Difference between revisions of "ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI)"
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
The figure below illustrates the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Continual Service Improvement (CSI) seven-step process. The individual steps overlayed by the more general Deming (plan-do-check-act) Cycle. | The figure below illustrates the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Continual Service Improvement (CSI) seven-step process. The individual steps overlayed by the more general Deming (plan-do-check-act) Cycle. | ||
| − | [[File:Seven Step CSI Process.png| | + | [[File:Seven Step CSI Process.png|450px|Seven-step improvement process, as defined in ITIL CSI]]<br /> |
source: Geant.Org | source: Geant.Org | ||
| − | == The Seven Step Improvement Process<ref>The Seven Step Improvement Process of ITIL CSI [https://www.invensislearning.com/articles/itil/overview-of-itil-csi-and-the-7-step-improvement-process invensis]</ref> == | + | == ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) Approach<ref>CSI Model - ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) Approach [https://www3.pinkelephant.com/ressource/pinklink/na/issue152/CSI%20-%20Bringing%20It%20To%20Life.pdf Pink Elephant]</ref> == |
| + | The CSI Model follows a six-step approach for reviewing, evaluation, planning, and implementing the Improvement process. These approaches are nothing but some pre-defined questions, for which the CSI process tries to find answers. | ||
| + | *Step 1 – What Is The Vision?: CSI is all about the Business, so when looking at the CSI Model the first step is to clearly understand the Business vision, strategy, goals and objectives. It is also important to understand ITs strategy, goals and objectives, and to ensure that they support the Businesses. | ||
| + | *Step 2 – Where Are We Now?: In order to be able to identify if you have improved, it is important to know where you started from. Answering this question is about performing an initial assessment, or measurements, in order to create a baseline upon which improvement effort success can be measured. Assessment can be done on availability and/or performance of IT Services. Assessments can also be done around processes such as a process maturity assessment. If you don’t have any basic measurements or metrics today you may need to start collecting these for three to six months and then get agreement on a baseline number. | ||
| + | *Step 3 – Where Do We Want To Be?: Set realistic targets for the improvement initiative. This may require setting short-term, mid-term and long-term targets. Targets can be set for availability measures for IT Services or a new maturity level for processes. Keep in mind that setting targets should be based on business requirements, and not on business wishes. If a customer says they want 99.999% availability, be sure that this is what they actually need to support the desired business outcomes they need to achieve. Also remember that for process maturity, the key is again to understand the value of a process to the business. Not all processes are equal and some processes will deliver more value to the business than others. The target should not be to have all processes at a level five maturity. You may find that being at a level three is all you need to deliver value. Create your Measurement Framework of Key Performance Indicators so that later on you can measure if you have achieved your targets. | ||
| + | *Step 4 – How Do We Get There?: This is the process improvement projects that are identified, agreed on and funded. Keep in mind that Senior Management often does not have the luxury of long projects. They are interested in getting quick improvements, so don’t overlook the quick wins that can be implemented around IT Services and/or processes | ||
| + | *Step 5 – Did We Get There?: Using the Key Performance Indictors defined in Step 3, continue to monitor, measure and report on your achievements. *Step 6 – How Do We Keep The Momentum Going?: Market your successes to Senior Management as well as the rest of the organization. It is important to use successes to gain more buy-in for additional improvement initiatives. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:CSI Model.png|400px|The CSI Model]]<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == The Seven Step Improvement Process<ref>The Seven Step Improvement Process of ITIL CSI [https://www.invensislearning.com/articles/itil/overview- | ||
| + | of-itil-csi-and-the-7-step-improvement-process invensis]</ref> == | ||
The focus of Continual Service Improvement is on service improvement to support business processes. To accomplish this, Continual Service Improvement uses a seven-step process plan for improvement which is crucial for CSI and other stages in the ITIL lifecycle. The main purpose of this process is to define and manage the steps required to identify, define, gather, process, analyze, present and implement the improvements which have been made over a period of time. The 7 step improvement process is essential in supporting CSI and operates across the entire service lifecycle. It focuses on identifying the improvement opportunities, not merely for processes and services, but for all the disciplines implemented as a part of the IT Service Lifecycle. | The focus of Continual Service Improvement is on service improvement to support business processes. To accomplish this, Continual Service Improvement uses a seven-step process plan for improvement which is crucial for CSI and other stages in the ITIL lifecycle. The main purpose of this process is to define and manage the steps required to identify, define, gather, process, analyze, present and implement the improvements which have been made over a period of time. The 7 step improvement process is essential in supporting CSI and operates across the entire service lifecycle. It focuses on identifying the improvement opportunities, not merely for processes and services, but for all the disciplines implemented as a part of the IT Service Lifecycle. | ||
