Upselling
Upselling is the process of encouraging customers to upgrade or include add-ons to the product or service they’re buying. The product or service being promoted is typically a more expensive product or add-ons which can increase the overall order value.[1]
Sometimes referred to as Suggestive selling, Upselling can take on many forms depending on the business category. At a retail store, an employee could suggest accessories to accompany a piece of apparel, such as a scarf and gloves to go with a new coat. In the restaurant setting, the waitstaff could point out side dishes to complement the main course a patron ordered. Similarly, at bars where food is served, bartenders might recommend appetizers to accompany drinks that were ordered, or vice versa. Bartenders may also suggest higher-end, pricier brands of beverages that are comparable to the type the patron has ordered.
This sales technique can be readily found in the automobile sales industry. A salesperson, after securing a customer’s commitment to purchase a vehicle, might offer to add supplements such as an extended warranty and roadside service. Depending on the make and model, they might also suggest including more features beyond the base model of the car. This could include buying a vehicle with more advanced audio equipment, a communications package that connects the driver’s phone to the vehicle’s dashboard, a rearview camera, a more powerful engine, or seat warmers. They might also try to convince them to upgrade to a different model that includes such features and others at a higher price compared with the original model they considered.
Travel planning, whether done through an agency or online platform, can feature suggestive selling. Typically, the travel booker will be offered recommendations on package deals for lodging and airfare, travelers insurance, ground transportation at the destination, as well as suggestions on tours to book and other sites to visit while on their journey. For recurring events, the traveler may be offered special rates to book in advance the same trip for the following year.[2]
Identifying Upselling Opportunities[3]
In a nutshell, the ideal upsell customers are the ones who are most engaged with your products and services. The whole concept of upselling is based on growing relationships with existing customers, meaning that upselling inherently involves regularly following up with clients to asses their current status and needs. That can involve a variety of methods, such as:
- Ask open-ended questions and listen to customers when they talk about their needs.
- Consider whether a product or service exists on the market already. If so, how can you improve upon it? If not, would it be possible to develop one?
- Investigate whether there are ways to improve upon your own existing product. If you already offer a satisfactory version, can you also provide an extraordinary version?
- Analyze your revenue sources. Seeing where your company earns the most can help to identify your clients’ needs and how to best upsell strategically.
- Determine what your market segment can actually use and afford. For example, if you are selling a software package to college students, you may not spot many opportunities to upsell them the business suite. On the other hand, you could potentially offer a student discount on a more comprehensive package.
- Look at customer data across departments. Customers have different contacts within a company depending on what they need. All of those contacts will have information about them.
- Learn more about your customers through information available online. Such as customer reviews, interactions over social media, page views, shares, etc.
Upselling should happen almost organically as a means of solving a problem or filling a need. Staying informed about what customers need from a variety of angles is the most effective way of identifying upselling opportunities.
Upselling Vs. Cross-Selling[4]
Upselling is the practice of encouraging customers to purchase a comparable higher-end product than the one in question, while cross-selling invites customers to buy related or complementary items. Though often used interchangeably, both offer distinct benefits and can be effective in tandem. Upselling and cross-selling are mutually beneficial when done properly, providing maximum value to customers and increasing revenue without the recurring cost of many marketing channels.
Cross-selling identifies products that satisfy additional, complementary needs that are unfulfilled by the original item. For example, a comb could be cross-sold to a customer purchasing a blow dryer. Oftentimes, cross-selling points users to products they would have purchased anyways; by showing them at the right time, a store ensures they make the sale. Upselling often employs comparison charts to market higher-end products to customers. Showing visitors that other versions or models may better fulfill their needs can increase average order value (AOV) and help users walk away more satisfied with their purchase. Companies that excel at upselling are effective at helping customers visualize the value they will get by ordering a higher-priced item.
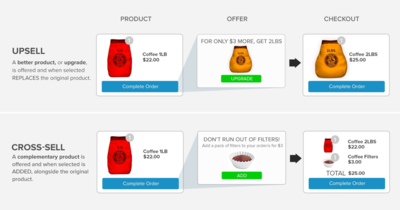
source: Bold
Cross-selling and upselling are similar in that they both focus on providing additional value to customers, instead of limiting them to already-encountered products. In both cases, the business objective is to increase order value by informing customers about additional product options they may not already know about. The key to success in both is to truly understand what your customers value and then responding with products and corresponding features that truly meet those needs.
