Difference between revisions of "Enterprise Release Management (ERM)"
m (The LinkTitles extension automatically added links to existing pages (https://github.com/bovender/LinkTitles).) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Enterprise Release | + | == What is Enterprise Release Management (ERM)? == |
| + | '''Enterprise Release Management (ERM)''' is a discipline within software engineering that focuses on managing, coordinating, and implementing software releases across an enterprise. It involves overseeing the development, deployment, and integration of software updates, enhancements, and fixes to ensure that they are delivered smoothly and align with an organization's strategic goals. ERM encompasses processes and practices that help plan, schedule, control, and deploy releases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
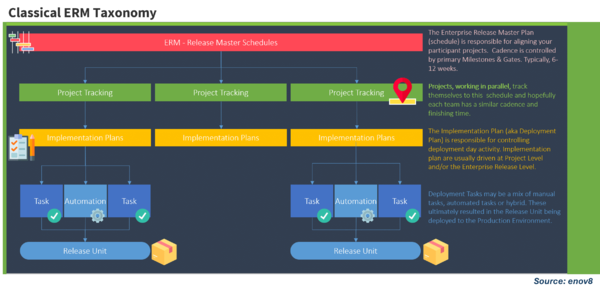
| + | [[File:Enterprise Release Management.png|600px|Enterprise Release Management Taxonomy]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Role and Purpose of Enterprise Release Management == | ||
| + | The primary role of ERM is to provide a structured environment for managing software releases that minimize the impact of changes on business operations. Key purposes include: | ||
| + | *Ensuring Stability and Reliability: Managing the risks associated with deploying new software versions by ensuring that all releases are tested and stable. | ||
| + | *Improving Efficiency: Streamlining the release process to reduce the time and resources needed for deployment. | ||
| + | *Enhancing Communication: Facilitating better communication among development, operations, and business teams to align release schedules with business requirements. | ||
| + | *Supporting Compliance: Ensuring the release process meets all regulatory compliance requirements is critical in finance and healthcare. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Components of Enterprise Release Management == | ||
| + | Effective ERM typically involves several key components: | ||
| + | *Release Policy: A set of guidelines that defines the types of releases an organization will manage, along with the standards for managing these releases. | ||
| + | *Release Planning: Involves scheduling and defining the scope of releases to align them with business goals and IT capacity. | ||
| + | *Release Coordination: Coordinating between multiple teams to ensure that all release aspects are managed effectively, from development through deployment. | ||
| + | *Environment Management: Managing the various environments (development, testing, staging, production) to ensure that they are correctly configured and that the software can be deployed reliably. | ||
| + | *Deployment Management: The technical aspect of deploying releases includes the final preparations for going live and the actual push to production environments. | ||
| + | *Release Automation: Utilizing tools and technologies to automate parts of the release process, thereby reducing manual errors and speeding up delivery. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Importance of Enterprise Release Management == | ||
| + | ERM is critical for organizations because it: | ||
| + | *Minimizes Downtime: Ensures that new software releases do not disrupt business operations. | ||
| + | *Supports Business Agility: Allows businesses to respond quickly to market changes by enabling faster and more frequent releases. | ||
| + | *Ensures Quality and Consistency: Helps maintain the quality of software deployments across different departments and teams. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Benefits of Enterprise Release Management == | ||
| + | *Implementing a robust ERM strategy offers several benefits: | ||
| + | *Enhanced Productivity: Streamlines processes, reducing the time and effort required to deploy new software releases. | ||
| + | *Reduced Risks: Minimizes the risks associated with introducing new software changes into the production environment. | ||
| + | *Better Stakeholder Satisfaction: Improves satisfaction levels among stakeholders by delivering features and fixes that more effectively and reliably meet their needs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Examples of Enterprise Release Management in Practice == | ||
| + | *Financial Services: A bank uses ERM to manage the deployment of a new online banking application, ensuring that all security measures are in place and that the release does not disrupt service to customers. | ||
| + | *Software Companies: A software company regularly updates its product suite, using ERM to manage multiple product releases simultaneously, ensuring compatibility and minimizing customer impact. | ||
| + | *Healthcare: A healthcare provider implements ERM to manage updates to its patient management system, ensuring that all releases meet strict compliance standards and improve patient care without introducing errors. | ||
| + | *Enterprise Release Management is a crucial function within larger organizations that rely on complex IT systems and software. By efficiently managing the release process, ERM helps ensure that software deployments contribute positively to the organization's operational performance and strategic goals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == See Also == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 00:05, 16 May 2024
What is Enterprise Release Management (ERM)?
Enterprise Release Management (ERM) is a discipline within software engineering that focuses on managing, coordinating, and implementing software releases across an enterprise. It involves overseeing the development, deployment, and integration of software updates, enhancements, and fixes to ensure that they are delivered smoothly and align with an organization's strategic goals. ERM encompasses processes and practices that help plan, schedule, control, and deploy releases.
Role and Purpose of Enterprise Release Management
The primary role of ERM is to provide a structured environment for managing software releases that minimize the impact of changes on business operations. Key purposes include:
- Ensuring Stability and Reliability: Managing the risks associated with deploying new software versions by ensuring that all releases are tested and stable.
- Improving Efficiency: Streamlining the release process to reduce the time and resources needed for deployment.
- Enhancing Communication: Facilitating better communication among development, operations, and business teams to align release schedules with business requirements.
- Supporting Compliance: Ensuring the release process meets all regulatory compliance requirements is critical in finance and healthcare.
Components of Enterprise Release Management
Effective ERM typically involves several key components:
- Release Policy: A set of guidelines that defines the types of releases an organization will manage, along with the standards for managing these releases.
- Release Planning: Involves scheduling and defining the scope of releases to align them with business goals and IT capacity.
- Release Coordination: Coordinating between multiple teams to ensure that all release aspects are managed effectively, from development through deployment.
- Environment Management: Managing the various environments (development, testing, staging, production) to ensure that they are correctly configured and that the software can be deployed reliably.
- Deployment Management: The technical aspect of deploying releases includes the final preparations for going live and the actual push to production environments.
- Release Automation: Utilizing tools and technologies to automate parts of the release process, thereby reducing manual errors and speeding up delivery.
Importance of Enterprise Release Management
ERM is critical for organizations because it:
- Minimizes Downtime: Ensures that new software releases do not disrupt business operations.
- Supports Business Agility: Allows businesses to respond quickly to market changes by enabling faster and more frequent releases.
- Ensures Quality and Consistency: Helps maintain the quality of software deployments across different departments and teams.
Benefits of Enterprise Release Management
- Implementing a robust ERM strategy offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Productivity: Streamlines processes, reducing the time and effort required to deploy new software releases.
- Reduced Risks: Minimizes the risks associated with introducing new software changes into the production environment.
- Better Stakeholder Satisfaction: Improves satisfaction levels among stakeholders by delivering features and fixes that more effectively and reliably meet their needs.
Examples of Enterprise Release Management in Practice
- Financial Services: A bank uses ERM to manage the deployment of a new online banking application, ensuring that all security measures are in place and that the release does not disrupt service to customers.
- Software Companies: A software company regularly updates its product suite, using ERM to manage multiple product releases simultaneously, ensuring compatibility and minimizing customer impact.
- Healthcare: A healthcare provider implements ERM to manage updates to its patient management system, ensuring that all releases meet strict compliance standards and improve patient care without introducing errors.
- Enterprise Release Management is a crucial function within larger organizations that rely on complex IT systems and software. By efficiently managing the release process, ERM helps ensure that software deployments contribute positively to the organization's operational performance and strategic goals.