Information Technology Asset Management (ITAM)
Definition of Information Technology Asset Management (ITAM)
IT Asset Management (ITAM) is a type of business management that is directly tied to an enterprise's IT infrastructure. ITAM is essentially a form of business process management (BPM) that focuses on the overall deployment, use and lifespan of products, rather than other IT management components.With ITAM, professionals review the an organization's total business hardware and software inventory and make comprehensive decisions about sourcing, use and all other aspects related to an asset lifecycle. ITAM managers are responsible for maintaining control over inventory and ensuring that business assets fit the organization's operating needs. Other ITAM goals include compliance with industry standards, best practices for environmental usage and efficient asset reuse or purchases.[1]
The optimum IT asset management system hits three main areas:
- Completeness. The tool should register any device that is attached to the network, even with an ad hoc connection, such as a smartphone or tablet. This comprehensive listing of network users helps IT teams to understand what is happening across the network and to apply suitable security to the organization’s data.
- Granularity. Two systems of the same product name often have differences inside. Granularity must apply to hardware and software, such as drivers and operating system version and patch level. For example, two servers of the same brand and model name could have varying amounts of installed memory, or a different make of hard disk drive. Gathering all this information in one system affords real value to IT asset management.
- Reportability. You must be able to access asset data in a meaningful manner. The IT asset management system must provide reports that are not just based on products, but also cover maintenance schedules, capability for devices to take patches and updates and the health of the equipment and the components within it.[2]
Evaluating an Information Technology Asset Management (ITAM) System[3]
When an organization is evaluating and later configuring an ITAM system, there are many key criteria to consider, including:
- Which assets you have and how they are expensed
- What you’re tracking – the real-time status of servers or websites or the physical tracking of assets
- Personnel resources – how much time is currently being spent on IT asset management and what is the potential cost savings of an automated solution
- Budgeting and Use Cases – which parts of the organization can contribute to the upfront costs associated with an advanced ITAM system – and how that contribution will be offset by the overall gains realized by the solution
- Customization – what are the requirements for your organization’s needs for customization. This could be based on pre-existing ITAM processes that are in place, based on ITIL Service Asset and Configuration Management, or could be based on organization-specific needs or software configurations
- Integration with help desk ticketing, services and/or other IT services/solutions
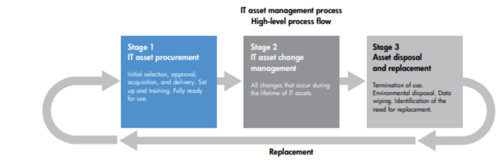
IT Asset Management Process[4]
A best practice is that large organizations should appoint an asset manager with direct access to the management team to be able to implement effectively the guidelines for realizing a sound asset management system.
- Stage 1: Asset request and procurement This stage includes every aspect of acquiring an asset, from initial request and selection to arrival and training the user to begin operating the IT-related equipment. The two broad processes in this stage involve user management and the approval process.
- Stage 2: Asset change management process This stage assimilates every change that occurs during the lifetime of an asset, referred to as IMAC (Install Move Add Change). Because every change represents a cost to the organization, the asset management helps determine if the change is cost effective or business effective.
- Stage 3: Asset disposal and replacement Termination or retirement management involves planning and managing the execution of retiring assets from the enterprise. It enables control and accountability for the retirement of organization-owned assets, guided by both financial and physical goals.
Benefits of IT Asset Management[5]
Asset Management supports the requirement along the entire lifetime cycle of their End-user IT equipment. With ITAM it is possible to establish and maintain IMAC (Install, Move, Add and Change) best practices, improve asset service levels and manage service risk and IT resources in a cost-effective manner and as part of a comprehensive ITSM program. A pragmatic and phased approach to adopting ITSM and ITAM processes is recommended to help to secure continued funding of your programs. This program development approach creates recurring business value, improves your organization’s IT maturity and provides success at every step.
- Uncover savings through process improvement and support for strategic decision making
- Gain control of the inventory
- Increase accountability to ensure compliance
- Enhance performance of assets and the life cycle management
- Risk reduction through standardization, proper documentation, loss detection
Business Benefits
After implementing the defined asset management policies, organizations will get below mentioned tangible benefits
- Maintain the complete IT Asset and configuration item (CI) list.
- Maintain Configuration Management Database (CMDB) with proper access control and confidentiality
- Maintain records for expired and decommissioned assets
- Conduct capacity reporting on replenishing assets and consumables
- Track and report on contract, license, AMC, support renewals etc
- Identify, track, and prioritize corporate assets, especially mission-critical assets required for business continuity planning
- Manage Contracts for the assets which are applicable
See Also
References
- ↑ What is Information Technology Asset Management (ITAM)? Techopedia
- ↑ The IT asset management system DCIMPro
- ↑ CWhat Criteria should be considered when evaluating an Information Technology Asset Management (ITAM) System? Stephen Watts
- ↑ The IT asset Management Process HP
- ↑ What are the Benefits of IT Asset Management? Elitser
Further Reading
- IT asset management: How to be efficient