Difference between revisions of "IT Architecture"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Simply put, '''IT Architecture''' is an organization's list of technology standards, principles, and policies, where the complex linkages between processes, infrastructure, data, and applications are defined to enable an organization's strategic objective and mitigate risks. | Simply put, '''IT Architecture''' is an organization's list of technology standards, principles, and policies, where the complex linkages between processes, infrastructure, data, and applications are defined to enable an organization's strategic objective and mitigate risks. | ||
| − | Also known as '''Information Technology Architecture''' or '''Technology Architecture''', '''IT Architecture''' is the process of development of methodical [[Information Technology (IT)|information technology]] specifications, models and guidelines, using a variety of Information Technology notations, for example [[Unified Modeling Language (UML)|UML]], within a coherent Information Technology architecture framework, following formal and informal Information Technology solution, [[Enterprise Architecture|enterprise architecture (EA)]], and [[Infrastructure Architecture|infrastructure architecture]] processes. These processes have been developed in the past few decades in response to the requirement for a coherent, consistent approach to the delivery of information technology capabilities. They have been developed by information technology product vendors and independent consultancies, based on real experiences in the information technology marketplace and collaboration amongst industry stakeholders, for example, the Open Group. Best practice Information Technology architecture encourages the use of open technology standards and global technology interoperability. Information Technology Architecture can also be called a high-level map or plan of the information assets in an [[organization]], including the physical design of the building that holds the hardware.<ref> | + | Also known as '''Information Technology Architecture''' or '''Technology Architecture''', '''IT Architecture''' is the process of development of methodical [[Information Technology (IT)|information technology]] specifications, models and guidelines, using a variety of Information Technology notations, for example [[Unified Modeling Language (UML)|UML]], within a coherent Information Technology architecture framework, following formal and informal Information Technology solution, [[Enterprise Architecture|enterprise architecture (EA)]], and [[Infrastructure Architecture|infrastructure architecture]] processes. These processes have been developed in the past few decades in response to the requirement for a coherent, consistent approach to the delivery of information technology capabilities. They have been developed by information technology product vendors and independent consultancies, based on real experiences in the information technology marketplace and collaboration amongst industry stakeholders, for example, the Open Group. Best practice Information Technology architecture encourages the use of open technology standards and global technology interoperability. Information Technology Architecture can also be called a high-level map or plan of the information assets in an [[organization]], including the physical design of the building that holds the hardware.<ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Information_technology_architecture Defining Information Technology Architecture]</ref> |
| − | Technology architecture associates application components from application architecture with technology components representing software and hardware components. Its components are generally acquired in the marketplace and can be assembled and configured to constitute the enterprise’s technological infrastructure. Technology architecture provides a more concrete view of the way in which application components will be realized and deployed. It enables the migration problems that can arise between the different steps of the IS evolution path to be studied earlier. It provides a more precise means of evaluating responses to constraints (nonfunctional requirements) concerning the IS, notably by estimating hardware and network sizing needs or by setting up server or storage redundancy. Technology architecture concentrates on logistical and location problems related to hardware location, IS management capabilities, and the sites where the different parts of the IS are used. Technology architecture also ensures the delivered application components work together, confirming that the required business integration is supported.<ref> | + | Technology architecture associates application components from application architecture with technology components representing software and hardware components. Its components are generally acquired in the marketplace and can be assembled and configured to constitute the enterprise’s technological infrastructure. Technology architecture provides a more concrete view of the way in which application components will be realized and deployed. It enables the migration problems that can arise between the different steps of the IS evolution path to be studied earlier. It provides a more precise means of evaluating responses to constraints (nonfunctional requirements) concerning the IS, notably by estimating hardware and network sizing needs or by setting up server or storage redundancy. Technology architecture concentrates on logistical and location problems related to hardware location, IS management capabilities, and the sites where the different parts of the IS are used. Technology architecture also ensures the delivered application components work together, confirming that the required business integration is supported.<ref>[https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780124199842000100 What is Technology Architecture]</ref> |
[https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/architecture Gartner defines IT Architecture] as, "A framework and set of guidelines to build new systems. IT architecture is a series of principles, guidelines, or rules used by an enterprise to direct the process of acquiring, building, modifying, and interfacing IT resources throughout the enterprise. These resources can include equipment, software, communications, development methodologies, modeling tools, and organizational structures." | [https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/architecture Gartner defines IT Architecture] as, "A framework and set of guidelines to build new systems. IT architecture is a series of principles, guidelines, or rules used by an enterprise to direct the process of acquiring, building, modifying, and interfacing IT resources throughout the enterprise. These resources can include equipment, software, communications, development methodologies, modeling tools, and organizational structures." | ||
Revision as of 17:28, 14 October 2022
Simply put, IT Architecture is an organization's list of technology standards, principles, and policies, where the complex linkages between processes, infrastructure, data, and applications are defined to enable an organization's strategic objective and mitigate risks.
Also known as Information Technology Architecture or Technology Architecture, IT Architecture is the process of development of methodical information technology specifications, models and guidelines, using a variety of Information Technology notations, for example UML, within a coherent Information Technology architecture framework, following formal and informal Information Technology solution, enterprise architecture (EA), and infrastructure architecture processes. These processes have been developed in the past few decades in response to the requirement for a coherent, consistent approach to the delivery of information technology capabilities. They have been developed by information technology product vendors and independent consultancies, based on real experiences in the information technology marketplace and collaboration amongst industry stakeholders, for example, the Open Group. Best practice Information Technology architecture encourages the use of open technology standards and global technology interoperability. Information Technology Architecture can also be called a high-level map or plan of the information assets in an organization, including the physical design of the building that holds the hardware.[1]
Technology architecture associates application components from application architecture with technology components representing software and hardware components. Its components are generally acquired in the marketplace and can be assembled and configured to constitute the enterprise’s technological infrastructure. Technology architecture provides a more concrete view of the way in which application components will be realized and deployed. It enables the migration problems that can arise between the different steps of the IS evolution path to be studied earlier. It provides a more precise means of evaluating responses to constraints (nonfunctional requirements) concerning the IS, notably by estimating hardware and network sizing needs or by setting up server or storage redundancy. Technology architecture concentrates on logistical and location problems related to hardware location, IS management capabilities, and the sites where the different parts of the IS are used. Technology architecture also ensures the delivered application components work together, confirming that the required business integration is supported.[2]
Gartner defines IT Architecture as, "A framework and set of guidelines to build new systems. IT architecture is a series of principles, guidelines, or rules used by an enterprise to direct the process of acquiring, building, modifying, and interfacing IT resources throughout the enterprise. These resources can include equipment, software, communications, development methodologies, modeling tools, and organizational structures."
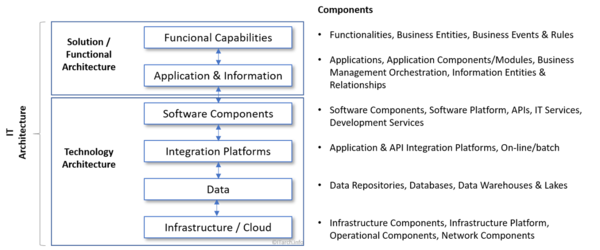
IT Architecture = Solution + Technical Architecture[3]
IT Architecture is the combination of a high-level functional solution architecture together with the alignment of the Technology Architecture.
It contains the main functional components, but also channels, architectural components, databases, and infrastructure. It is the view that aligns business and technology as it shows the overall solution blueprint. Once you want to put double-click on each of the architectures, you get a more detailed solution or technical architecture.
See Also
Enterprise Architecture
IT Infrastructure
Information Technology (IT)