ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
Definition of ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) is the fifth and final stage of ITIL Service Lifecycle under ITIL’s IT Service Management Framework (ITSM). It aims to deal with measures to be adopted to improve the service quality by learning from past successes and failures. Continual Service Improvement also aligns and realigns IT Services to the changing business requirements by identifying and implementing changes for improvements. For doing this, it takes the similar approach described in Deming Cycle (PDSA Cycle). The ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI) describes the best practices for achieving incremental and large-scale improvements in services quality, operational efficiency, and business continuity. It effectively describes and utilizes the concept of Key Performance Indicator (KPI), which is a metrics-driven process, for reviewing, evaluating, and benchmarking performance of services. CSI is part of all the stages and ITSM processes and services It is important to consider CSI processes subject to improve as well.
The CSI Practice relies upon five major guiding principles defined in the CSI book:
- The CSI Approach
- Seven Step Improvement Process
- The Deming Cycle
- Professor Kotter’s Eight Steps for Successful Transformation
- Knowledge Management
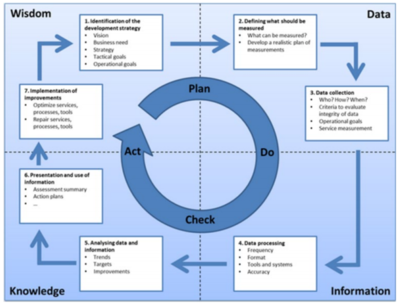
The figure below illustrates the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Continual Service Improvement (CSI) seven-step process. The individual steps overlayed by the more general Deming (plan-do-check-act) Cycle.