Difference between revisions of "Personnel Management"
(Created page with "'''Content Coming Soon'''") |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ''' | + | == What is personnel Management?<ref>[http://www.masters-in-human-resources.org/faq/what-is-personnel-management Definition of Personnel Management]</ref> == |
| + | '''Personnel management''' is defined as an administrative specialization that focuses on hiring and developing employees to become more valuable to the company. It is sometimes considered to be a sub-category of human resources that only focuses on administration. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == The Evolvement of Personnel Management<ref>[http://digitalassets.lib.berkeley.edu/irle/ucb/text/lb001826.pdf The Evolvement of Personnel Management]</ref> == | ||
| + | There are a number of approaches toward personnel that have evolved over time as well as, including the newer approaches.<br /> | ||
| + | (a) Mechanical Approach towards Personnel: The reasoning here is that if machines can be made more productive by extreme specialization, so can men. This approach has also been called the 'factor-of-production concept'. It implies that labor must be classified with capital and raw material as a factor of production to be procured as cheaply as possible and utilized to the fullest. The fact that human beings are involved in this is of human the mechanical approach usually results in the creation of various management problems-personnel problems. Although this philosophy towards labor is changing and has changed, there are still many managers, especially in South Africa, whose attitudes are strongly influenced by this old philosophy.<br /> | ||
| + | (b) Paternalism: In this approach management must assume- a fatherly and protective attitude towards employees. By merely supplying benefits, eg. housing, transport, recreation, and pensions, managements are not necessarily paternalistic. It is the attitude and the manner of implementation that determine whether or not management is paternal in its dealings with employees, To be paternalistic two characteristics are necessary. | ||
| + | *Firstly, the profit motive should not be prominent in management's decision to provide such employee services. | ||
| + | *Secondly, the decision concerning what services to provide and how to provide them belongs solely to management. The father makes the decision that he feels is best for the child. Paternalism died largely during the depression of the 1930s, though certain managements still use this approach in their dealings with employees. How many managers consult their black employees before deciding on these benefits and services?<br /> | ||
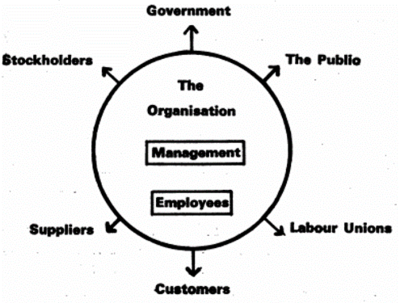
| + | (c) Social System Approach: In this approach, the organization is perceived as the control agency operating in an open system. Employees are perceived as power sources whose development can be aligned with basic organizational goals. As the diagram below indicates, the employee group is only one of many groups to which the manager must relate (FLIPPO,19). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Personnel_Management1.png|400px|Personnel Management 1]]<br /> | ||
| + | source: Berkeley | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | This more mature approach also explains the various roles a person has to play. From this flows role expectations, role conflicts, etc., and the influence this has on human behavior.<br /> | ||
| + | (d) Newer Approaches to Personnel Management: The basic mission of personnel is conceived by BiICKER (1965) to be a; 'huge balancing act'. Personnel is responsible for balancing the demand for and supply of people, of balancing the organization's need for certain experience and skills with the labor market's supply of these skills and experience. Everything the personnel man does has an effect on one side of the balance or the other. In the same vein Myers (1970) speaks of the 'counterbalancing' influence where personnel management counter- -balances line management's emphasis on production, with emphasis on human relations. He says further that the personnel specialist as a 'change agent' interacts with the line manager to define conditions for the mutual achievement of organizational and individual goals. The primary purpose of personnel as a change agent is to maximize the achievement of organizational objectives through the best utilization of human resources. Interaction is emphasized by MEGGINSON (1967) who says that the function of management is to blend human and material resources and technology into a harmonious relationship that will contribute to the improvement of the company and society. He developed the following hypotheses:<br /> | ||
