Service Knowledge Management System (SKMS)
Service Knowledge Management System (SKMS) is a set of tools and databases used to manage (i.e. collect, store, update, analyze, present, and archive) organizations’ data, information, and knowledge.
Data, information, and knowledge are stored in SKMS. SKMS is used in everyday life to manage infrastructure and services, solve incidents and problems, or to make strategic decisions. SKMS contains many different types of data, information, and knowledge, such as:
- Service portfolio data
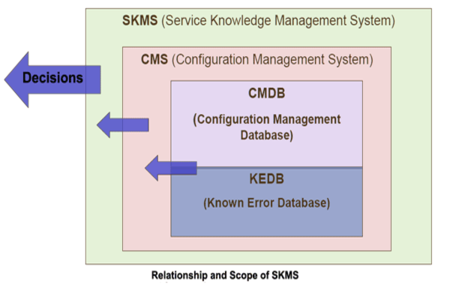
- Configuration Management System (CMS)
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs), Operation Level Agreements (OLAs), Underpinning Contracts (UCs)
- Information Security policy
- Business Plans
- Cost Allocation Model
- Budget
- Capacity Plan
- Availability Plan
- Known Error Database (KEDB)
- IT Projects and respective data
- Customer Information
- …etc.[1]
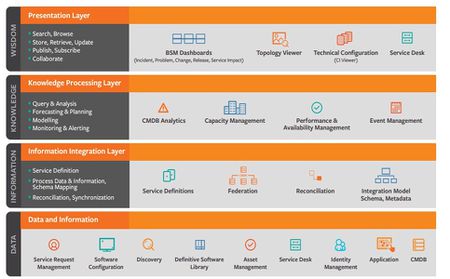
The Four Layers of SKMS[2]
The Service Knowledge Management System (SKMS) is divided into four distinct layers. Each of the layers has its own work area and is divided according to its level of information processing. The four layers are:
- Data and Information Layer: This data and information layer collects and stores the data that must be managed by Knowledge Management, including all the documents, files, applications status, etc. This layer mostly contains multiple data sources, as well as the tools that can be used by team members to properly apply data as knowledge. For example, it included a configuration management database (CMDB), definitive media library (DML), known error database (KEDB), and other configuration, management, and audit tools and applications.
- Information Integration Layer: The Information Integration Layer of SKMS helps to integrate all of the information from relevant business units of the organization in one place. If your organization works with partners, then the information related to those partners may also be found in this layer. This layer also helps to evaluate and analyze the data received from the first layer to get the relationship structure and store them in the integrated configuration management database (iCMDB).
- Knowledge Processing: The Knowledge Processing Layer provides an interface for users to report information that can be analyzed. The objective of this layer is to analyze, report, and monitor every bit of information that is received from other SKMS levels. A major part of this layer is performance management, which is used to determine whether your team members are meeting their performance goals. This layer facilitates you to monitor performance scorecards to help improve the productivity of your team.
- Presentation Layer: At the presentation layer, all the knowledge that is collected, analyzed, and structured is presented to the users for further use. The Presentation Layer facilitates authorized users to access information. In this SKMS presentation layer, users are provided with some visual materials that allow them to search, browse, and update the information they find in the system. Depending on the organizational policy, users may also be given the chance to contribute to improving the knowledge base.
See Also
A Service Knowledge Management System (SKMS) is a comprehensive system that enables organizations to collect, organize, analyze, and share knowledge across all levels of IT services management. It's an integral part of IT Service Management (ITSM) as outlined in the IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) framework. The SKMS supports the entire lifecycle of IT services, from initial strategy and design through to continuous improvement processes. By centralizing knowledge, the SKMS facilitates informed decision-making, enhances efficiency, improves service quality, and underpins the delivery of value to customers and stakeholders.
The SKMS consists of several layers, including:
- Data Layer: Contains raw data collected from various sources within the IT environment, such as logs and system metrics.
- Information Layer: Organizes the raw data into a more structured format, making it easier to understand and analyze, such as reports and dashboards.
- Knowledge Layer: Transforms information into knowledge by adding context, insights, and experiences, facilitating problem-solving and decision-making processes.
- Wisdom Layer: Applies knowledge to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions that align with the organization's goals and objectives.
Components of an SKMS may include Configuration Management Databases (CMDBs), known error databases, and service portfolios, among others. These components work together to provide a holistic view of the IT service management landscape, enabling better service delivery, operational efficiency, and strategic planning.
- IT Service Management (ITSM): Discussing the process-based practice intended to align the delivery of IT services with the needs of the organization and its users.
- IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL): Covering the set of detailed practices for IT service management that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of business.
- Configuration Management Database (CMDB): Explaining a database used to store information about hardware and software assets (known as Configuration Items or CIs) and their relationships.
- Knowledge Management: Discussing the process of creating, sharing, using, and managing the knowledge and information of an organization to enhance learning and innovation.
- Change Management: Covering methods and manners in which a company describes and implements change within its processes and organization.
- Incident Management: Explaining the process of identifying, analyzing, and correcting hazards to prevent a future re-occurrence, often used in managing IT issues.
- Problem Management: Discussing the process aimed at diagnosing the root causes of incidents and then determining the resolution to those problems.
- Service Catalog: Covering the structured collection of IT services that are available for deployment within an organization, including detailed information about each service.
- Continuous Improvement Process (CIP): Explaining the ongoing effort to improve products, services, or processes by making incremental improvements over time or achieving breakthrough improvements all at once.
- Data Analytics: Discussing the techniques to analyze raw data in order to make conclusions about that information, supporting the data layer of the SKMS.