Stakeholder
Business Doctionary defines Stakeholder as "A person, group or organization that has interest or concern in an organization. Stakeholders can affect or be affected by the organization's actions, objectives and policies."[1]
The international standard providing guidance on social responsibility, ISO 26000, defines a stakeholder as an “individual or group that has an interest in any decision or activity of an organization.”
Stakeholders can be internal or external. Internal stakeholders are people whose interest in a company comes through a direct relationship, such as employment, ownership or investment. External stakeholders are those people who do not directly work with a company but are affected in some way by the actions and outcomes of said business. Suppliers, creditors and public groups are all considered external stakeholders.[2]
Types of Stakeholders
Types of stakeholders include:
- Primary: those who are directly affected, either positively or negatively, by an organization’s actions
- Secondary: those who are indirectly affected by an organization’s actions
Stakeholder Analysis[3]
Stakeholder analysis is defined as a tool organizations can use to clearly identify key stakeholders for a project or other activity, understand where stakeholders stand, and develop cooperation between the stakeholders and the project team. The main objective is to ensure successful outcomes for the project or the changes to come. Stakeholder analysis is frequently used during the preparation phase of a project and is an excellent way to assess the attitudes of stakeholders towards changes or critical actions. It can be done once or on a regular basis to track changes in stakeholder attitudes over time. The stakeholder analysis is generally considered a highly confidential document because it often contains sensitive information.
Benefits of Creating a Stakeholder Analysis
- Provides clear understanding of stakeholders’ interests
- Offers mechanisms to influence other stakeholders
- Enables full understanding of potential risks
- Identifies key people to be informed about the project during the execution phase
- Provides awareness of negative stakeholders as well as their adverse effects on the project
Stakeholder Analysis Matrix
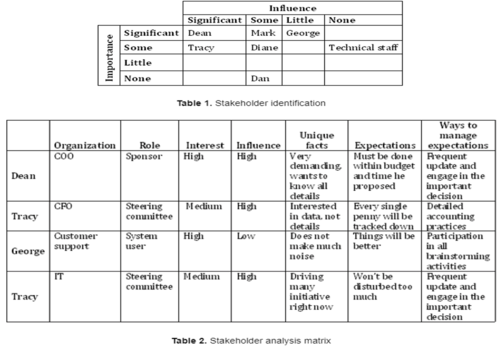
- Step 1. Stakeholder identification: Create a stakeholder matrix (Table 1) that will be used to identify key stakeholders and their positions. List the level of “influence” on the X axis (top row) and the level of “importance” on the Y axis (first column).
- Step 2. List all key stakeholders in the appropriate cells (Table 1).
- Step 3. Stakeholder analysis: Create a second matrix (Table 2). List all key stakeholders in the first column. List relevant information regarding them in the top row, using as many columns as needed.
- Step 4. Complete the information in the table by conducting interviews or through discussions with the project sponsor or another high- level resource.
- Step 5. Prepare an action plan to engage the stakeholders who could have a negative impact on the project or could be severely impacted by the actions.
- ↑ Definition = What does Stakeholder Mean? Bisoness Dictionary
- ↑ Internal and External Stakeholders Investopedia
- ↑ Stakeholder Analysis: Benefits and Matrix Asq.org