| + | (i) "A company's productivity]] and resulting profitability are directly proportional to the quantity and quality of its human resources."<br /> | ||
| + | (ii) "The efficiency and effectiveness of employers' productivity results from the recognition of, and enhancement of, the human dignity of each individual employee."<br /> | ||
| + | (iii) "The supply and caliber of the human resource can be effectively enhanced through education, training, and personal development." | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Personnel Management Duties<ref>[https://www.thebalancecareers.com/personnel-management-1917581 Personnel Management Duties]</ref> == | ||
| + | *Hiring across many organizations which is done by a single person or group of persons. Recruiters look at checkbox lists and match candidates' resumes to that list. | ||
| + | *Compensation and benefits departments which create strict rules around pay grades and increases. For instance, enforcing a limit on annual increases of no more than 10 percent and preventing promotions of more than one salary grade. The important part is to create consistency. | ||
| + | *New employee orientation which consists of helping employees fill out their benefits paperwork, showing them where the break room is, and handing out a copy of the employee handbook. The focus is on getting the paperwork adequately completed and filed away. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
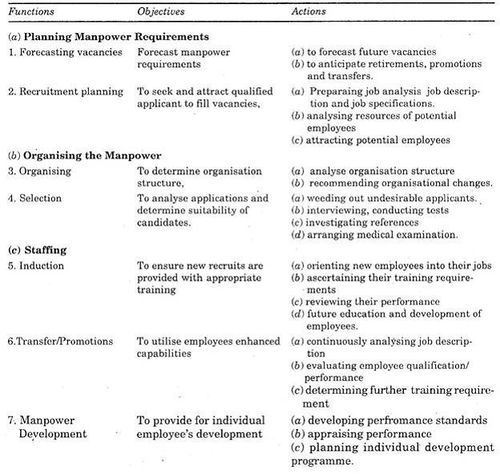
| + | == Functions and Objectives of Personnel Management<ref>[http://www.businessmanagementideas.com/personnel-management/personnel-management-meaning-functions-and-principles/6248 Functions and Objectives of Personnel Management]</ref> == | ||
| + | Major functions and objectives are given hereunder: | ||
| + | Personnel Management functions are generally divided into planning, organising, staffing, motivating and controlling aspects. Major functions and objectives are given in the table below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Personnel Management.jpg|500px|Personnel Management]]<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === The Process of Personnel Management === | ||
| + | The following are the steps involved in the process of personnel management:<br /> | ||
| + | a) Human resource planning and forecasting,<br /> | ||
| + | b) Recruitment,<br /> | ||
| + | c) Selection,<br /> | ||
| + | d) Training and development,<br /> | ||
| + | e) Performance appraisal and<br /> | ||
| + | f) Promotion and demotion. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Principles of Personnel Management<ref>[http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/133796/9/09_chapter%201.pdf Principles of Personnel Management]</ref> == | ||
| + | Personnel management has been based on certain benchmark principles for high levels of success. These principles change as conditions change including human behavior patterns. The following are some of the popular and practice-oriented principles: | ||
| + | (a) Persons should be dealt with as complete individuals | ||
| + | (b) Employees should be made to feel worthwhile | ||
| + | (c) Fairness and justice | ||
| + | (d) Rewards should be earned and not given | ||
| + | (e) Employees should be supplied with relevant information | ||
| + | (f) Proper judgment of the strength and intelligence of the persons, and | ||
| + | (g) Equal wage for equal work. | ||
| + | These principles cover recruitment, training, and rewarding them properly. Importance should be given to their feelings and experiences. They should be made to feel confident, proud, and satisfied with their services and rewards. Their productive functions depend on the spirit of care and sharing around them. 'Fairness' should be the catchphrase on both sides. The employees should be rewarded and not gifted. The communication system between the managers and employees should be properly developed and unnecessary secrecy and suspicion should be avoided altogether. While the strength and intelligence of the employees are properly judged and recognized, there should not be any discrimination in wages among all those who serve equally. Equal pay should be given to equal work. Gender discrimination also should be avoided. In sum, the employees should be encouraged to feel proud, rewarded, and satisfied as far as their jobs are concerned. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Role of Personnel Manager<ref>[https://www.managementstudyguide.com/personnel-management.htm Role of Personnel Manager]</ref> == | ||
