Difference between revisions of "Gartner's Hype Cycle Methodology"
(Created page with "'''Content Coming Soon'''") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Gartner Hype Cycles''' provide a graphic representation of the maturity and adoption of [[Information Technology (IT)|technologies]] and [[Application|applications]], and how they are potentially relevant to solving real [[Business|business]] problems and exploiting new opportunities. Gartner Hype Cycle methodology gives you a view of how a technology or application will evolve over time, providing a sound source of insight to manage its deployment within the context of your specific [[Business Goals|business goals]]. |
| + | |||
| + | Each year, Gartner creates more than 100 Hype Cycles in various domains to enable clients to track [[Innovation Maturity Model|innovation maturity]] and future potential. Hype Cycles characterize the typical progression of innovation, from overenthusiasm through a period of disillusionment to an eventual understanding of the innovation’s relevance and role in a [[Market|market]] or domain.<ref>Definition - What is Gartner's Hype Cycle Methodology? [https://www.gartner.com/en/research/methodologies/gartner-hype-cycle Gartner]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
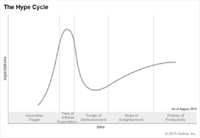
| + | [[File:Gartner Hype Cycle.png|200px|Gartner's Hype Cycle]]<br /> | ||
| + | source: Gartner | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == History of Hype Cycle<ref>History of Hype Cycle [https://www.cleverism.com/everything-need-know-gartner-hype-cycle/ Cleverism]</ref> == | ||
| + | The concept of Hype Cycle was introduced by an analyst called Jackie Fenn in the year 1995. For several years of trying to bring this technology into the industry view, the [[Organization|organization]] began to use Hype Cycle charts of new and budding technologies. If we now go back and see the growth of old technologies, we will be able to observe and validate the curves and arches in the graphical representation. As an effective example, in the year 2005, a technology called [[Business Process Management (BPM)|Business Process Management or BPM]] suites was at the top of the Hype Cycle which means that its hype at that time was at the highest. Now a decade later, BPM has most certainly lived up to the Hype. But it is also interesting to note that the technology of Tablets was at the bottom at that time, but it has now emerged to be very useful all over the world. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you consider the year 2014, the technology that was at the peak of Hype Cycles was ‘Internet of Things’ and the technology at the bottom is ‘White Cloud Computing’. We know where they both are today. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Criticisms of Gartner's Hype Cycle<ref>Criticisms of Gartner's Hype Cycle [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hype_cycle Wikipedia]</ref> == | ||
| + | There have been numerous criticisms of the hype cycle, prominent among which are that it is not a cycle, that the outcome does not depend on the nature of the [[Information Technology (IT)|technology]] itself, that it is not scientific in nature, and that it does not reflect changes over time in the speed at which technology develops. Another is that it is limited in its application, as it prioritizes economic considerations in [[Decision Cycle|decision-making processes]]. It seems to assume that a business' performance is tied to the hype cycle, whereas this may actually have more to do with the way a company devises its [[Brand Strategy|branding strategy]]. A related criticism is that the "cycle" has no real benefits to the development or[[Marketing|marketing]] of new technologies and merely comments on pre-existing trends. Specific disadvantages when compared to, for example, technology readiness level are: | ||
| + | *The cycle is not scientific in nature, and there is no [[Data|data]] or analysis that would justify the cycle. | ||
| + | *With the (subjective) terms disillusionment, enlightenment and expectations it can not be described objectively or clearly where technology now really is. | ||
| + | *The terms are misleading in the sense that one gets the wrong idea what they can use a technology for. The user does not want to be disappointed, so should they stay away from technology in the Trough of Disillusionment? | ||
| + | *No action perspective is offered to move technology to a next phase. | ||
| + | *This appears to be a very simplified impulse response of an elastic system representable by a differential equation. Perhaps more telling would be to formulate a system model with solutions conforming to observable behavior. | ||
| + | An analysis of Gartner Hype Cycles since 2000 shows that few technologies actually travel through an identifiable hype cycle, and that in practice most of the important technologies adopted since 2000 were not identified early in their adoption cycles. | ||
Revision as of 15:30, 18 February 2021
Gartner Hype Cycles provide a graphic representation of the maturity and adoption of technologies and applications, and how they are potentially relevant to solving real business problems and exploiting new opportunities. Gartner Hype Cycle methodology gives you a view of how a technology or application will evolve over time, providing a sound source of insight to manage its deployment within the context of your specific business goals.
Each year, Gartner creates more than 100 Hype Cycles in various domains to enable clients to track innovation maturity and future potential. Hype Cycles characterize the typical progression of innovation, from overenthusiasm through a period of disillusionment to an eventual understanding of the innovation’s relevance and role in a market or domain.[1]
History of Hype Cycle[2]
The concept of Hype Cycle was introduced by an analyst called Jackie Fenn in the year 1995. For several years of trying to bring this technology into the industry view, the organization began to use Hype Cycle charts of new and budding technologies. If we now go back and see the growth of old technologies, we will be able to observe and validate the curves and arches in the graphical representation. As an effective example, in the year 2005, a technology called Business Process Management or BPM suites was at the top of the Hype Cycle which means that its hype at that time was at the highest. Now a decade later, BPM has most certainly lived up to the Hype. But it is also interesting to note that the technology of Tablets was at the bottom at that time, but it has now emerged to be very useful all over the world.
If you consider the year 2014, the technology that was at the peak of Hype Cycles was ‘Internet of Things’ and the technology at the bottom is ‘White Cloud Computing’. We know where they both are today.
Criticisms of Gartner's Hype Cycle[3]
There have been numerous criticisms of the hype cycle, prominent among which are that it is not a cycle, that the outcome does not depend on the nature of the technology itself, that it is not scientific in nature, and that it does not reflect changes over time in the speed at which technology develops. Another is that it is limited in its application, as it prioritizes economic considerations in decision-making processes. It seems to assume that a business' performance is tied to the hype cycle, whereas this may actually have more to do with the way a company devises its branding strategy. A related criticism is that the "cycle" has no real benefits to the development ormarketing of new technologies and merely comments on pre-existing trends. Specific disadvantages when compared to, for example, technology readiness level are:
- The cycle is not scientific in nature, and there is no data or analysis that would justify the cycle.
- With the (subjective) terms disillusionment, enlightenment and expectations it can not be described objectively or clearly where technology now really is.
- The terms are misleading in the sense that one gets the wrong idea what they can use a technology for. The user does not want to be disappointed, so should they stay away from technology in the Trough of Disillusionment?
- No action perspective is offered to move technology to a next phase.
- This appears to be a very simplified impulse response of an elastic system representable by a differential equation. Perhaps more telling would be to formulate a system model with solutions conforming to observable behavior.
An analysis of Gartner Hype Cycles since 2000 shows that few technologies actually travel through an identifiable hype cycle, and that in practice most of the important technologies adopted since 2000 were not identified early in their adoption cycles.