Difference between revisions of "Managed Service Provider (MSP)"
(Created page with "A '''Managed Service Provider (MSP)''' is an outsourced third-party company that manages and assumes the responsibility of a defined set of day-to-day manageme...") |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | A | + | == What is a Managed Service Provider (MSP)? == |
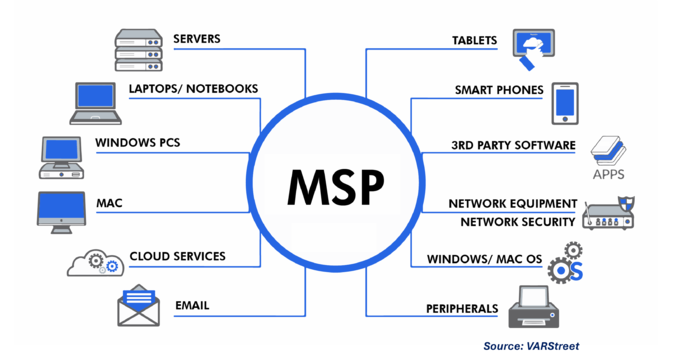
| + | A Managed Service Provider (MSP) is a company that remotely manages a customer's IT infrastructure and/or end-user systems, typically on a proactive basis and under a subscription model. This can include managing networks, applications, security, and other IT services. Businesses often use MSPs to reduce IT operational costs, improve technology scalability, and allow for a more predictable budgeting for IT expenses. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Managed Service Providers.png|700px|Managed Service Providers]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Role and Purpose of Managed Service Providers == | ||
| + | The primary role of an MSP is to ensure that an organization's IT systems are running efficiently and effectively without the need for the organization to manage these systems directly. The purposes include: | ||
| + | *Outsourcing IT Operations: Handling daily IT operations to free up business resources for core activities. | ||
| + | *Enhancing IT Performance: Providing expertise and proactive monitoring ensures IT systems operate optimally. | ||
| + | *Risk Management: Offering robust cybersecurity and data backup solutions to protect against data breaches and other IT risks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Usage of Managed Service Providers == | ||
| + | MSPs are used across various organizational scales and industries: | ||
| + | *Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs): SMEs utilize MSPs to obtain cost-effective IT management without hiring a full in-house IT staff. | ||
| + | *Large Corporations: Large companies may use MSPs to manage specific IT functions such as security monitoring or network management to supplement their in-house IT teams. | ||
| + | *Government and Nonprofits: These organizations often turn to MSPs to handle IT needs within budget constraints while focusing on their primary objectives. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Importance of Managed Service Providers == | ||
| + | MSPs are crucial because they: | ||
| + | *Provide Expertise and Specialization: MSPs bring specialized knowledge that may be too costly or impractical for businesses to develop internally. | ||
| + | *Offer Scalability: They allow businesses to scale their IT capabilities up or down based on demand without needing to manage additional staff or resources directly. | ||
| + | *Ensure Compliance: MSPs can help organizations meet regulatory compliance standards related to IT, such as data protection regulations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Benefits of Managed Service Providers == | ||
| + | Engaging an MSP offers several advantages: | ||
| + | *Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for large capital expenditures in IT and converts IT costs to variable costs. | ||
| + | *Focus on Core Business: Allows companies to concentrate on their core business functions without the distraction of complex IT decisions. | ||
| + | *Proactive Solutions: Offers proactive support to identify and fix issues before they become problems. | ||
| + | *Enhanced Security: Provides advanced security measures, regular updates, and maintenance to protect against threats. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Examples of Managed Service Providers in Practice == | ||
| + | *Cybersecurity Management: An MSP may offer 24/7 monitoring and immediate incident response services to protect clients' data and IT systems from cyber threats. | ||
| + | *Network Operations: Managing and optimizing a company’s network infrastructure to ensure fast and reliable access to applications and services. | ||
| + | *Cloud Services: Administering and overseeing a company's cloud operations, including data storage, cloud software management, and computing resources. | ||
| + | Managed Service Providers play an essential role in today's business environment by offering specialized IT services that enable companies to improve efficiency, focus on their core business, and manage IT costs effectively. Through their comprehensive and proactive approaches, MSPs help businesses maintain a competitive edge by leveraging the latest technologies and best practices in IT management. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == See Also == | ||
| + | *[[IT Sourcing (Information Technology Sourcing)]]: Discussing the broader concept of IT sourcing, of which MSPs are a critical component | ||
| + | *[[Outsourcing]]: Highlighting why companies outsource IT functions. | ||
| + | *[[Cloud Computing]]: Explaining how MSPs integrate and manage cloud services for businesses, including public, private, and hybrid cloud environments. | ||
| + | *[[Cyber Security]]: Covering the cybersecurity solutions offered by MSPs, such as monitoring, threat detection, and response services, which are essential for protecting client data and systems. | ||
| + | *[[Network Management]]: Discussing the management of network infrastructure, including network design, monitoring, and maintenance, which are typical services provided by MSPs. | ||
| + | *Data Center Management: Explaining how MSPs handle data center operations, including server and storage management, to ensure high availability and performance. | ||
| + | *Help Desk Services: MSPs provide help desk services, which support end-users with troubleshooting, software support, and general technical assistance. | ||
| + | *[[Compliance]]: MSPs assist businesses in complying with various regulations by managing security protocols and ensuring that systems meet required standards. | ||
| + | *[[Business Continuity]] and [[Disaster recovery]]: Linking to how MSPs develop and implement business continuity and disaster recovery plans to ensure that business operations can continue in the face of disruptions. | ||
| + | *[[Service Level Agreement (SLA)]]: Explaining the importance of SLAs in the MSP business model, detailing how these agreements define the standards of service that clients can expect. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:42, 8 May 2024
What is a Managed Service Provider (MSP)?
