Customer Value Analysis (CVA)
Customer Value Analysis (CVA) refers to a research method that is used to identify how an organization is perceived by consumers of an organization and their competitors. The CVA is extremely important because it allows an organization to gauge how they are judged in comparison to their industry rivals.[1]
The purpose of Customer Value Analysis (CVA) is to maximize Customer Satisfaction and loyalty by measuring value, benchmarking against competitors, and identifying potential threats to customer relationships. It is important for organizations to use CVA in order to accurately gauge how their brand is perceived compared to their rivals and develop content that potential customers will find valuable and relevant. Ultimately, the goal of CVA is to generate leads and sales.
CVA represents the quintessential benefit a marketing research study can have on an organization. Customer Value Analysis empowers organizations with superior business intelligence capable of unlocking complex market opportunities. This tool helps our clients define the actions that will result in a competitive advantage.
If you are involved in a competitive industry, our customer value analysis product can serve as the cornerstone of your company's Customer Retention strategy and strategic marketing management plan. Forward Analytics has utilized the tools and metrics of customer value analysis for corporate clients, in all sectors of the economy, including producers and suppliers of industrial, consumer, and service products. While similar in appearance to traditional customer satisfaction and image and awareness studies, customer value analysis provides more accurate and useable competitive information for marketing, planning, and strategic positioning services. Built on the idea that customers measure "value", and make business decisions, based on the relationships of quality and price, Forward Analytics has designed a research methodology that evaluates the relative importance of a complete set of factors (products, services, relationships, image, and PRICE) and the perceived performance of all competitors on those factors.
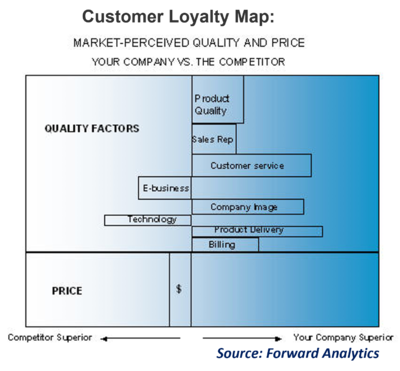
The following customer value analysis chart draws direct comparisons between you and your competitors. The market-perceived quality profile and market-perceived price profile are the heart of customer value analysis. The information provided is essential in generating a successful customer retention strategy. Each bar represents how much better or worse your company is performing on all factors, or attributes, relative to the competitor. This comparison includes both quality and price perceptions. If the bar extends to the right, your company is perceived as performing better than the competitor and represents an opportunity for market share gain. If the bar extends to the left, you are perceived as performing worse than your competitor on that attribute.
While the length of the bar indicates the comparative strength (or weakness) of the market-perceived performance, the thickness of each bar is proportionate to the importance weight of the attribute according to your customers and potential customers. Also, the thickness in the price bar is proportionate to its importance relative to the overall combined thickness of quality factors.[2]
Measuring Customer Value[3]
There are the following important ways you can use to measure customer value. Let’s check them out.
- Identify Customer Benefits: Below are some of the factors that are closely tied to customer benefits.
- Product or service quality
- A better solution
- Unique customer experience
- Customer service quality
- Total Customer Costs: Segment your customer costs into tangible and intangible costs.
- Tangible Costs
- The price of your product or service
- Installation or onboarding costs
- The cost of accessing your product or service
- Maintenance costs
- Renewal costs
- Intangible Costs
- Time invested in buying your product or service
- A poor customer experience
- Physical or emotional stress people suffer because of buying or installing your product
- A poor brand reputation
- Tangible Costs
- Time spent understanding how your product or service works
- Find the Difference Between Customer Benefits and Customer Costs
- Use the formulas below to calculate customer value analysis (CVA).
- Customer value analysis (CV) = Total Customer Benefits – Total Customer Costs
Benefits of Customer Value Analysis (CVA)[4]
One of the tools used in a customer value analysis is the customer survey. The purpose of the survey is to provide customers with the opportunity to share their thoughts on specific goods or services offered by the company, along with comments and critiques that could be used to help enhance some aspect of the product. Data collected using this customer satisfaction tool can influence the nature of the product itself, or possibly have an impact on the marketing and sales techniques used to present those products to new and potential clients. As a bonus, this process of customer satisfaction marketing helps increase rapport with customers, which only aids in increasing customer loyalty.
Another benefit of customer value analysis is gaining a better understanding of how customers make use of the products, and how they perceive the cost in relation to those uses. This can sometimes help a company that offers average-quality goods to get insights into why a company that offers a superior product can command higher prices and still capture more market share. From this perspective, a customer value analysis is not supposed to reinforce the company’s concept of itself, but provide the incentive to improve and push quality boundaries while still offering products that consumers will view as being priced equitably.
See Also
Customer Value Analysis (CVA) is a methodical approach used by businesses to measure the value that consumers place on a product or service compared to its competitors. It involves assessing various factors such as quality, features, performance, and price, to understand what drives customer satisfaction and loyalty. Through CVA, companies can identify their competitive advantages and areas needing improvement. This analysis helps in developing strategies to enhance product offerings, adjust pricing, and improve overall customer experience.
- Value Proposition: Discussing the promise of value to be delivered to and recognized by a customer, and a belief from the customer that value will be experienced. A strong value proposition is crucial for creating customer value.
- Competitive Analysis: Covering the strategy of identifying major competitors and researching their products, sales, and marketing strategies. Competitive analysis is an essential component of CVA, as it helps in understanding how a company's offerings compare with those of its competitors.
- Market Segmentation: Discussing the process of dividing a broad consumer or business market into sub-groups of consumers (known as segments) based on some type of shared characteristics. Market segmentation allows for a more targeted CVA by identifying specific customer needs and values within different segments.
- Customer Satisfaction: Explaining the degree to which a product or service meets or surpasses customer expectations. Customer satisfaction surveys are often used in CVA to measure how well a company delivers value to its customers.
- Perceived Quality: Covering the customer's perception of the overall quality or superiority of a product or service with respect to its intended purpose, relative to alternatives. Perceived quality is a key factor in customer value analysis.
- Price Sensitivity: Discussing how the price of a product or service influences the customer's buying behavior. Price sensitivity analysis is important in CVA for understanding the impact of pricing on perceived value.
- Brand Equity: Explaining the value premium that a company generates from a product with a recognizable name when compared to a generic equivalent. Brand equity can significantly influence customer value perceptions.
- Customer Loyalty: Covering the likelihood of previous customers to continue buying from a specific retailer or brand. Customer loyalty is both an input and outcome of effective CVA, as it reflects the company's ability to deliver superior value.
- Customer Experience (CX): Discussing the total journey of a customer's interactions with a brand. Enhancing CX is a strategy for increasing customer value, which can be informed by insights from CVA.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Explaining all the direct and indirect costs associated with acquiring, using, and disposing of a product or service. TCO considerations are part of assessing the overall value delivered to customers.
- SWOT Analysis: Covering the strategic planning technique used to identify Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to business competition or project planning. SWOT analysis can complement CVA by providing a broader context for strategic decision-making.
- Data Analytics: Discussing the techniques to analyze data for better decision-making. Data analytics plays a critical role in CVA by processing customer feedback, sales data, and market research to derive actionable insights on customer value.
References