Difference between revisions of "Blockchain"
m (The LinkTitles extension automatically added links to existing pages (https://github.com/bovender/LinkTitles).) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | A | + | == What is Blockchain? == |
| + | A '''blockchain''' is an electronic, secure, public, distributed, and linked list of records, called blocks, used to create a verifiable, and permanent ledger of transactions: | ||
*Each transaction is between two parties | *Each transaction is between two parties | ||
*Each transaction records the public identifier or key of both parties with a timestamp in a block | *Each transaction records the public identifier or key of both parties with a timestamp in a block | ||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
*A set of blocks chained together forms a ledger | *A set of blocks chained together forms a ledger | ||
*Each copy of the ledger is complete i.e. it contains all the blocks in a chain so it contains all transactions recorded. | *Each copy of the ledger is complete i.e. it contains all the blocks in a chain so it contains all transactions recorded. | ||
| − | *Copies of this ledger are distributed | + | *Copies of this ledger are distributed among owners |
*To alter a recorded transaction, all "owners" of the copies of a ledger must consent | *To alter a recorded transaction, all "owners" of the copies of a ledger must consent | ||
| + | The blockchain is an incorruptible digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value. | ||
| − | |||
[[File:Blockchain.png|600px|Blockchain]]<br /> | [[File:Blockchain.png|600px|Blockchain]]<br /> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
| − | == Who Created Blockchain?<ref> | + | == Who Created Blockchain?<ref>[https://lisk.io/academy/blockchain-basics/what-is-blockchain Who Created Blockchain?]</ref> == |
| + | The first recorded mention of blockchain technology came in a document, or whitepaper, published in 2008 by the mysterious founder or founders of Bitcoin, only known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Speculation about the true identity of this undeniably brilliant coder has continued to this day, with Nakamoto claiming in early correspondences to be a man living in Japan, born on 5th April 1975. However, due to his decision to document Bitcoin in English and his mastery of the language, the general belief in the blockchain community is that Nakamoto is of non-Japanese descent and either European or North American. As blockchain, and as such the Bitcoin network, is transparent, anyone can view Satoshi Nakamoto’s Bitcoin holding. He is known to currently hold roughly one million Bitcoins. | ||
| − | + | There are several theories as to why Satoshi Nakamoto decided to remain anonymous, however, the general consensus is that he was a timid developer who simply did not wish for the attention that would have undoubtedly come with creating such a disruptive technology. It is also worth knowing that Satoshi Nakamoto did not build every aspect of the blockchain from scratch. In fact, none of the technologies used in the blockchain were particularly new and had been around for several years. However, it is when they are used in combination with one another that they create the revolutionary offering that is blockchain technology. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == The Blockchain Technology<ref>[https://www.coindesk.com/information/what-is-blockchain-technology The Blockchain Technology]</ref> == | |
| − | == The Blockchain Technology<ref> | + | Blockchain represents an innovation in information registration and distribution that eliminates the need for a trusted party to facilitate digital relationships. Yet, blockchain technology, for all its merits, is not a new technology. Rather, it is a combination of proven technologies applied in a new way. It was the particular orchestration of three technologies (the Internet, private key cryptography, and a protocol governing incentivization) that made bitcoin creator Satoshi Nakamoto’s idea so useful. |
| − | |||
| − | Blockchain represents an | ||
| Line 31: | Line 30: | ||
source: [https://www.coindesk.com/information/what-is-blockchain-technology Coindesk] | source: [https://www.coindesk.com/information/what-is-blockchain-technology Coindesk] | ||
| − | The result is a | + | The result is a system for digital interactions that does not need a trusted third party. The work of securing digital relationships is implicit — supplied by the elegant, simple, yet robust network architecture of blockchain technology itself. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | *It’s Distributed: Blockchain creates a shared system of record among | + | == What Makes Blockchain Better for Business<ref>[https://www.ibm.com/blockchain/what-is-blockchain What Makes Blockchain Better for Business]</ref> == |
| + | *It’s Distributed: Blockchain creates a shared system of record among business network members, eliminating the need to reconcile disparate ledgers. | ||
*It’s Permissioned: Each member of the network must have access privileges. Information is shared only on a need-to-know basis. | *It’s Permissioned: Each member of the network must have access privileges. Information is shared only on a need-to-know basis. | ||
*It’s Immutable: Consensus is required from all members and all validated transactions are permanently recorded. Even a system administrator can’t delete a transaction. | *It’s Immutable: Consensus is required from all members and all validated transactions are permanently recorded. Even a system administrator can’t delete a transaction. | ||
| + | == See Also == | ||
| + | *[[Disruptive Technology]] | ||
| + | *[[Bitcoin]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
Latest revision as of 18:44, 7 February 2023
What is Blockchain?
