Difference between revisions of "Digital Watermarking"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
*Hidden communication<ref>What does Digital Watermarking mean? [https://www.techopedia.com/definition/24927/digital-watermarking Techopedia]</ref> | *Hidden communication<ref>What does Digital Watermarking mean? [https://www.techopedia.com/definition/24927/digital-watermarking Techopedia]</ref> | ||
| − | Digital Watermarking Lifecycle Phases | + | |
| + | == Digital Watermarking Lifecycle Phases<ref>Digital Watermarking Lifecycle Phases [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_watermarking Wikipedia]</ref> == | ||
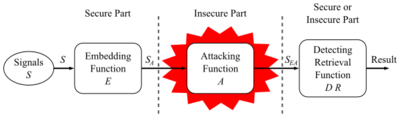
The information to be embedded in a signal is called a digital watermark, although in some contexts the phrase digital watermark means the difference between the watermarked signal and the cover signal. The signal where the watermark is to be embedded is called the host signal. A watermarking system is usually divided into three distinct steps, embedding, attack, and detection. In embedding, an algorithm accepts the host and the data to be embedded, and produces a watermarked signal. | The information to be embedded in a signal is called a digital watermark, although in some contexts the phrase digital watermark means the difference between the watermarked signal and the cover signal. The signal where the watermark is to be embedded is called the host signal. A watermarking system is usually divided into three distinct steps, embedding, attack, and detection. In embedding, an algorithm accepts the host and the data to be embedded, and produces a watermarked signal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:General digital watermark lifecycle phases.png|400px|General digital watermark lifecycle phases]]<br /> | ||
Then the watermarked digital signal is transmitted or stored, usually transmitted to another person. If this person makes a modification, this is called an attack. While the modification may not be malicious, the term attack arises from copyright protection application, where third parties may attempt to remove the digital watermark through modification. There are many possible modifications, for example, lossy compression of the data (in which resolution is diminished), cropping an image or video, or intentionally adding noise. | Then the watermarked digital signal is transmitted or stored, usually transmitted to another person. If this person makes a modification, this is called an attack. While the modification may not be malicious, the term attack arises from copyright protection application, where third parties may attempt to remove the digital watermark through modification. There are many possible modifications, for example, lossy compression of the data (in which resolution is diminished), cropping an image or video, or intentionally adding noise. | ||
Revision as of 20:15, 6 January 2021
Digital Watermarking is the method of embedding data into digital multimedia content. This is used to verify the credibility of the content or to recognize the identity of the digital content's owner. Digital watermarking can be employed for multiple purposes, such as:
- Copyright protection
- Source tracking
- Broadcast tracking, such as watermarked videos from global news organizations
- Hidden communication[1]
Digital Watermarking Lifecycle Phases[2]
The information to be embedded in a signal is called a digital watermark, although in some contexts the phrase digital watermark means the difference between the watermarked signal and the cover signal. The signal where the watermark is to be embedded is called the host signal. A watermarking system is usually divided into three distinct steps, embedding, attack, and detection. In embedding, an algorithm accepts the host and the data to be embedded, and produces a watermarked signal.
Then the watermarked digital signal is transmitted or stored, usually transmitted to another person. If this person makes a modification, this is called an attack. While the modification may not be malicious, the term attack arises from copyright protection application, where third parties may attempt to remove the digital watermark through modification. There are many possible modifications, for example, lossy compression of the data (in which resolution is diminished), cropping an image or video, or intentionally adding noise.
Detection (often called extraction) is an algorithm which is applied to the attacked signal to attempt to extract the watermark from it. If the signal was unmodified during transmission, then the watermark still is present and it may be extracted. In robust digital watermarking applications, the extraction algorithm should be able to produce the watermark correctly, even if the modifications were strong. In fragile digital watermarking, the extraction algorithm should fail if any change is made to the signal.
The Future of Digital Watermarking[3]
A number of companies, such as the Digimarc Corporation, Sony and IBM have introduced digital watermarking software applications that allow individuals to imbed watermarks within image, audio and video files to protect them from copyright infringement. The watermarks may be viewed with software and can reveal either a unique identification code that can be traced to the copyright owner or specific information about the copyright owner.
Companies are also offering on-line tracking services so that the copyright owner can see how the owner's materials are used via the Web. These processes will continue to help the fight against electronic copyright infringement.
- ↑ What does Digital Watermarking mean? Techopedia
- ↑ Digital Watermarking Lifecycle Phases Wikipedia
- ↑ The Future of Digital Watermarking Legal Zoom