Difference between revisions of "Digital Watermarking"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Classification of Digital Watermarking Techniques<ref>Classification of Digital Watermarking Techniques [https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ervin_Sejdic/publication/313793218_Digital_Watermarking/links/5a5f85730f7e9b964a1cc690/Digital-Watermarking.pdf Srdjan Stankovic, Irena Orovic, Ervin Sejdic]</ref> == | == Classification of Digital Watermarking Techniques<ref>Classification of Digital Watermarking Techniques [https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ervin_Sejdic/publication/313793218_Digital_Watermarking/links/5a5f85730f7e9b964a1cc690/Digital-Watermarking.pdf Srdjan Stankovic, Irena Orovic, Ervin Sejdic]</ref> == | ||
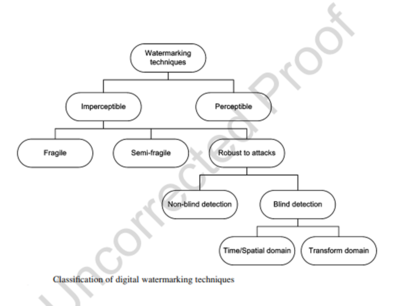
| − | A number of different watermarking techniques have been developed. Most of them can be classified into one of the categories shown in the Figure below. From the perceptual aspect, the watermark can be classified as either perceptible or imperceptible. | + | A number of different watermarking techniques have been developed. Most of them can be classified into one of the categories shown in the Figure below. From the perceptual aspect, the watermark can be classified as either |
| + | *perceptible or | ||
| + | *imperceptible. | ||
Noticeable watermark visibly changes the original content. It is sometimes used to protect images and videos, but generally it is not very popular nowadays. This technique involves embedding characters that uniquely identify the owners of the content and appear as a background image, or as a visible sign. However, water mark of this type can be removed. | Noticeable watermark visibly changes the original content. It is sometimes used to protect images and videos, but generally it is not very popular nowadays. This technique involves embedding characters that uniquely identify the owners of the content and appear as a background image, or as a visible sign. However, water mark of this type can be removed. | ||
Almost all currently used techniques fall into the class of imperceptible techniques. Imperceptible techniques are further divided into | Almost all currently used techniques fall into the class of imperceptible techniques. Imperceptible techniques are further divided into | ||
| Line 13: | Line 15: | ||
*semi-fragile and | *semi-fragile and | ||
*fragile watermarking techniques. | *fragile watermarking techniques. | ||
| − | Fragile watermarking assumes embedding of certain watermark that will be significantly damaged or removed in an attempt to 38 modify the content. These techniques are useful in proving the data authenticity. | + | Fragile watermarking assumes embedding of certain watermark that will be significantly damaged or removed in an attempt to 38 modify the content. These techniques are useful in proving the data authenticity.<br /> |
| − | In semi-fragile watermarking, the watermark should be resistant to certain signal processing techniques (e.g., compression), while it is fragile under any other attack. | + | In semi-fragile watermarking, the watermark should be resistant to certain signal processing techniques (e.g., compression), while it is fragile under any other attack.<br /> |
However, the most commonly used techniques are based on robust watermarking. Robust techniques involve embedding a watermark in the original signal, such that the watermark removal causes serious degradation of the signal quality. Watermark should be designed to be robust to the standard signal processing approaches (compression, filtering, etc.), as well as to intentional attempts to remove the watermark. | However, the most commonly used techniques are based on robust watermarking. Robust techniques involve embedding a watermark in the original signal, such that the watermark removal causes serious degradation of the signal quality. Watermark should be designed to be robust to the standard signal processing approaches (compression, filtering, etc.), as well as to intentional attempts to remove the watermark. | ||
Watermarking techniques are further divided by the domains in which the water mark is embedded. Namely, the watermark can be embedded directly in the signal domain, or in one of the transform domains. The choice of the watermarking domain depends on the type of multimedia data and the watermarking application. The most frequently used transform domains are based on the DFT, DCT, and DWT transforms. The transform domain watermarking is more convenient for modeling the spectral characteristics of watermark according to the human perceptual model.For highly nonstationary signals, the modeling can be achieved by using time frequency transforms. | Watermarking techniques are further divided by the domains in which the water mark is embedded. Namely, the watermark can be embedded directly in the signal domain, or in one of the transform domains. The choice of the watermarking domain depends on the type of multimedia data and the watermarking application. The most frequently used transform domains are based on the DFT, DCT, and DWT transforms. The transform domain watermarking is more convenient for modeling the spectral characteristics of watermark according to the human perceptual model.For highly nonstationary signals, the modeling can be achieved by using time frequency transforms. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Watermarking Techniques.png|400px|Watermarking Techniques]]<br /> | ||
== Digital Watermarking Lifecycle Phases<ref>Digital Watermarking Lifecycle Phases [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_watermarking Wikipedia]</ref> == | == Digital Watermarking Lifecycle Phases<ref>Digital Watermarking Lifecycle Phases [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_watermarking Wikipedia]</ref> == | ||
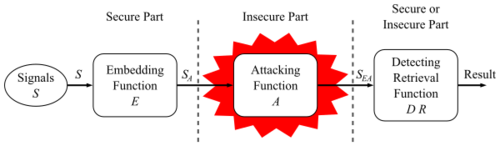
The information to be embedded in a signal is called a digital watermark, although in some contexts the phrase digital watermark means the difference between the watermarked signal and the cover signal. The signal where the watermark is to be embedded is called the host signal. A watermarking system is usually divided into three distinct steps, embedding, attack, and detection. In embedding, an algorithm accepts the host and the data to be embedded, and produces a watermarked signal. | The information to be embedded in a signal is called a digital watermark, although in some contexts the phrase digital watermark means the difference between the watermarked signal and the cover signal. The signal where the watermark is to be embedded is called the host signal. A watermarking system is usually divided into three distinct steps, embedding, attack, and detection. In embedding, an algorithm accepts the host and the data to be embedded, and produces a watermarked signal. | ||
| + | |||
[[File:General digital watermark lifecycle phases.png|500px|General digital watermark lifecycle phases]]<br /> | [[File:General digital watermark lifecycle phases.png|500px|General digital watermark lifecycle phases]]<br /> | ||
