Customer Data
Customer Data is the behavioral, demographic and personal information about customers collected by businesses and marketing companies to understand, communicate and engage with customers. Customer data is defined as the information your customers provide while interacting with your business via your website, mobile applications, surveys, social media, marketing campaigns, and other online and offline avenues. Customer data is a cornerstone to a successful business strategy. Data-driven organizations realize the importance of this and take action to ensure that they collect the necessary customer data points that would enable them to improve customer experience and fine-tune business strategy over time.[1]
Businesses today are awash in more data than ever before. There’s transactional data, demographic data, and virtually infinite amounts of behavioral data. Add it all up and you’ve got data from anonymous ad impressions to known customer purchases, all the way through to product usage and customer service. Customer data is a superset of all this data together. Typically this data is stored in silos, whether organizational or technological, making it very difficult for companies to provide consistent customer experiences across various channels and consumer devices.[2]
Types of Customer Data[3]
There are four main kinds of customer data that CDPs collect and organize.
- Identity Data: Identity data builds the foundation of each customer profile in a CDP. This type of data allows businesses to uniquely identify each customer and prevent costly replications. Identity data includes:
- Name information, such as first and last name
- Demographic information, such as age and gender
- Location information, such as address, city, and zip code
- Contact information, such as phone number and email address
- Social information, such as Twitter handle and LinkedIn address
- Professional information, such as job title and company
- Account information, such as company-specific user IDs and account numbers
- Descriptive Data: Descriptive data expands on identity data and gives you a fuller picture of your customer. The categories of descriptive data will vary based on the type of company. For example, a car dealership may collect lifestyle details about their customers’ cars, whereas a diaper company would collect details about the number of children in customers’ families. Descriptive data includes:
- Career information, such as previous employers, industry, income, and job level
- Lifestyle information, such as the type of home, vehicle, and pet
- Family information, such as the number of children and marital status
- Hobby information, such as magazine subscriptions and gym memberships
- Quantitative or Behavioral Data: Quantitative data allows businesses to understand how each customer has engaged with their organization, whether through certain actions, reactions, or transactions. Quantitative data includes:
- Transaction information, such as the number and type of purchased or returned products, the number of abandoned carts, and order dates
- This information also includes RFM analysis — recency (How recent did this customer make a purchase?), frequency (How often does this customer make a purchase?), and monetary value (How much does this customer spend on a purchase?)
- Email communication information, such as email opens, email click-throughs, email responses, and dates
- Online activity information, such as website visits, website click-throughs, product views, and social media engagement
- Customer service information, such as communication dates, query details, and service representative details
- Transaction information, such as the number and type of purchased or returned products, the number of abandoned carts, and order dates
- Qualitative Data: Qualitative data provides context for customer profiles; it gives customer data personality. This type of data collects any motivations, opinions, or attitudes expressed by a business’s customers — whether relevant to the company or not. Qualitative data includes:
- Motivation information, such as How did you hear about us?, Why did you purchase this?, or What made you choose this product over others?
- Opinion information, such as How would you rate this product?, How would you rate our customer service?, or How likely are you to recommend us?
- Attitude information, such as favorite color, animal, textile, or food
Customer Data - Ownership[4]
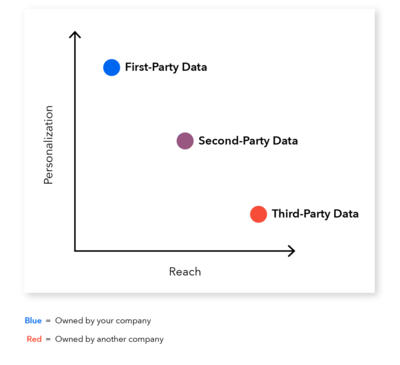
Customer data is not only a valuable asset but also a responsibility. With growing concerns around online privacy, companies must now speak to the source, ownership and distribution of their customers’ data. Luckily, most modern companies can choose how and where to collect and use their data. Customer data falls into three types: first-, second- and third-party data, each having implications regarding privacy.
- First-Party Data: First-party data is information collected and owned by the company with which a user has interacted firsthand. Companies collect their customers’ behaviors, demographics and preferences through in-house software or systems for use in marketing campaigns or product development.
- Second-Party Data: Second-party data describes first-party data that companies share with trusted partners. This customer data, the exchange of which is limited to those partnerships, enables marketers to reach a wider audience while still delivering personalized content.
- Third-Party Data: Third-party data gets collected by an outside source that has had no direct relationship with the user. This data gets stored and distributed to companies targeting large audiences, striving to cast wide marketing nets with little personalization.