| Line 47: | Line 60: | ||
| − | == Scope of Continual Service Improvement< | + | == Scope of Continual Service Improvement<ref>cope of Continual Service Improvement [https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nabin_Lamichhane/publication/334400797_Implementing_Continual_Service_Improvement_In_Business_Enterprises_A_Proposal_To_Improve_Business_Effectiveness_Of_Nepal/links/5d27871a299bf1547cad2d93/Implementing-Continual-Service-Improvement-In-Business-Enterprises-A-Proposal-To-Improve-Business-Effectiveness-Of-Nepal.pdf Nabin Lamichhane]</ref> == |
The CSI Implementation process may vary and the correct way to implement it rely upon the organization's goal; it may be long term goals or short time dependent on the nature and policy of the organization. | The CSI Implementation process may vary and the correct way to implement it rely upon the organization's goal; it may be long term goals or short time dependent on the nature and policy of the organization. | ||
Generally the scope looks into three areas of ITSM. | Generally the scope looks into three areas of ITSM. | ||
Revision as of 19:58, 12 January 2021
Definition of ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) is the fifth and final stage of ITIL Service Lifecycle under ITIL’s IT Service Management Framework (ITSM). It aims to deal with measures to be adopted to improve the service quality by learning from past successes and failures. Continual Service Improvement also aligns and realigns IT Services to the changing business requirements by identifying and implementing changes for improvements. For doing this, it takes the similar approach described in Deming Cycle (PDSA Cycle). The ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) describes the best practices for achieving incremental and large-scale improvements in services quality, operational efficiency, and business continuity. It effectively describes and utilizes the concept of Key Performance Indicator (KPI), which is a metrics-driven process, for reviewing, evaluating, and benchmarking performance of services. CSI is part of all the stages and ITSM processes and services It is important to consider CSI processes subject to improve as well.
The CSI Practice relies upon five major guiding principles defined in the CSI book:
- The CSI Approach
- Seven Step Improvement Process
- The Deming Cycle
- Professor Kotter’s Eight Steps for Successful Transformation
- Knowledge Management
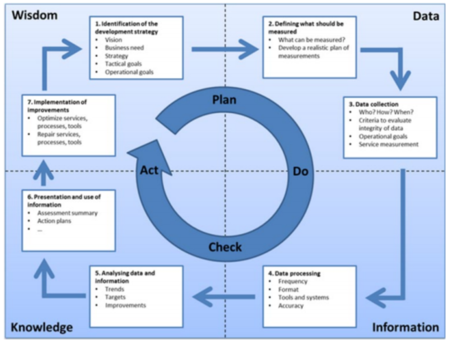
The figure below illustrates the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Continual Service Improvement (CSI) seven-step process. The individual steps overlayed by the more general Deming (plan-do-check-act) Cycle.
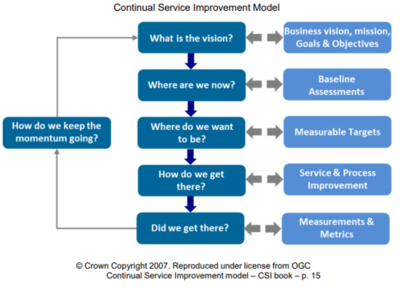
ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) Approach[1]
The CSI Model follows a six-step approach for reviewing, evaluation, planning, and implementing the Improvement process. These approaches are nothing but some pre-defined questions, for which the CSI process tries to find answers.
- Step 1 – What Is The Vision?: CSI is all about the Business, so when looking at the CSI Model the first step is to clearly understand the Business vision, strategy, goals and objectives. It is also important to understand ITs strategy, goals and objectives, and to ensure that they support the Businesses.
- Step 2 – Where Are We Now?: In order to be able to identify if you have improved, it is important to know where you started from. Answering this question is about performing an initial assessment, or measurements, in order to create a baseline upon which improvement effort success can be measured. Assessment can be done on availability and/or performance of IT Services. Assessments can also be done around processes such as a process maturity assessment. If you don’t have any basic measurements or metrics today you may need to start collecting these for three to six months and then get agreement on a baseline number.
- Step 3 – Where Do We Want To Be?: Set realistic targets for the improvement initiative. This may require setting short-term, mid-term and long-term targets. Targets can be set for availability measures for IT Services or a new maturity level for processes. Keep in mind that setting targets should be based on business requirements, and not on business wishes. If a customer says they want 99.999% availability, be sure that this is what they actually need to support the desired business outcomes they need to achieve. Also remember that for process maturity, the key is again to understand the value of a process to the business. Not all processes are equal and some processes will deliver more value to the business than others. The target should not be to have all processes at a level five maturity. You may find that being at a level three is all you need to deliver value. Create your Measurement Framework of Key Performance Indicators so that later on you can measure if you have achieved your targets.