A Managed Service Provider (MSP) is a company that remotely manages a customer's IT infrastructure and/or end-user systems, typically on a proactive basis and under a subscription model. This can include managing networks, applications, security, and other IT services. Businesses often use MSPs to reduce IT operational costs, improve technology scalability, and allow for a more predictable budgeting for IT expenses.
Role and Purpose of Managed Service Providers
The primary role of an MSP is to ensure that an organization's IT systems are running efficiently and effectively without the need for the organization to manage these systems directly. The purposes include:
- Outsourcing IT Operations: Handling daily IT operations to free up business resources for core activities.
- Enhancing IT Performance: Providing expertise and proactive monitoring ensures IT systems operate optimally.
- Risk Management: Offering robust cybersecurity and data backup solutions to protect against data breaches and other IT risks.
Usage of Managed Service Providers
MSPs are used across various organizational scales and industries:
- Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs): SMEs utilize MSPs to obtain cost-effective IT management without hiring a full in-house IT staff.
- Large Corporations: Large companies may use MSPs to manage specific IT functions such as security monitoring or network management to supplement their in-house IT teams.
- Government and Nonprofits: These organizations often turn to MSPs to handle IT needs within budget constraints while focusing on their primary objectives.
Importance of Managed Service Providers
MSPs are crucial because they:
- Provide Expertise and Specialization: MSPs bring specialized knowledge that may be too costly or impractical for businesses to develop internally.
- Offer Scalability: They allow businesses to scale their IT capabilities up or down based on demand without needing to manage additional staff or resources directly.
- Ensure Compliance: MSPs can help organizations meet regulatory compliance standards related to IT, such as data protection regulations.
Benefits of Managed Service Providers
Engaging an MSP offers several advantages:
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for large capital expenditures in IT and converts IT costs to variable costs.
- Focus on Core Business: Allows companies to concentrate on their core business functions without the distraction of complex IT decisions.
- Proactive Solutions: Offers proactive support to identify and fix issues before they become problems.
- Enhanced Security: Provides advanced security measures, regular updates, and maintenance to protect against threats.
Examples of Managed Service Providers in Practice
- Cybersecurity Management: An MSP may offer 24/7 monitoring and immediate incident response services to protect clients' data and IT systems from cyber threats.
- Network Operations: Managing and optimizing a company’s network infrastructure to ensure fast and reliable access to applications and services.
- Cloud Services: Administering and overseeing a company's cloud operations, including data storage, cloud software management, and computing resources.
Managed Service Providers play an essential role in today's business environment by offering specialized IT services that enable companies to improve efficiency, focus on their core business, and manage IT costs effectively. Through their comprehensive and proactive approaches, MSPs help businesses maintain a competitive edge by leveraging the latest technologies and best practices in IT management.
See Also
- IT Sourcing (Information Technology Sourcing): Discussing the broader concept of IT sourcing, of which MSPs are a critical component
- Outsourcing: Highlighting why companies outsource IT functions.
- Cloud Computing: Explaining how MSPs integrate and manage cloud services for businesses, including public, private, and hybrid cloud environments.
- Cyber Security: Covering the cybersecurity solutions offered by MSPs, such as monitoring, threat detection, and response services, which are essential for protecting client data and systems.
- Network Management: Discussing the management of network infrastructure, including network design, monitoring, and maintenance, which are typical services provided by MSPs.
- Data Center Management: Explaining how MSPs handle data center operations, including server and storage management, to ensure high availability and performance.
- Help Desk Services: MSPs provide help desk services, which support end-users with troubleshooting, software support, and general technical assistance.
- Compliance: MSPs assist businesses in complying with various regulations by managing security protocols and ensuring that systems meet required standards.
- Business Continuity and Disaster recovery: Linking to how MSPs develop and implement business continuity and disaster recovery plans to ensure that business operations can continue in the face of disruptions.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA): Explaining the importance of SLAs in the MSP business model, detailing how these agreements define the standards of service that clients can expect.