Business Drivers
A business driver is a resource, process or condition that is vital for the continued success and growth of a business. A company must identify its business drivers and attempt to maximize any that are under their control. There are always outside business drivers that a company cannot influence, such as economic conditions or trade relations with other nations.[1]
Business drivers are the key inputs and activities that drive the operational and financial results of a business. Common examples of business drivers are salespeople, number of stores, website traffic, number and price of products sold, units of production, etc. In order to make internal choices about business strategy or build a financial model to value a company, it’s critical to gain a solid understanding of the main drivers of a business.
Identifying and monitoring the key drivers of your business is critical to boosting profitability. A key business driver is something that has a major impact on the performance of your specific business. A whole range of internal and external factors affects the performance of every small business. The secret is to focus on a handful of key drivers that:
- reflect the performance and progress of your business
- are measurable
- can be compared to a standard, such as a budget or last year's figures, or an industry average
- can be acted upon
The range of business drivers varies enormously from business to business. For example:
- sales leads in a capital goods or service business
- sales per square meter in a retail business
- machine downtime in a factory
- 'first time fix' in a maintenance business
Even direct competitors may use different drivers to improve their business performance. For example, prime location is not a key driver for an internet-based business selling computer parts, but it is for a 'bricks and mortar' competitor that relies on well-located retail stores to attract foot traffic.[2]
Key Business Drivers[3]
According to Ivy Exec’s top executive coach, Dr. Susan Bernstein, the 5 key business drivers that leaders focus on the most are as follows:
- Profitability: Are we continuously driving revenue up and costs down?
- Productivity: Are we producing our goods and services in a way that is ever-more efficient and effective?
- Time to Market: Are we moving from concept to sale fast enough to keep a competitive edge?
- Customer Satisfaction: Are we making our customers happy enough to become and remain loyal fans?
- Stakeholder Impact: Are we performing in a way that benefits stakeholders at all levels?
Reporting on Business Drivers[4]
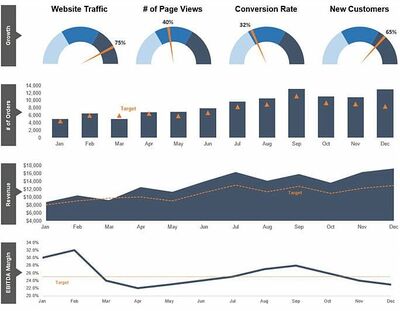
For any professional working in financial planning and analysis (FP&A), a big part of the job will be reporting on key business drivers with charts, graphs, and tables. Once the data has been collected, the job of the financial analyst is to present it in a way that’s easy to understand. A popular method is to create a dashboard that summarizes the key metrics and that helps executives and key decision-makers visualize what’s happening in the business.
See Also
Business
Business-to-Business (B2B)
Business Application
Business-Driven Development (BDD)
Business-to-Business Gateway
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
Business Accelerator
Business Activity Monitoring (BAM)
Business Analysis
Business Analytics
Business Application
Business Application Programming Interface (BAPI)
Business Architecture
Business Asset
Business Capability
Business Capability Modeling
Business Ethics
Business Case
Business Centric Methodology (BCM)
Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
Business Cycle
Business Diversification
Business Driven Technology
Business Drivers
Business Ecosystem
Business Environment and Internal Control Factors (BEICF)
Business Excellence
Business Expansion
Business Function
Business Function Model
Business IT Alignment
Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Business Incubator
Business Insurance
Business Integration
Business Intelligence
Business Interruption Insurance
Business Life Cycle
Business Logic
Business Management System (BMS)
Business Model Innovation (BMI)
Business Model for Information Security (BMIS)
Business Motivation Model (BMM)
Business Objects
Business Operations
Business Oriented Architecture (BOA)
Business Mission
Business Vision
Business Model
Business Goals
Business Objective
Corporate Structure
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
IT Strategy (Information Technology Strategy)
IT Governance
Enterprise Architecture
IT Sourcing (Information Technology Sourcing)
IT Operations (Information Technology Operations)
References
- ↑ Definition - What does Business Driver mean? Techopedia
- ↑ Identifying your Business Drivers NAB
- ↑ 5 Key Business Drivers Ivy Exec
- ↑ Reporting on Business Drivers Corporate Finance Institute
Further Reading
- How to identify the Business Driver of my company? evolve design
- Strategic Planning: Developing Business Drivers for Performance Improvement cmu.edu