A blockchain is an electronic, secure, public, distributed, and linked list of records, called blocks, used to create a verifiable, and permanent ledger of transactions:
- Each transaction is between two parties
- Each transaction records the public identifier or key of both parties with a timestamp in a block
- A block contains many transactions
- Each block is linked using a cryptographic hash to the previous and next record thereby forming a chain.
- A set of blocks chained together forms a ledger
- Each copy of the ledger is complete i.e. it contains all the blocks in a chain so it contains all transactions recorded.
- Copies of this ledger are distributed among owners
- To alter a recorded transaction, all "owners" of the copies of a ledger must consent
The blockchain is an incorruptible digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value.
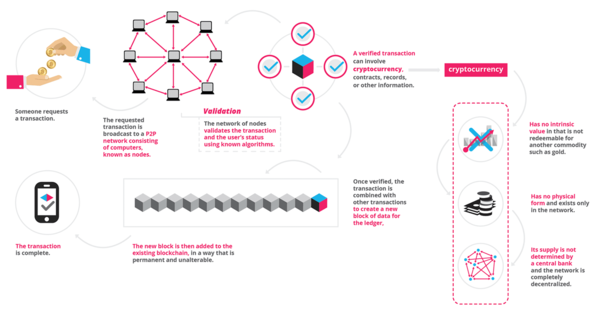
Source: Blockgeeks
Who Created Blockchain?[1]
The first recorded mention of blockchain technology came in a document, or whitepaper, published in 2008 by the mysterious founder or founders of Bitcoin, only known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Speculation about the true identity of this undeniably brilliant coder has continued to this day, with Nakamoto claiming in early correspondences to be a man living in Japan, born on 5th April 1975. However, due to his decision to document Bitcoin in English and his mastery of the language, the general belief in the blockchain community is that Nakamoto is of non-Japanese descent and either European or North American. As blockchain, and as such the Bitcoin network, is transparent, anyone can view Satoshi Nakamoto’s Bitcoin holding. He is known to currently hold roughly one million Bitcoins.
There are several theories as to why Satoshi Nakamoto decided to remain anonymous, however, the general consensus is that he was a timid developer who simply did not wish for the attention that would have undoubtedly come with creating such a disruptive technology. It is also worth knowing that Satoshi Nakamoto did not build every aspect of the blockchain from scratch. In fact, none of the technologies used in the blockchain were particularly new and had been around for several years. However, it is when they are used in combination with one another that they create the revolutionary offering that is blockchain technology.
The Blockchain Technology[2]
Blockchain represents an innovation in information registration and distribution that eliminates the need for a trusted party to facilitate digital relationships. Yet, blockchain technology, for all its merits, is not a new technology. Rather, it is a combination of proven technologies applied in a new way. It was the particular orchestration of three technologies (the Internet, private key cryptography, and a protocol governing incentivization) that made bitcoin creator Satoshi Nakamoto’s idea so useful.
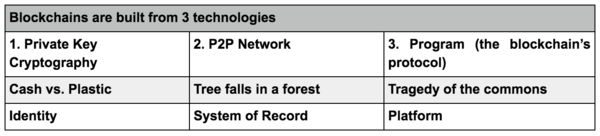
source: Coindesk
The result is a system for digital interactions that does not need a trusted third party. The work of securing digital relationships is implicit — supplied by the elegant, simple, yet robust network architecture of blockchain technology itself.
What Makes Blockchain Better for Business[3]
- It’s Distributed: Blockchain creates a shared system of record among business network members, eliminating the need to reconcile disparate ledgers.
- It’s Permissioned: Each member of the network must have access privileges. Information is shared only on a need-to-know basis.
- It’s Immutable: Consensus is required from all members and all validated transactions are permanently recorded. Even a system administrator can’t delete a transaction.
See Also
