + | *Reconciliation: Regularly checking that records are accurate and consistent with actual transactions. | ||
| + | *Physical Controls: Implementing security measures such as locks, safes, or electronic access controls to protect assets. | ||
| + | *Information Processing Controls: Ensuring data integrity in automated systems through data entry controls, error checking, and data validation procedures. | ||
| − | == | + | == Importance of Control Activities == |
| + | Control activities are crucial because they: | ||
| + | *Mitigate Risks: Directly address identified risks, helping to prevent or reduce the impact of those risks on the organization. | ||
| + | *Enhance Accountability: Establish clear lines of responsibility and accountability within the organization. | ||
| + | *Support Decision Making: Provide accurate and reliable information that supports strategic planning and decision-making. | ||
| + | == Benefits of Control Activities == | ||
| + | Implementing effective control activities offers several benefits: | ||
| + | *Improved Reliability of Financial Reporting: Ensures that financial statements are accurate and comply with standards and regulations. | ||
| + | *Enhanced Operational Performance: Reduces inefficiencies and errors in operations, leading to better overall performance. | ||
| + | *Strengthened Compliance Posture: Helps avoid legal or regulatory penalties and damage to reputation by ensuring compliance with relevant requirements. | ||
| + | == Examples of Control Activities == | ||
| + | *Segregation of Duties: Dividing responsibilities among different people to reduce the risk of error or fraud. For example, one person handles the cash register, another approves refunds, and a third reconciles the records. | ||
| + | *Approval and Authorization: Requiring specific forms or electronic approvals for activities like expenditure, hiring, or contract agreements to ensure these actions are within organizational policies. | ||
| + | *Audit Trails: Maintaining detailed logs of transactions and changes to data, which can be reviewed to detect and trace sources of discrepancies or fraudulent activities. | ||
| + | *Employee Training and Awareness Programs: Regularly training employees on compliance requirements, ethical behavior, and procedures to prevent mishandling of resources or violations of policy. | ||
| + | Control activities are integral to an organization’s internal control system, serving as a defense mechanism against various risks that can impede the achievement of its objectives. Organizations can ensure more secure, efficient, and compliant operations by systematically implementing and reviewing these activities. | ||
| − | ==References== | + | == See Also == |
| + | *[[Internal Control]]: Explaining the broader framework within which control activities operate, including the overall objectives and importance of internal controls in corporate governance. | ||
| + | *[[Risk Management]]: Discussing how identifying, assessing, and managing risks is fundamental to formulating effective control activities. | ||
| + | *[[Audit Trail]]: Detailing how audits assess the effectiveness of control activities and ensure compliance with policies and regulations. | ||
| + | *[[Corporate Governance]]: Explaining how control activities contribute to good corporate governance by ensuring that business processes are conducted reliably and ethically. | ||
| + | *[[Compliance]]: Covering the specific control activities that ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations, which can prevent legal or regulatory penalties for the organization. | ||
| + | *[[Financial Reporting]]: Linking to how control activities relate to the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting, which is crucial for internal decision-making and investor confidence. | ||
| + | *[[Information Technology Controls (IT Controls)]]: Discussing controls related to IT systems that support business processes, including access controls, data integrity, and network security. | ||
| + | *Segregation of Duties (SoD): Detailing this specific type of control activity that is designed to prevent error and fraud by ensuring that no single individual has control over all phases of a transaction. | ||
| + | *Preventive and Detective Controls: Explaining the difference between preventive controls, which are designed to deter undesired events, and detective controls, which are aimed at discovering any undesired acts that occur. | ||
| + | *Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Discussing how SOPs enforce consistent execution of tasks, serving as a type of control activity to ensure operational efficiency and effectiveness. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:45, 8 May 2024
What are Control Activities?
Control Activities are the policies, procedures, and mechanisms an organization implements to ensure that management's directives to mitigate risks to achieving objectives are carried out. They form a fundamental part of internal control systems designed to address operational effectiveness and efficiency, reliable financial reporting, and compliance with laws and regulations. Control activities can be preventive or detective in nature and are implemented across all levels of the organization.