- Step 4 – How Do We Get There?: This is the process improvement projects that are identified, agreed on and funded. Keep in mind that Senior Management often does not have the luxury of long projects. They are interested in getting quick improvements, so don’t overlook the quick wins that can be implemented around IT Services and/or processes
- Step 5 – Did We Get There?: Using the Key Performance Indictors defined in Step 3, continue to monitor, measure and report on your achievements. *Step 6 – How Do We Keep The Momentum Going?: Market your successes to Senior Management as well as the rest of the organization. It is important to use successes to gain more buy-in for additional improvement initiatives.
The Seven Step Improvement Process[2]
The focus of Continual Service Improvement is on service improvement to support business processes. To accomplish this, Continual Service Improvement uses a seven-step process plan for improvement which is crucial for CSI and other stages in the ITIL lifecycle. The main purpose of this process is to define and manage the steps required to identify, define, gather, process, analyze, present and implement the improvements which have been made over a period of time. The 7 step improvement process is essential in supporting CSI and operates across the entire service lifecycle. It focuses on identifying the improvement opportunities, not merely for processes and services, but for all the disciplines implemented as a part of the IT Service Lifecycle.
Scope of the Seven-Step Improvement Process
The scope of the CSI seven-step improvement process contains the following areas:
- The seven-step improvement process includes analysis of the performance and actual capabilities of the services and processes throughout the lifecycle, partners, and technology.
- It includes continuously aligning the portfolio of IT services of the organization to the present and future business requirements.
- It makes the best use of whatever the technology that the organization possesses and tries to acquire and utilize new technology when a business case demands it.
- To determine the capabilities of the personnel in the enterprise and to inquire if the right people with the relevant skills are working in appropriate positions.
Value of the Seven-Step Improvement Process
With the help of aforementioned seven-step Improvement processes in ITIL Continuous Service improvement, current and future business requirements are met by constant monitoring and analyzing service delivery. Indeed, it also enables repetitive assessment of the present situation against business requirements and identifies the opportunities available for improving the provision of service to the customers.
Principles and Basic Concepts of the Seven-Step Improvement Process
Continual Service Improvements should center on increasing efficiency, maximizing the effectiveness, reducing the cost of service, and underlying IT service management. And the only way to accomplish the task is to ensure that the improvement opportunities are identified throughout the service lifecycle.
- The service providers operate in a very competitive market and they need to assess their services against the expectations in the market persistently.
- New delivery mechanisms such as cloud computing can increase the efficiency of the service and need to be considered for implementation.
- The service provided must be compared to the present market offerings to ensure that the service adds actual business value to the clients, so that the service provider remains competitive.
- The services must be regularly reviewed to keep up with the latest technological advances to ensure that the services they are delivering are the most efficient.
Stages in the Seven-Step Improvement Process
The below mentioned seven steps constitute what is known as a knowledge spiral. The knowledge gathered from one level becomes the input to the other level. It moves from operational management to tactical management and finally strategic management. Feedback from any stage of the service lifecycle can be used to identify improvement opportunities for any other stage of the lifecycle. The stages in the 7 step improvement process are listed below:
- Identify the approach for improvement: Prior to implementing an improvement strategy, it’s necessary to understand the necessity for continuous improvement. We must take into account the final goals we have set for the business and see how the IT organization can assist in achieving those targets through continuous improvements. Whilst accomplishing this, consider future and present plans as well.
- Define what should be measured: A comparison should be made amid what we can ideally measure and what we can actually measure. Gaps should be identified and a realistic measurement plan should be incorporated to support the strategy for improvement.
- Collect the essential data: Data is gathered through persistent monitoring. The process of monitoring can be done either through manually or technology can be utilized to the fullest to automate the entire process and simplify it.
- Process the data: Once the data is collected through continuous monitoring, it is then converted into the form required by the audience. This can be considered as a conversion of metrics into Key Performance Indicator (KPI) results and change the available data into information.
- Analyze the information and data: The multiple sources of data are combined to transform the information into knowledge, which is further analyzed to find the gaps and their impact on the overall business. The information is further evaluated considering all the relevant internal and external factors. It also helps to answer questions regarding something that is good or bad and is it expected and in line with the targets.
