Difference between revisions of "Information Technology Systems"
(Created page with "What are Information Technology Systems? Information Technology Systems (ITS) refer to the combination of hardware, software, networks, and databases that are integrated and c...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | What are Information Technology Systems? | + | == What are Information Technology Systems? == |
| − | Information Technology Systems (ITS) refer to the combination of hardware, software, networks, and databases that are integrated and coordinated to collect, process, store, and disseminate data. ITS encompasses the technology infrastructure used in organizations to support business processes, communication, and services. These systems are critical for managing information efficiently and are central to | + | Information Technology Systems (ITS) refer to the combination of hardware, software, networks, and databases that are integrated and coordinated to collect, process, store, and disseminate data. ITS encompasses the technology infrastructure used in organizations to support business processes, communication, and services. These systems are critical for managing information efficiently and are central to almost every sector's operations. |
| − | Role and Purpose of Information Technology Systems | + | |
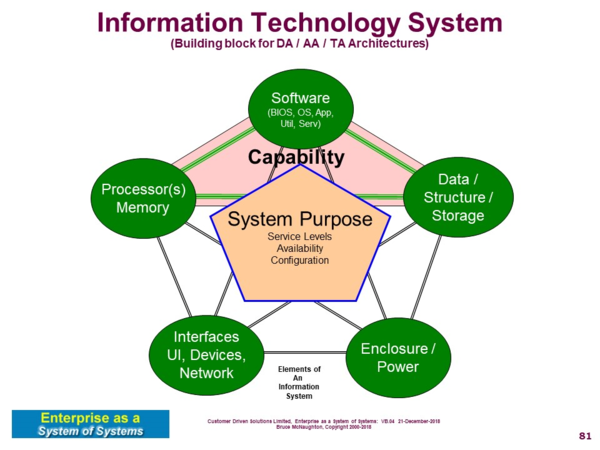
| + | [[File:Information Technology System.png|600px|Information Technology System]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Role and Purpose of Information Technology Systems == | ||
The primary role of ITS is to facilitate the flow of information and enable efficient business operations through technology. The purposes include: | The primary role of ITS is to facilitate the flow of information and enable efficient business operations through technology. The purposes include: | ||
| + | *Data Management: Organize, store, and retrieve vast data quickly and securely. | ||
| + | *Process Automation: Automate routine tasks to increase efficiency and reduce human error. | ||
| + | *Communication Enhancement: Enable effective communication within an organization and with external stakeholders through various platforms. | ||
| + | *Decision Support: Provide crucial data and analytical tools to help organizations make informed decisions. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | == Usage of Information Technology Systems == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Usage of Information Technology Systems | ||
Information Technology Systems are used in a variety of ways across different sectors: | Information Technology Systems are used in a variety of ways across different sectors: | ||
| + | *Business: For customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and supply chain management (SCM). | ||
| + | *Healthcare: To manage patient records, schedule appointments, and support telemedicine. | ||
| + | *Education: For learning management systems (LMS), student information systems (SIS), and online educational resources. | ||
| + | *Government: In e-governance applications, public records management, and security systems. | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | == Importance of Information Technology Systems == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Importance of Information Technology Systems | ||
ITS are crucial because they: | ITS are crucial because they: | ||
| + | *Enhance Productivity: ITS increases overall productivity by automating tasks and optimizing processes. | ||
| + | *Improve Accuracy: Automated systems reduce human errors in data entry and processing. | ||
| + | *Support Scalability: Technology systems can be scaled up or down based on organizational needs, supporting growth and adaptation. | ||
| + | *Enable Innovation: ITS provides the tools necessary for innovation, helping organizations to develop new products, services, and processes. | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | == Benefits of Information Technology Systems == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Benefits of Information Technology Systems | ||
Implementing robust ITS offers several advantages: | Implementing robust ITS offers several advantages: | ||
| + | *Operational Efficiency: Streamlines operations and reduces costs by improving process efficiency. | ||
| + | *Data Accessibility: Enhances data accessibility, allowing for better management and utilization. | ||
| + | *Security: Provides advanced solutions for securing sensitive information and against data breaches. | ||
| + | *Competitive Advantage: Offers tools that can lead to a competitive advantage by improving customer service and enabling faster response times. | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | == Examples of Information Technology Systems in Practice == | |
| − | + | *Online Retailing: Use an integrated ITS to manage inventory, process payments, and handle customer relations. | |
| − | + | *Banking Sector: Deployment of secure online banking systems that allow for transaction processing, fraud detection, and customer service management. | |
| − | + | *Manufacturing: Use of ITS for automating production lines, managing supply chains, and ensuring quality control. | |
| − | Examples of Information Technology Systems in Practice | ||
| − | Online Retailing: Use | ||
| − | Banking Sector: Deployment of secure online banking systems that allow for transaction processing, fraud detection, and customer service management. | ||
| − | Manufacturing: Use of ITS for automating production lines, managing supply chains, and ensuring quality control. | ||
Information Technology Systems form the backbone of modern organizational operations, enhancing efficiency, improving communication, and enabling data-driven decision-making. As technology evolves, the role of ITS is becoming more integral to achieving strategic goals and maintaining competitiveness in the global market. | Information Technology Systems form the backbone of modern organizational operations, enhancing efficiency, improving communication, and enabling data-driven decision-making. As technology evolves, the role of ITS is becoming more integral to achieving strategic goals and maintaining competitiveness in the global market. | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
| − | Hardware: | + | *[[Hardware]]: Discusses the various hardware components, such as servers, computers, network devices, and peripherals of IT systems. |
| − | Software: Explaining the range of software solutions used in IT systems, including operating systems, application software, and specialized enterprise software. | + | *[[Software]]: Explaining the range of software solutions used in IT systems, including operating systems, application software, and specialized enterprise software. |
| − | + | *[[Network]]: Covers networking fundamentals, including LAN, WAN, internet connectivity, and wireless communication, which are essential for IT systems. | |