Upselling Examples[5]
Here are some examples of upselling:
- A customer is looking at standard earbuds in an electronics store and the salesperson suggests a model with noise canceling.
- A client is looking for an email management platform and the website displays three packages. Each package shows what functions and automation are available, showing the customer how much value they can get from the more expensive packages.
- A client uses a website-building platform to build a free webpage. They receive an email from the platform when there are discounts on premium packages.
- A business owner visits a print shop for business cards. They intended to use a basic design, but the salesperson helps them see the value in a professionally designed business card. The business owner chooses a glossy finish to best display the colors.
- A diner visits a restaurant and orders an iced tea. The server offers to add raspberry or peach flavoring for a small fee.
- A customer is buying a new smartphone. The salesperson learns they use their phone to take pictures of their family events and outings, so they suggest a phone with a higher-end camera and more storage space than the customer was originally considering.
- A customer is buying a new laptop and the cashier offers to add a protection plan. When the customer asks for details, the cashier gives him two options and outlines what each plan covers.
- A client is looking at publishing packages and chooses a print-on-demand package. The client orders a professional book cover design added to the package for an additional fee.
- A customer orders a suit from a retailer. The salesperson lets the customer know that they have a tailor on-site that can alter the suit within the week for a discounted rate.
Types of Upselling[6]
- Premium Versions. Offering premium versions of products such as flower arrangements that are sold at several levels of quality.
- Options. Optional features such as a catalog of options for a car.
- Customization. Allowing the customer to customize a design or look for a product such as color.
- Services. Services such as support or professional services. For example, software may be sold with consulting services. This allows the vendor to establish a close relationship with the customer than may lead to extensive future business.
- Risk. Risk related products such as extended warranty or insurance.
- Financing. Offer to finance a purchase with a credit option.
- Complementary Items. Cross-selling items that complement the product. For example, offering WIFI plans with mobile devices.
- Popular Items. Offering popular items that aren't exactly complementary to the product. For example an ecommerce site may suggest a best selling book as an add-on with the purchase of strawberry jam.
- Priority Items. In many cases, upselling may be focused on selling items that are a strategic priority for the seller. For example, a store credit card which may be difficult to upsell but which may be priority as it allows the firm to establish a long term relationship with the customer.
The Importance of Upselling[7]
Although sales techniques tend to invoke negative feelings in us, when done right, they can actually improve our shopping experience. Online retailers rely heavily on upselling and cross-selling techniques for several reasons:
- Upselling helps retailers build deeper relationships with customers: Upselling is not a dirty tactic if you put it into perspective. If it focuses on helping your customers ‘win’ by suggesting premiums, upgrades or add-ons that will eventually deliver more value and make them feel like they got the better deal, it will turn out to be a customer happiness tactic that also generates additional revenues.
- It’s easier to upsell to existing customers than to acquire new ones: Lead generation is an expensive practice. It is much easier and cheaper to optimize the sale to a customer who already trusts you and has bought something from you in the past or is about to make a purchase now than to sell to a new prospect who has never heard of your brand. As we mentioned before you have a 60-70% chance of selling to an existing customer and only a 5-20% chance of selling to a stranger. It’s an easy win for a lot of eCommerce businesses on a mission to accelerate their growth and improve the bottom line.
- Upselling leads to increased Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Customer Lifetime Value is the net profit contribution a customer makes to your company over time. You can split your customers into three main categories: not profitable, profitable and very profitable. Higher CLV means each customer generates more revenue for your business without you having to invest anything extra, which also means your company has more money to spend on acquiring new customers. Upselling is one of the most effective ways to turn shoppers into very profitable customers and keep them coming back.
- Customers come back for more: Upselling is unique in the way it adds value to customers that makes them want to come back for more. By creating an easy way to make life straightforward for customers you are ensuring that they will return in the future if they need more of what you are selling. Be sure to offer great customer service along with your upselling efforts to guarantee happy customers no matter what happens.
Upselling Best Practices[8]
Upselling can help a business generate additional income when done properly. Best practices include:
- Avoid recommending a product or service that is significantly more expensive than the product being purchased.
- Don’t be too pushy or aggressive. Accept “no thank you” as a response.
- Focus on the customer’s needs and how the value-added offer will help meet those needs.
- Upsell when possible and appropriate so no opportunity is missed.
