Customer Perceived Value (CPV)
Business Dictionary defines Customer Perceived Value (CPV) as "the anticipated benefit from a consumer's perspective of a product or service." The customer perceived value stems from tangible, psychological and social advantages, and since it affects demand for a product, it needs to be taken into account when setting prices.[1]
Customer perceived value is a concept widely used in marketing and branding circles. Customer perceived value is the notion that the success of a product or service is largely based on whether customers believe it can satisfy their wants and needs. In other words, when a company develops its brand and markets its products, customers ultimately determine how to interpret and react to marketing messages. Companies spend significant time researching the market to get a sense of how customers think and feel. Customer perceived value is the notion that the success of a product or service your business offers hinges on whether customers believe it can satisfy their wants and needs.[2]
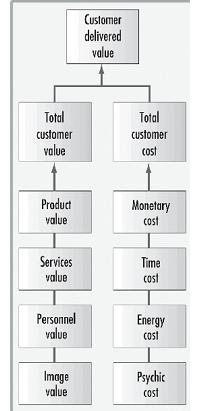
Customer Perceived Value is the evaluated value that a customer perceives to obtain by buying a product. It is the difference between the total obtained benefits according to the customer perception and the cost that he had to pay for that. Customer perceived value is seen in terms of satisfaction of needs a product or service can offer to a potential customer. The customer will buy the same product again only if he perceives to be getting some value out of the product. Hence delivering this value becomes the motto of marketers.
Customer Perceived Value = Total Perceived Benefits – Total Perceived Costs
The CPV is kind of an evaluation done by customer on what value a product or a service would be able to provide if he/she buys it by paying money.[3]
source: Marketing91
See Also
Customer Perceived Value (CPV) is the evaluation by a customer of the worth of a product or service based on what is received (benefits) versus what is given up (costs) to acquire and use it. This perception significantly influences buying decisions, brand loyalty, and customer satisfaction. CPV is not solely determined by price but includes intangible factors such as brand prestige, customer service experience, and personal relevance. Businesses aim to enhance CPV by improving product quality, offering exceptional service, and creating emotional connections, all while managing costs.
- Value Proposition: Discussing the promise of value to be delivered and a belief from the customer that value will be experienced. A strong value proposition is crucial for creating high customer perceived value.
- Brand Equity: Covering the value premium that a company generates from a product with a recognizable name when compared to a generic equivalent. Brand equity can significantly influence CPV by enhancing the perceived benefits of a product or service.
- Price Sensitivity: Discussing how the price of a product or service influences the customer's buying behavior. Price sensitivity is closely related to customer perceived value, as perceptions of value affect how price changes impact demand.
- Customer Satisfaction: Explaining the degree to which a product or service meets or surpasses customer expectations. Customer satisfaction is often a direct outcome of high customer perceived value.
- Customer Experience (CX): Discussing the total journey of a customer's interactions with a brand. Enhancing CX is a strategy for increasing CPV by ensuring all touchpoints contribute positively to the perceived value.
- Service Quality: Covering the customers' perception of how well a service meets or exceeds their expectations. Service quality is a key determinant of CPV, especially in service-oriented industries.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Explaining all the direct and indirect costs associated with acquiring, using, and disposing of a product or service. TCO is a consideration in the customer's assessment of CPV.
- Customer Loyalty: Discussing the outcome of sustained CPV, where satisfied customers demonstrate repeat purchasing behavior and loyalty to a brand or company.
- Market Segmentation: Covering the process of dividing a broad consumer or business market into sub-groups of consumers based on shared characteristics. Understanding different segments allows businesses to tailor CPV strategies to meet diverse customer needs.
- Product Differentiation: Discussing the process of distinguishing a product or service from others to make it more attractive to a particular target market. Differentiation can enhance CPV by increasing the perceived benefits.
- Emotional Branding: Explaining the practice of building brands that appeal directly to a customer's emotional state, needs, and aspirations. Emotional connections can significantly elevate CPV.
- Consumer Behavior: Covering the study of individuals, groups, or organizations and the processes they use to select, secure, use, and dispose of products, services, experiences, or ideas to satisfy needs and the impacts that these processes have on the consumer and society.
References
Further Reading
- Applications of Customer Perceived Value (CPV) in the Indsutries ConsumerBehaviorGroup9
- Customer Perceived Value: Understanding What Appeals to the Consumer Gina Winsky