| − | Database Management: Discussing database technologies and their role in managing and storing organizational data efficiently within IT systems. | + | *[[Database Management System (DBMS)]]: Discussing database technologies and their role in managing and storing organizational data efficiently within IT systems. |
| − | Cloud Computing: Explaining how cloud services such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are integrated into IT systems to enhance scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. | + | *[[Cloud Computing]]: Explaining how cloud services such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are integrated into IT systems to enhance scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. |
| − | + | *[[Cyber Security]]ecurity: Linking to the importance of cybersecurity in protecting IT systems from threats and vulnerabilities, including the methods and tools used to secure data and network resources. | |
| − | System Architecture: Discussing the architecture of IT systems, including the design principles, frameworks, and configurations that support business operations. | + | *System Architecture: Discussing the architecture of IT systems, including the design principles, frameworks, and configurations that support business operations. |
| − | IT Governance: Covering IT governance practices that ensure IT systems align with organizational goals and comply with regulations and standards. | + | *[[IT Governance]]: Covering IT governance practices that ensure IT systems align with organizational goals and comply with regulations and standards. |
| − | Business Intelligence | + | *[[Business Intelligence]] and [[Business Analytics]]: Explaining how BI tools and analytics are implemented within IT systems to help organizations make informed decisions based on data analysis. |
| − | IT Service Management (ITSM): | + | *[[IT Service Management (ITSM)]]: Discusses ITSM frameworks like ITIL that guide the management of IT services, focusing on service delivery and support. |
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 20:18, 8 May 2024
What are Information Technology Systems?
Information Technology Systems (ITS) refer to the combination of hardware, software, networks, and databases that are integrated and coordinated to collect, process, store, and disseminate data. ITS encompasses the technology infrastructure used in organizations to support business processes, communication, and services. These systems are critical for managing information efficiently and are central to almost every sector's operations.
Role and Purpose of Information Technology Systems
The primary role of ITS is to facilitate the flow of information and enable efficient business operations through technology. The purposes include:
- Data Management: Organize, store, and retrieve vast data quickly and securely.
- Process Automation: Automate routine tasks to increase efficiency and reduce human error.
- Communication Enhancement: Enable effective communication within an organization and with external stakeholders through various platforms.
- Decision Support: Provide crucial data and analytical tools to help organizations make informed decisions.
Usage of Information Technology Systems
Information Technology Systems are used in a variety of ways across different sectors:
- Business: For customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and supply chain management (SCM).
- Healthcare: To manage patient records, schedule appointments, and support telemedicine.
- Education: For learning management systems (LMS), student information systems (SIS), and online educational resources.
- Government: In e-governance applications, public records management, and security systems.
Importance of Information Technology Systems
ITS are crucial because they:
- Enhance Productivity: ITS increases overall productivity by automating tasks and optimizing processes.
- Improve Accuracy: Automated systems reduce human errors in data entry and processing.
- Support Scalability: Technology systems can be scaled up or down based on organizational needs, supporting growth and adaptation.
- Enable Innovation: ITS provides the tools necessary for innovation, helping organizations to develop new products, services, and processes.
Benefits of Information Technology Systems
Implementing robust ITS offers several advantages:
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlines operations and reduces costs by improving process efficiency.
- Data Accessibility: Enhances data accessibility, allowing for better management and utilization.
- Security: Provides advanced solutions for securing sensitive information and against data breaches.
- Competitive Advantage: Offers tools that can lead to a competitive advantage by improving customer service and enabling faster response times.
Examples of Information Technology Systems in Practice
- Online Retailing: Use an integrated ITS to manage inventory, process payments, and handle customer relations.
- Banking Sector: Deployment of secure online banking systems that allow for transaction processing, fraud detection, and customer service management.
- Manufacturing: Use of ITS for automating production lines, managing supply chains, and ensuring quality control.
Information Technology Systems form the backbone of modern organizational operations, enhancing efficiency, improving communication, and enabling data-driven decision-making. As technology evolves, the role of ITS is becoming more integral to achieving strategic goals and maintaining competitiveness in the global market.
See Also
- Hardware: Discusses the various hardware components, such as servers, computers, network devices, and peripherals of IT systems.
- Software: Explaining the range of software solutions used in IT systems, including operating systems, application software, and specialized enterprise software.
- Network: Covers networking fundamentals, including LAN, WAN, internet connectivity, and wireless communication, which are essential for IT systems.
- Database Management System (DBMS): Discussing database technologies and their role in managing and storing organizational data efficiently within IT systems.
- Cloud Computing: Explaining how cloud services such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are integrated into IT systems to enhance scalability, flexibility, and efficiency.
- Cyber Securityecurity: Linking to the importance of cybersecurity in protecting IT systems from threats and vulnerabilities, including the methods and tools used to secure data and network resources.
- System Architecture: Discussing the architecture of IT systems, including the design principles, frameworks, and configurations that support business operations.
- IT Governance: Covering IT governance practices that ensure IT systems align with organizational goals and comply with regulations and standards.
- Business Intelligence and Business Analytics: Explaining how BI tools and analytics are implemented within IT systems to help organizations make informed decisions based on data analysis.
- IT Service Management (ITSM): Discusses ITSM frameworks like ITIL that guide the management of IT services, focusing on service delivery and support.