Difference between revisions of "Network Architecture"
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
=== Cloud Architecture === | === Cloud Architecture === | ||
When constructing a network, ORACLE recommends studying the different traffic patterns over the network. Cloud computing offers many benefits, but if constructed poorly, a cloud infrastructure can be inefficient. For example, a single network interface used with a multi-node configuration will not be able to accommodate high cloud network traffic. Utilizing different networks/subnetworks to isolate traffic maximizes efficiency and improves functionality. Types of traffic may include guests, storage, or management. | When constructing a network, ORACLE recommends studying the different traffic patterns over the network. Cloud computing offers many benefits, but if constructed poorly, a cloud infrastructure can be inefficient. For example, a single network interface used with a multi-node configuration will not be able to accommodate high cloud network traffic. Utilizing different networks/subnetworks to isolate traffic maximizes efficiency and improves functionality. Types of traffic may include guests, storage, or management. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Components of Modern Network Architectures<ref>Components of Modern Network Architectures [https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/enterprise-networks/what-is-network-architecture.html#~components Cisco]</ref> == | ||
| + | The industry is now using architectures that ease the burden of building and maintaining computer networks for the digital age. | ||
| + | *Intent-based networking (IBN): An intent-based network takes an organization's desired outcomes at a high level as input and sets up the network to achieve these objectives. It does so by automating operations extensively, analyzing network performance, pinpointing problematic areas, providing all-around security, and integrating with business processes. | ||
| + | *Controller-led: Network controllers are foundational to intent-based networking and are essential to scaling and securing networks in the digital era. Controllers dramatically simplify operations and help organizations respond rapidly to changing business requirements. They automate networking functions by translating business intent into device configurations, and they monitor the network devices continuously to help ensure performance and security. | ||
| + | *Multidomain: Multiple networks in an enterprise communicate with one another through their controllers. Such cross-network, or multidomain, integrations generally involve exchanging relevant operating parameters to help ensure that desired business outcomes that span networking domains are achieved. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Network Architecture and OSI Model == | ||
| + | The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) defines and codifies the concept of layered network architecture. Abstraction layers are used to subdivide a communications system further into smaller manageable parts. A layer is a collection of similar functions that provide services to the layer above it and receives services from the layer below it. On each layer, an instance provides services to the instances at the layer above and requests service from the layer below. | ||
Revision as of 14:00, 8 July 2021
What is Network Architecture?[1]
Network Architecture is the complete framework of an organization's computer network. The diagram of the network architecture provides a full picture of the established network with detailed view of all the resources accessible. It includes hardware components used for communication, cabling and device types, network layout and topologies, physical and wireless connections, implemented areas and future plans. In addition, the software rules and protocols also constitute to the network architecture. This architecture is always designed by a network manager/administrator with coordination of network engineers and other design engineers.
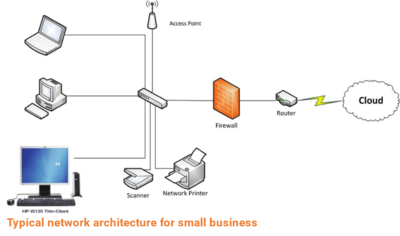
source: Shadi Aljawarneh
Evolving Network Architecture[2]
Network architecture matters not just for internal operations but also for consumer interaction with companies. Consumerization and increased use of technology have made it crucial that companies provide platforms that are user-friendly and, for the most part, glitch-free. Consumers do not want slow and cumbersome shopping experiences or processes that require many steps. For example, many companies now offer auto fill-in capabilities so repeat customers have less hassle when checking out. Cloud architecture enables better market agility through traffic partitioning.
Cloud Architecture
When constructing a network, ORACLE recommends studying the different traffic patterns over the network. Cloud computing offers many benefits, but if constructed poorly, a cloud infrastructure can be inefficient. For example, a single network interface used with a multi-node configuration will not be able to accommodate high cloud network traffic. Utilizing different networks/subnetworks to isolate traffic maximizes efficiency and improves functionality. Types of traffic may include guests, storage, or management.
Components of Modern Network Architectures[3]
The industry is now using architectures that ease the burden of building and maintaining computer networks for the digital age.
- Intent-based networking (IBN): An intent-based network takes an organization's desired outcomes at a high level as input and sets up the network to achieve these objectives. It does so by automating operations extensively, analyzing network performance, pinpointing problematic areas, providing all-around security, and integrating with business processes.
- Controller-led: Network controllers are foundational to intent-based networking and are essential to scaling and securing networks in the digital era. Controllers dramatically simplify operations and help organizations respond rapidly to changing business requirements. They automate networking functions by translating business intent into device configurations, and they monitor the network devices continuously to help ensure performance and security.
- Multidomain: Multiple networks in an enterprise communicate with one another through their controllers. Such cross-network, or multidomain, integrations generally involve exchanging relevant operating parameters to help ensure that desired business outcomes that span networking domains are achieved.
Network Architecture and OSI Model
The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) defines and codifies the concept of layered network architecture. Abstraction layers are used to subdivide a communications system further into smaller manageable parts. A layer is a collection of similar functions that provide services to the layer above it and receives services from the layer below it. On each layer, an instance provides services to the instances at the layer above and requests service from the layer below.
- ↑ Definition - What Does Network Architecture Mean? Techopedia
- ↑ Evolving Network Architecture RSI security
- ↑ Components of Modern Network Architectures Cisco