| + | The personnel manager is the head of the personnel department. S/he performs both managerial and operative functions of management. The role can be summarized as: | ||
| + | *Personnel manager provides assistance to top management- The top management is the people who decide and frame the primary policies of the concern. All kinds of policies related to personnel or workforce can be framed out effectively by the personnel manager. | ||
| + | *S/he advises the line manager as a staff specialist- The personnel manager acts like a staff advisor and assists the line managers in dealing with various personnel matters. | ||
| + | *As a counselor,- As a counselor, the personnel manager attends to the problems and grievances of employees and guides them. He tries to solve them in the best of his capacity. | ||
| + | *Personnel manager acts as a mediator- He is a linking pin between management and workers. | ||
| + | *S/he acts as a spokesman- Since he is in direct contact with the employees, he is required to act as a representative of the organization in committees appointed by the government. He represents the company in training programs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == See Also == | ||
| + | *[[Performance Metrics]] | ||
| + | *[[Performance Management]] | ||
| + | *[[Performance Appraisal]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Further Reading == | ||
| + | *[https://www.theseus.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/106220/Tiskevits_Aleksandr.pdf?sequence=1 Personnel management in medium-sized companies] | ||
| + | *[http://digitalassets.lib.berkeley.edu/irle/ucb/text/lb001826.pdf A Systems Approach to Personnel Management] | ||
| + | *[https://www.ipa.ie/_fileUpload/Documents/CPMR_DP_16_Personnel_Management_to_HR_%20KeyIssues_Challenges.pdf From Personnel Management to HRM: Key Issues and Challenges] | ||
| + | *[https://www.emeraldinsight.com/doi/abs/10.1108/eb055275?journalCode=pr Personnel Management: A Framework for Analysis] | ||
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
Revision as of 23:49, 18 January 2023
What is personnel Management?[1]
Personnel management is defined as an administrative specialization that focuses on hiring and developing employees to become more valuable to the company. It is sometimes considered to be a sub-category of human resources that only focuses on administration.
The Evolvement of Personnel Management[2]
There are a number of approaches toward personnel that have evolved over time as well as, including the newer approaches.
(a) Mechanical Approach towards Personnel: The reasoning here is that if machines can be made more productive by extreme specialization, so can men. This approach has also been called the 'factor-of-production concept'. It implies that labor must be classified with capital and raw material as a factor of production to be procured as cheaply as possible and utilized to the fullest. The fact that human beings are involved in this is of human the mechanical approach usually results in the creation of various management problems-personnel problems. Although this philosophy towards labor is changing and has changed, there are still many managers, especially in South Africa, whose attitudes are strongly influenced by this old philosophy.
(b) Paternalism: In this approach management must assume- a fatherly and protective attitude towards employees. By merely supplying benefits, eg. housing, transport, recreation, and pensions, managements are not necessarily paternalistic. It is the attitude and the manner of implementation that determine whether or not management is paternal in its dealings with employees, To be paternalistic two characteristics are necessary.
- Firstly, the profit motive should not be prominent in management's decision to provide such employee services.
- Secondly, the decision concerning what services to provide and how to provide them belongs solely to management. The father makes the decision that he feels is best for the child. Paternalism died largely during the depression of the 1930s, though certain managements still use this approach in their dealings with employees. How many managers consult their black employees before deciding on these benefits and services?
(c) Social System Approach: In this approach, the organization is perceived as the control agency operating in an open system. Employees are perceived as power sources whose development can be aligned with basic organizational goals. As the diagram below indicates, the employee group is only one of many groups to which the manager must relate (FLIPPO,19).
This more mature approach also explains the various roles a person has to play. From this flows role expectations, role conflicts, etc., and the influence this has on human behavior.
