Cognitive Computing
Cognitive Computing (CC) is the simulation of human thought processes in a computer model. It is a technology platform based on the scientific disciplines of artificial intelligence and signal processing. In summary, a cognitive computer ploughs through un/structured data, to find hidden knowledge and present data in an actionable form. It is worth noting that CC is an iterative process, with humans verifying or discarding any new discoveries. This allows the system to ‘learn’ over time, and become better at identifying patterns.[1]
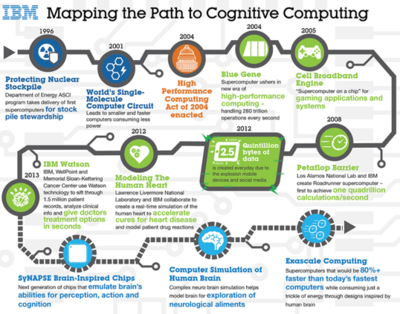
Looking back at the origin of Cognitive computing, it was first mentioned by Alan Turing in 1950, through his ‘Computing Machinery and Intelligence’ paper. He proposed the Turing Test, to assess a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent human behavior. The science behind Cognitive computing has only recently gained momentum, with advancements made within fields such as data mining and natural language processing. The graph below shows a timeline of the progression of Cognitive computing:
- ↑ Definition - What Does Cognitive Computing mean? Stanford.edu