Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA)
Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA) is a set of security services and frameworks that allow the creation of a secure infrastructure for client/server applications and services. It is a secure application development framework that equips applications with security capabilities for delivering secure Web and e-commerce applications.[1]
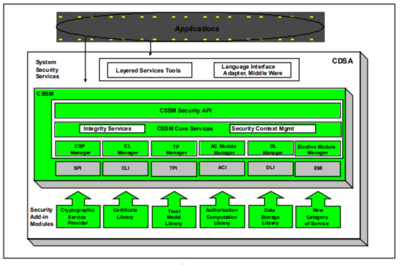
CDSA Layers[2]
CDSA is made up of three basic layers:
- System Security Services
- The Common Security Services Manager (CSSM)
- Security Add -in Modules
- System Security Services: System Security Services are bet ween applications and CSSM services. Software at this layer provides a high -
level abstraction of security services such as secure e-mail, secure file systems, or secure communications. Applications can invoke the CSSM APIs directly, or use these layered services t o access security services on a platf orm.
- The Common Security Service Manager (CSSM): CSSM provides a set of core services that are common to all categories of security services. CSSM defines five basic categories of services:
- Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) modules: CSPs perform crypt ographic operations such as bulk encrypting, digesting, and digital signat ures.
- Trust Policy (TP) modules: TPs implement policies defined by authorities and institutions and set the level of trust required to carry out
specific actions (such as issuing a check or gaining access to confidential intellectual property).
- Certificate Library (CL) modules: CLs manage c ertif icates and revocation list s, and access t o remote signing capabilities such as Certification Authorities (CA).
- Data Storage Library (DL) modules: DLs provide stable storage for security-related data objects, including certificates cryptographic keys and policy objects.
- Authorization Computation (AC) modules: ACs define a general authorisation evaluation service that computes whether a set of credentials and samples are authorized to perform a specific operation on a specific object.
- Elective (EM) Modules: EMs add new and compelling security features not encompassed by the current set of service modules. For example one new feature that vendors might add to CDSA is a biometrics authentication. In addition, CSSM provides two additional core services:
- Integrity Services: The int egrity services are used by CSSM itself to verify and guarantee the integrity of all the other components within the CSSM environment
- Security Context Management: CSSM provides context management functions (such as session inf or mation) to facilitate applications to utilise
the security services
- Security Add-in Modules: This layer is made up of service provider modules that offer basic components — cryptographic algorithms,base certificate manipulation facilities, and storage etc.
- ↑ Definition - What Does Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA) Mean? Techopedia
- ↑ CDSA Layers GIAC