- Offer side-by-side comparisons so the customer can see the value in the premium version.
- Educate the customer as part of the upsell so the customer understands the risk of not taking advantage of the offer.
- Offer an in-the-moment-only discounted price to encourage the customer to make an immediate decision.
Successful in-person upselling might require training or coaching in appropriate techniques. Understanding how to upsell effectively can generate additional income, but doing it the wrong way could alienate the customer.
Benefits of Upselling[9]
- Increases Profits: It is no secret that a customer that buys more means that your institution will make more money. Growth for your business does not mean simply retaining the customers that you have: it is necessary that you continue to grow your wallet allocation for the current customers you have. The great untapped market in your business might be your actual customers: even amongst customers that believe strongly trusted their bank, for example, they only dedicate 25% of their total investments to their primary bank. Once you have gained your customer’s trust, there is still an incredible amount of investments they could be making with you if you use upselling and cross-selling to your advantage!
- Increases Customer Loyalty: When businesses refer to upselling, too often what comes to mind is greasy car salesmen offering services and products that customers do need to weasel them out of a few dollars. In reality, though, this could not be further from the truth. The point of upselling is to give the customer all of their options so they can make a knowledgeable choice. It shows customers that you care and expect their needs. In fact, upselling and cross-selling is closely related to customer satisfaction. They develop loyalty for the banks that they feel look out for their financial well-being. Customer loyalty can be a problem in the sales industry: it is common for customers to lack engagement and leave quickly. Any action that businesses can take to increase loyalty will help minimize the costs of losing customers, especially new customers. Not only does customer satisfaction mean a reduction in churn rates, but they also offer the best opportunity for free marketing. In the age of information, there are few people that will trust their business to an institution without checking reviews on it first. Happy customers are the best form of advertisement that you cannot buy.
- Increase in ROI: Signing on new customers can be a costly undertaking. Upselling and cross-selling to your customers allow you to see a profit quickly and receive a better return on your investment. You already did the hard work of marketing, finding and selling successfully to your customer; your business would be wise to get as much from the interaction as possible. You leave money on the table when you neglect upselling and cross-selling. Offer customers products that are relevant to what they are looking to get as much of a return as possible.
- Increases Customer Lifetime Value: Not only will upselling or cross-selling bring in a greater initial profit after signing on the customer, but the overall value of the customer over the course of their lifetime will also be greater. If you sell a credit card after a home loan for a customer to furnish their new house, for example, you will be bringing in much more profit over the course of the years than you would with a mortgage payment alone. Not only will you increase their lifetime value by increasing the amount they buy, but by increasing their loyalty. You will see much more from a customer that stays loyal to you. Again, the increase in customer loyalty will pay off over the long run.
- Balances Growth Between New and Existing Customers: Research has shown that increasing customer retention by as little as 5% increases profits anywhere from 25% all the way up to 95%. Maintaining a balance, then, between the customers that you sign on initially and the ones that you maintain is absolutely essential to the survival of your institution. Maintain a healthy ratio of new to existing customers to help to ensure that your business is making a profit. While gaining new clientele is a healthy goal, also keep in mind ways to keep the clients that you sign on. One way to do this is through upselling and cross-selling. Customers who feel that a company continues to look after their needs by offering relevant and helpful products and services will be far more likely to stay.
- Offers Convenience and Flexibility for Customers: The benefits of upselling and cross-selling are not just for businesses. In fact, it works so well for businesses because it works well for customers too. Many customers do not want to shop around for a new institution when they need a certain product or service. By offering them more choices or relevant add-ons, they do not have to take a risk with a new company to get what they need. Most customers will stay with what they like if they know what is available. Since you have established trust with the customer, you can have the first shot of their business by telling them the related products and services you offer. When you upsell or cross-sell to a customer, you give them the convenience of staying with you and the flexibility to choose what they need.
See Also
References
- ↑ Definition - What Does Upselling Mean? Magento
- ↑ How Suggestive Selling/Upselling Works? Investopedia
- ↑ How to Identify Upselling Opportunities Salesforce
- ↑ The Difference Between Upselling and Cross-Selling BigCommerce
- ↑ Upselling Examples indeed
- ↑ 9 Types of Upselling Simplicable
- ↑ Why Is Upselling Important? Oberlo
- ↑ Upselling Best Practices Shopify
- ↑ Benefits of Upselling Map my Customers