- Proper presentation and utilization of information: The information which is gathered and analyzed needs to be presented in a proper manner with the right amount of detail so that the information is comprehensible and provides the required amount of detail to support informed decision making.
- Implement the improvements: A change implemented with continuous improvement sets a new baseline for the entire process. The knowledge obtained should be combined with the previous experience and are used to make informed decisions and necessary improvements. The improvements which are made must focus on optimizing and correcting the services, processes, and tools.
The 7 step improvement process is a vital process of CSI and thus identifies the opportunities available for improving services, tools, processes, etc. The process initiates service measurement, service reporting, and improvement. This helps to define the service baseline and processes, metrics, KPIs, critical success factors, and corrective measures are taken to identify and improve the gaps in the IT service management. ITIL CSI desires a commitment from the people working throughout the service lifecycle. It requires enduring attention to monitoring, analyzing, a well thought plan, and reporting results aiming towards improvement.
Scope of Continual Service Improvement[3]
The CSI Implementation process may vary and the correct way to implement it rely upon the organization's goal; it may be long term goals or short time dependent on the nature and policy of the organization. Generally the scope looks into three areas of ITSM.
- ITSM Processes
- IT Services
- The Service Lifecycle
Cartlidge & Lillycrop(2007) thinks it is very hard to decide from where to start, but one of the above three areas can be taken as a starting point. Case ITIL (2006) suggests the organizations to address the pain points first for getting value of Investment (VOI) as well as gaining the business and functional group support. Case (2009) opines some quick wins like low hanging fruits can be experienced during the implementing process.
- ITSM Processes- Where Do we start?: Organizations are not aware of from where to start the implementation of CSI in business. They can approach through change management, Incident Management and problem management by going into mature documenting process. Case (2009) argues change management as a control process and helps in attaining a maturity level for organizations protecting the production environment with the efficiency and effectiveness the process requires. Request for Change (RFC) can be a quick win if one doesn‟t exist, or change advisory board highlighting the possible changes, procedures to implement changes, creating risk models and so forth.
- IT Services- Where do we start? Case (2009) states that it is crucial to choose right IT services once the ITSM process is implemented in our business, to ensure the business value is delivered. But the problem is to identify the right services but can be simply done through identifying the services falling out to meet the satisfaction levels or which are continuously giving a threat. In case of absence of service level data a discussion is to be carried on with the business highlighting the services that are deemed mission critical. Impact assessment is to be conducted either to give continuity to the service or discard the service.
- Service lifecycle-where do we start ? Starting the improvement initiatives of processes organization will find our many turning points for making improvements in the service lifecycle itself. Thus it is crucial that organization keeps tracks of the communication and feedbacks between different service lifecycle phases. Organizations should look for improvement opportunities associated with the business requirements Case (2009) and Nickols (2010).
CSI is often viewed as an ad hoc activity within IT services. The activity is only triggered when someone in IT management flags up that there is a problem. This is not the right way to address CSI. Often these reactionary events are not even providing continual improvement, but simply stopping a single failure from occurring again. CSI takes a commitment from everyone in IT working throughout the service lifecycle to be successful at improving services and service management processes. It requires ongoing attention, a well-thought-out plan, and consistent attention to monitoring, analysing and reporting results with an eye toward improvement. Improvements can be incremental in nature but also require a huge commitment to implement a new service or meet new business requirements seven steps of improvement, each of which needs attention. There is no reward for taking a short cut or not addressing each step in a sequential nature. If any step is missed, there is a risk of not being efficient and effective in meeting the goals of CSI. IT services must ensure that proper staffing and tools are identified and implemented to support CSI activities. It is also important to understand the difference between what should be measured and what can be measured. Start small – don’t expect to measure everything at once. Understand the organizational capability to gather and process the data. Be sure to spend time analysing data as this is where the real value comes in. Without analysis of the data, there is no real opportunity to truly improve services or service management processes. Think through the strategy and plan for reporting and using the data. Reporting is partly a marketing activity. It is important that IT managers focus on the value added to the organization as well as reporting on issues and achievements. In order for steps 5 to 7 to be carried out correctly, it is imperative that the target audience is considered when packaging the information. An organization can find improvement opportunities throughout the entire service lifecycle. An IT organization does not need to wait until a service or service management process is transitioned into the operations area to begin identifying improvement opportunities.
- ↑ CSI Model - ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) Approach Pink Elephant
- ↑ The Seven Step Improvement Process of ITIL CSI [https://www.invensislearning.com/articles/itil/overview- of-itil-csi-and-the-7-step-improvement-process invensis]
- ↑ cope of Continual Service Improvement Nabin Lamichhane