(d) Newer Approaches to Personnel Management: The basic mission of personnel is conceived by BiICKER (1965) to be a; 'huge balancing act'. Personnel is responsible for balancing the demand for and supply of people, of balancing the organization's need for certain experience and skills with the labor market's supply of these skills and experience. Everything the personnel man does has an effect on one side of the balance or the other. In the same vein Myers (1970) speaks of the 'counterbalancing' influence where personnel management counter- -balances line management's emphasis on production, with emphasis on human relations. He says further that the personnel specialist as a 'change agent' interacts with the line manager to define conditions for the mutual achievement of organizational and individual goals. The primary purpose of personnel as a change agent is to maximize the achievement of organizational objectives through the best utilization of human resources. Interaction is emphasized by MEGGINSON (1967) who says that the function of management is to blend human and material resources and technology into a harmonious relationship that will contribute to the improvement of the company and society. He developed the following hypotheses:
(i) "A company's productivity]] and resulting profitability are directly proportional to the quantity and quality of its human resources."
(ii) "The efficiency and effectiveness of employers' productivity results from the recognition of, and enhancement of, the human dignity of each individual employee."
(iii) "The supply and caliber of the human resource can be effectively enhanced through education, training, and personal development."
Personnel Management Duties[3]
- Hiring across many organizations which is done by a single person or group of persons. Recruiters look at checkbox lists and match candidates' resumes to that list.
- Compensation and benefits departments which create strict rules around pay grades and increases. For instance, enforcing a limit on annual increases of no more than 10 percent and preventing promotions of more than one salary grade. The important part is to create consistency.
- New employee orientation which consists of helping employees fill out their benefits paperwork, showing them where the break room is, and handing out a copy of the employee handbook. The focus is on getting the paperwork adequately completed and filed away.
Functions and Objectives of Personnel Management[4]
Major functions and objectives are given hereunder: Personnel Management functions are generally divided into planning, organising, staffing, motivating and controlling aspects. Major functions and objectives are given in the table below:
The Process of Personnel Management
The following are the steps involved in the process of personnel management:
a) Human resource planning and forecasting,
b) Recruitment,
c) Selection,
d) Training and development,
e) Performance appraisal and
f) Promotion and demotion.
Principles of Personnel Management[5]
Personnel management has been based on certain benchmark principles for high levels of success. These principles change as conditions change including human behavior patterns. The following are some of the popular and practice-oriented principles: (a) Persons should be dealt with as complete individuals (b) Employees should be made to feel worthwhile (c) Fairness and justice (d) Rewards should be earned and not given (e) Employees should be supplied with relevant information (f) Proper judgment of the strength and intelligence of the persons, and (g) Equal wage for equal work. These principles cover recruitment, training, and rewarding them properly. Importance should be given to their feelings and experiences. They should be made to feel confident, proud, and satisfied with their services and rewards. Their productive functions depend on the spirit of care and sharing around them. 'Fairness' should be the catchphrase on both sides. The employees should be rewarded and not gifted. The communication system between the managers and employees should be properly developed and unnecessary secrecy and suspicion should be avoided altogether. While the strength and intelligence of the employees are properly judged and recognized, there should not be any discrimination in wages among all those who serve equally. Equal pay should be given to equal work. Gender discrimination also should be avoided. In sum, the employees should be encouraged to feel proud, rewarded, and satisfied as far as their jobs are concerned.
Role of Personnel Manager[6]
The personnel manager is the head of the personnel department. S/he performs both managerial and operative functions of management. The role can be summarized as:
- Personnel manager provides assistance to top management- The top management is the people who decide and frame the primary policies of the concern. All kinds of policies related to personnel or workforce can be framed out effectively by the personnel manager.
- S/he advises the line manager as a staff specialist- The personnel manager acts like a staff advisor and assists the line managers in dealing with various personnel matters.
- As a counselor,- As a counselor, the personnel manager attends to the problems and grievances of employees and guides them. He tries to solve them in the best of his capacity.
- Personnel manager acts as a mediator- He is a linking pin between management and workers.
- S/he acts as a spokesman- Since he is in direct contact with the employees, he is required to act as a representative of the organization in committees appointed by the government. He represents the company in training programs.
See Also
References