Role and Purpose of Control Activities
The primary role of control activities is to prevent errors or fraud and to detect and correct them if they occur. The purposes include:
- Ensuring Compliance: Helping organizations comply with relevant laws, regulations, and policies.
- Safeguarding Assets: Protecting physical and intangible assets from loss due to fraud, waste, unauthorized use, or accidents.
- Promoting Operational Efficiency: Improving the efficiency and effectiveness of operations by ensuring that resources are used appropriately.
Usage of Control Activities
Control activities are used in various aspects of organizational operations:
- Authorization of Transactions: Ensuring that all transactions are authorized by personnel within predefined limits.
- Reconciliation: Regularly checking that records are accurate and consistent with actual transactions.
- Physical Controls: Implementing security measures such as locks, safes, or electronic access controls to protect assets.
- Information Processing Controls: Ensuring data integrity in automated systems through data entry controls, error checking, and data validation procedures.
Importance of Control Activities
Control activities are crucial because they:
- Mitigate Risks: Directly address identified risks, helping to prevent or reduce the impact of those risks on the organization.
- Enhance Accountability: Establish clear lines of responsibility and accountability within the organization.
- Support Decision Making: Provide accurate and reliable information that supports strategic planning and decision-making.
Benefits of Control Activities
Implementing effective control activities offers several benefits:
- Improved Reliability of Financial Reporting: Ensures that financial statements are accurate and comply with standards and regulations.
- Enhanced Operational Performance: Reduces inefficiencies and errors in operations, leading to better overall performance.
- Strengthened Compliance Posture: Helps avoid legal or regulatory penalties and damage to reputation by ensuring compliance with relevant requirements.
Examples of Control Activities
- Segregation of Duties: Dividing responsibilities among different people to reduce the risk of error or fraud. For example, one person handles the cash register, another approves refunds, and a third reconciles the records.
- Approval and Authorization: Requiring specific forms or electronic approvals for activities like expenditure, hiring, or contract agreements to ensure these actions are within organizational policies.
- Audit Trails: Maintaining detailed logs of transactions and changes to data, which can be reviewed to detect and trace sources of discrepancies or fraudulent activities.
- Employee Training and Awareness Programs: Regularly training employees on compliance requirements, ethical behavior, and procedures to prevent mishandling of resources or violations of policy.
Control activities are integral to an organization’s internal control system, serving as a defense mechanism against various risks that can impede the achievement of its objectives. Organizations can ensure more secure, efficient, and compliant operations by systematically implementing and reviewing these activities.
See Also
- Internal Control: Explaining the broader framework within which control activities operate, including the overall objectives and importance of internal controls in corporate governance.
- Risk Management: Discussing how identifying, assessing, and managing risks is fundamental to formulating effective control activities.
- Audit Trail: Detailing how audits assess the effectiveness of control activities and ensure compliance with policies and regulations.
- Corporate Governance: Explaining how control activities contribute to good corporate governance by ensuring that business processes are conducted reliably and ethically.
- Compliance: Covering the specific control activities that ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations, which can prevent legal or regulatory penalties for the organization.
- Financial Reporting: Linking to how control activities relate to the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting, which is crucial for internal decision-making and investor confidence.
- Information Technology Controls (IT Controls): Discussing controls related to IT systems that support business processes, including access controls, data integrity, and network security.
- Segregation of Duties (SoD): Detailing this specific type of control activity that is designed to prevent error and fraud by ensuring that no single individual has control over all phases of a transaction.
- Preventive and Detective Controls: Explaining the difference between preventive controls, which are designed to deter undesired events, and detective controls, which are aimed at discovering any undesired acts that occur.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Discussing how SOPs enforce consistent execution of tasks, serving as a type of control activity to ensure operational efficiency and effectiveness.