RCSA (Risk Control Self Assessment)
What is RCSA (Risk Control Self Assessment)?
RCSA, or Risk Control Self Assessment, is a systematic approach organizations use to identify, assess, and manage operational risks. It is a proactive tool that involves the self-evaluation of risk exposures and the effectiveness of controls by the employees closest to the operational processes. This methodology allows for a bottom-up review of risks, ensuring that all potential vulnerabilities are identified and addressed before they result in significant harm.
Role and Purpose of RCSA
The primary role of RCSA is to empower employees to take an active role in managing risks within their areas of responsibility. The purposes include:
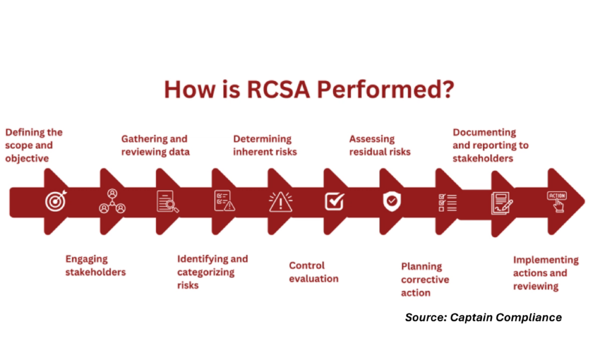
- Risk Identification: Employees identify and document potential risks impacting their operations.
- Risk Evaluation: Assess the likelihood and potential impact of identified risks.
- Control Assessment: Evaluate the effectiveness of existing controls and identify areas where additional controls are needed.
Usage of RCSA
RCSA is utilized across various sectors and industries as part of a comprehensive risk management strategy:
- Financial Services: Banks and insurance companies use RCSA to assess operational, credit, and market risks inherent in their daily activities.
- Healthcare: To identify and mitigate risks related to patient safety, data privacy, and regulatory compliance.
- Manufacturing: For assessing risks related to supply chain disruptions, equipment failures, and safety hazards.
Importance of RCSA
RCSA is crucial because it:
- Enhances Risk Awareness: Encourages organizational employees to consider how their actions and decisions contribute to risk exposure.
- Improves Risk Management: Provides a detailed view of potential risks at different organizational levels, allowing for more effective risk management strategies.
- Supports Regulatory Compliance: Helps ensure compliance with various industry regulations by demonstrating proactive risk management practices.
Benefits of RCSA
Implementing RCSA offers several advantages:
- Proactive Risk Mitigation: Allows organizations to identify and address risks before they lead to significant losses.
- Empowered Employees: Engages employees in the risk management process, enhancing their understanding of risks and their role in controlling them.
- Continuous Improvement: Provides a framework for ongoing assessment and improvement of risk controls.
Examples of RCSA in Practice
- Financial Institution: A bank conducts an RCSA to evaluate the risks associated with a new online banking platform, focusing on cybersecurity threats and compliance with financial regulations.
- Hospital: Uses RCSA to assess risks in patient care processes, aiming to identify potential points of failure that could lead to patient harm and to improve overall safety protocols.
- Retail Company: A retail chain employs RCSA to manage risks related to inventory management and customer data protection, especially considering the rise in online transactions.
RCSA is an essential component of modern risk management frameworks. By involving employees who directly interact with various processes and systems, organizations can gain a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of their risk profile, leading to better risk control and overall operational resilience.
See Also
- Risk Management: Discussing the broader field of risk management, detailing how RCSA fits into the overall framework of identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks.
- Operational Risk: Explaining operational risk specifically, as RCSA is often used to assess and manage this type of risk within organizations.
- Internal Audit: Covering how RCSA can be a tool used by internal audit functions to provide assurance that risk management processes are effective and that major risks are identified and managed.
- Corporate Governance: Discussing the role of RCSA in supporting good corporate governance by ensuring that risks are properly managed per organizational objectives and compliance requirements.
- IT Governance
- Compliance: Linking to how RCSA helps organizations comply with laws and regulations by identifying areas where compliance risks exist and assessing the effectiveness of controls in place to mitigate these risks.
- Business Continuity Planning (BCP): Explaining how RCSA contributes to business continuity planning by identifying potential risks to business operations and evaluating the effectiveness of controls to address such risks.
- Internal Control: Discussing the various control activities that can be evaluated through RCSA, such as preventive controls, detective controls, and corrective actions.
- Enterprise Risk Management (ERM): Discussing how RCSA is integrated into broader ERM strategies to ensure comprehensive risk coverage and alignment with strategic objectives.