Difference between revisions of "WiBe Framework"
m (The LinkTitles extension automatically added links to existing pages (https://github.com/bovender/LinkTitles).) |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | WiBe stands for Wirtschaftlichkeitsbetrachtung and is a method for estimating and calculating the profitability of IT projects. It was developed for the German Federal Ministry of the Interior and has been improved several times. It has been used in various public projects involving information technology. Hence, it is an established and proven method for profitability analysis of such projects with an emphasis on in-house development.<ref> | + | WiBe stands for Wirtschaftlichkeitsbetrachtung and is a method for estimating and calculating the profitability of IT projects. It was developed for the German Federal Ministry of the Interior and has been improved several times. It has been used in various public projects involving information technology. Hence, it is an established and proven method for profitability analysis of such projects with an emphasis on in-house development.<ref>[https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/cd1b/64292e73ebbdde38fe3e792eb5af5271535c.pdf Defining WiBe Framework -Stefan Wagner, Songmin Xie et al.]</ref> |
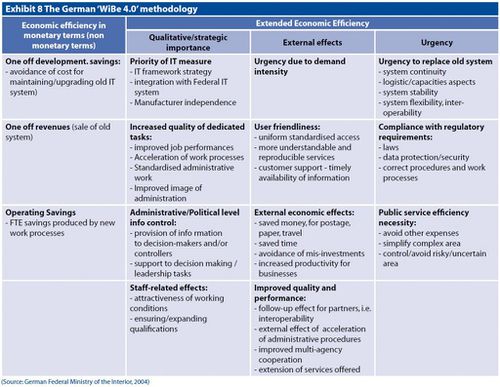
| − | WiBe | + | WiBe methodology is based on economic efficiency assessment with a particular focus on e-administration elements. As such it is meant to assess investments in the field of e-government. It is focused on services and efficiency while applying costs and best practices. WiBe has 3 main areas of impact. The first one is “Monetary economic efficiency” which is divided into two subcategories of “Benefits” and “Costs” for a project. The second area is “Extended economic efficiency” which is also divided into two subcategories of “Urgency of the measure” and“Qualitative, strategic importance”. The last area is related to “Economic efficiency from an external point of view” and is considered to be an optional part of WiBe methodology. For measurement and assessment of impacts, it uses a standardized catalog of criteria. It is focused on bringing results to stakeholders with methodical calculations and project costs related to anticipated benefits and documentation. As one of the final results it also tries to present gains for the end users and stakeholders. Worth mentioning is that WiBe methodology is used by German Government and administrative bodies.<ref>[http://www.academia.edu/1180761/Methodologies_for_Measuring_E-Government_Development_The_Croatian_Case What is WiBe Methodology -Neven Vrček]</ref> |
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
===See Also=== | ===See Also=== | ||
| − | [[MAREVA_Methodology|MAREVA Methodology]] | + | *[[MAREVA_Methodology|MAREVA Methodology]] |
| − | [[Value_Measuring_Methodology_(VMM)|Value Measuring Methodology (VMM)]] | + | *[[Value_Measuring_Methodology_(VMM)|Value Measuring Methodology (VMM)]] |
Latest revision as of 11:14, 23 December 2022
WiBe stands for Wirtschaftlichkeitsbetrachtung and is a method for estimating and calculating the profitability of IT projects. It was developed for the German Federal Ministry of the Interior and has been improved several times. It has been used in various public projects involving information technology. Hence, it is an established and proven method for profitability analysis of such projects with an emphasis on in-house development.[1]
WiBe methodology is based on economic efficiency assessment with a particular focus on e-administration elements. As such it is meant to assess investments in the field of e-government. It is focused on services and efficiency while applying costs and best practices. WiBe has 3 main areas of impact. The first one is “Monetary economic efficiency” which is divided into two subcategories of “Benefits” and “Costs” for a project. The second area is “Extended economic efficiency” which is also divided into two subcategories of “Urgency of the measure” and“Qualitative, strategic importance”. The last area is related to “Economic efficiency from an external point of view” and is considered to be an optional part of WiBe methodology. For measurement and assessment of impacts, it uses a standardized catalog of criteria. It is focused on bringing results to stakeholders with methodical calculations and project costs related to anticipated benefits and documentation. As one of the final results it also tries to present gains for the end users and stakeholders. Worth mentioning is that WiBe methodology is used by German Government and administrative bodies.[2]
source: WiBe Framework - wibe-tco,com
See Also