| + | |||
Then the watermarked digital signal is transmitted or stored, usually transmitted to another person. If this person makes a modification, this is called an attack. While the modification may not be malicious, the term attack arises from copyright protection application, where third parties may attempt to remove the digital watermark through modification. There are many possible modifications, for example, lossy compression of the data (in which resolution is diminished), cropping an image or video, or intentionally adding noise. | Then the watermarked digital signal is transmitted or stored, usually transmitted to another person. If this person makes a modification, this is called an attack. While the modification may not be malicious, the term attack arises from copyright protection application, where third parties may attempt to remove the digital watermark through modification. There are many possible modifications, for example, lossy compression of the data (in which resolution is diminished), cropping an image or video, or intentionally adding noise. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 40: | ||
Companies are also offering on-line tracking services so that the copyright owner can see how the owner's materials are used via the Web. These processes will continue to help the fight against electronic copyright infringement. | Companies are also offering on-line tracking services so that the copyright owner can see how the owner's materials are used via the Web. These processes will continue to help the fight against electronic copyright infringement. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 21:15, 6 January 2021
Digital Watermarking is the method of embedding data into digital multimedia content. This is used to verify the credibility of the content or to recognize the identity of the digital content's owner. Digital watermarking can be employed for multiple purposes, such as:
- Copyright protection
- Source tracking
- Broadcast tracking, such as watermarked videos from global news organizations
- Hidden communication[1]
Classification of Digital Watermarking Techniques[2]
A number of different watermarking techniques have been developed. Most of them can be classified into one of the categories shown in the Figure below. From the perceptual aspect, the watermark can be classified as either
- perceptible or
- imperceptible.
Noticeable watermark visibly changes the original content. It is sometimes used to protect images and videos, but generally it is not very popular nowadays. This technique involves embedding characters that uniquely identify the owners of the content and appear as a background image, or as a visible sign. However, water mark of this type can be removed. Almost all currently used techniques fall into the class of imperceptible techniques. Imperceptible techniques are further divided into
- robust techniques
- semi-fragile and
- fragile watermarking techniques.
Fragile watermarking assumes embedding of certain watermark that will be significantly damaged or removed in an attempt to 38 modify the content. These techniques are useful in proving the data authenticity.
In semi-fragile watermarking, the watermark should be resistant to certain signal processing techniques (e.g., compression), while it is fragile under any other attack.
However, the most commonly used techniques are based on robust watermarking. Robust techniques involve embedding a watermark in the original signal, such that the watermark removal causes serious degradation of the signal quality. Watermark should be designed to be robust to the standard signal processing approaches (compression, filtering, etc.), as well as to intentional attempts to remove the watermark.
Watermarking techniques are further divided by the domains in which the water mark is embedded. Namely, the watermark can be embedded directly in the signal domain, or in one of the transform domains. The choice of the watermarking domain depends on the type of multimedia data and the watermarking application. The most frequently used transform domains are based on the DFT, DCT, and DWT transforms. The transform domain watermarking is more convenient for modeling the spectral characteristics of watermark according to the human perceptual model.For highly nonstationary signals, the modeling can be achieved by using time frequency transforms.
Digital Watermarking Lifecycle Phases[3]
The information to be embedded in a signal is called a digital watermark, although in some contexts the phrase digital watermark means the difference between the watermarked signal and the cover signal. The signal where the watermark is to be embedded is called the host signal. A watermarking system is usually divided into three distinct steps, embedding, attack, and detection. In embedding, an algorithm accepts the host and the data to be embedded, and produces a watermarked signal.
Then the watermarked digital signal is transmitted or stored, usually transmitted to another person. If this person makes a modification, this is called an attack. While the modification may not be malicious, the term attack arises from copyright protection application, where third parties may attempt to remove the digital watermark through modification. There are many possible modifications, for example, lossy compression of the data (in which resolution is diminished), cropping an image or video, or intentionally adding noise.
Detection (often called extraction) is an algorithm which is applied to the attacked signal to attempt to extract the watermark from it. If the signal was unmodified during transmission, then the watermark still is present and it may be extracted. In robust digital watermarking applications, the extraction algorithm should be able to produce the watermark correctly, even if the modifications were strong. In fragile digital watermarking, the extraction algorithm should fail if any change is made to the signal.
The Future of Digital Watermarking[4]
A number of companies, such as the Digimarc Corporation, Sony and IBM have introduced digital watermarking software applications that allow individuals to imbed watermarks within image, audio and video files to protect them from copyright infringement. The watermarks may be viewed with software and can reveal either a unique identification code that can be traced to the copyright owner or specific information about the copyright owner.
Companies are also offering on-line tracking services so that the copyright owner can see how the owner's materials are used via the Web. These processes will continue to help the fight against electronic copyright infringement.
References
- ↑ What does Digital Watermarking mean? Techopedia
- ↑ Classification of Digital Watermarking Techniques Srdjan Stankovic, Irena Orovic, Ervin Sejdic
- ↑ Digital Watermarking Lifecycle Phases Wikipedia
- ↑ The Future of Digital Watermarking Legal Zoom