Service Level Management (SLM)
Service Level Management (SLM) is a process used in IT service management (ITSM) to define, monitor, and review the performance of IT services. The goal of SLM is to maintain and gradually improve business productivity and customer satisfaction by ensuring that the service delivery and support meet the agreed service levels.
Purpose and Role: The primary purpose of SLM is to establish clear service delivery standards and ensure that IT services align with business objectives. SLM defines service level agreements (SLAs) that outline the expected level of service between a service provider and a customer.
Service Level Management (SLM) deals with negotiating, agreeing, and documenting existing services with some level of policies. SLM deals with the following two kinds of agreements:
- Service Level Agreement (SLA)
- Operational Level Agreement (OLA)
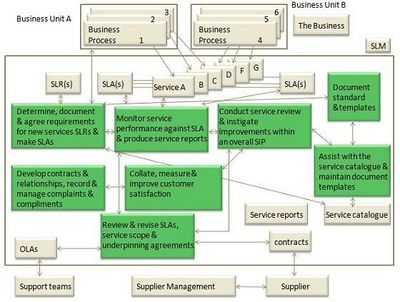
The following diagram describes activities involved in SLM process
Components: Key components of SLM include:
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): These are formal agreements that define the level of service expected from the service provider.
- Operational Level Agreements (OLAs): These are agreements between the IT service provider and another part of the same organization that assists with the provision of the service.
- Underpinning Contracts (UCs): These are contracts with external suppliers that support the service provider's delivery of IT services.
Importance: SLM is critical to ensuring that IT services meet the needs of the business and customers. By defining clear performance metrics and standards, SLM helps prevent misunderstandings and conflicts over the level of service expected.
History: SLM has its roots in ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), a set of detailed practices for IT service management that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of the business.
Benefits: SLM benefits include improved customer satisfaction through more reliable service delivery, clearer communication and understanding between service providers and customers, and better alignment between IT services and business objectives.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Improved service delivery, greater customer satisfaction, reduced risk of service failures, and improved communication between IT and business units.
- Cons: It can be time-consuming to establish and manage SLAs, and it may be challenging to accurately define service levels that align with business objectives.
Examples: For instance, a cloud service provider may establish an SLA with a customer that outlines specifics about uptime (e.g., the service will be available 99.99% of the time), speed (e.g., data will be transmitted at a certain speed), and support (e.g., issues will be resolved within a certain timeframe). The provider uses SLM processes to monitor service performance and ensure it meets the standards outlined in the SLA.
See Also
Service Level Management (SLM) is a fundamental IT service management (ITSM) process defined within the IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) framework. SLM focuses on negotiating, agreeing upon, and documenting the expected level of service between a service provider and its customers, then ensuring that these agreed-upon service levels are met. SLM encompasses the planning, coordination, measurement, reporting, and management of the quality of IT services, ensuring alignment with the business objectives and customer needs.
Key activities involved in Service Level Management include:
- Defining Services: Clearly articulating the IT services provided, including their scope, and understanding customer needs and expectations.
- Negotiating SLAs: Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are formal documents that outline the service expectations, metrics, responsibilities, and penalties for not meeting the agreed-upon service levels.
- Developing OLAs: Operational Level Agreements (OLAs) are agreements with internal groups or departments that support the SLA commitments, specifying the responsibilities of each internal support group.
- Monitoring Service Performance: Continuously monitoring service performance against SLA targets, using key performance indicators (KPIs) and other metrics.
- Reporting and Communication: Regularly reporting service performance to stakeholders and conducting service reviews to discuss performance, improvements, and changes.
- Managing Service Improvement: Identifying areas for service improvement and implementing initiatives to enhance service quality and efficiency.
- Managing Relationships: Fostering good relationships between the service provider and its customers, as well as among internal support teams, to ensure effective communication and collaboration.
SLM is critical for maintaining high customer satisfaction, improving service quality, and aligning IT services with the strategic goals of the organization. It also plays a key role in managing expectations, minimizing misunderstandings, and building trust between IT service providers and their customers.
- IT Service Management (ITSM): Discussing the overall discipline that SLM is a part of, focusing on delivering and supporting IT services.
- IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL): Covering the set of detailed practices for IT service management that includes SLM as a core process.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA): Explaining the agreements between service providers and customers that define the expected level of service.
- Service Level Objective (SLO)
- Service Level Requirements (SLR)
- Operational Level Agreement (OLA): Discussing the agreements within the organization that support SLA commitments by outlining internal support responsibilities.
- Key Performance Indicator (KPI): Covering the metrics used to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of IT services and the performance of SLM.
- Continual Service Improvement (CSI): Explaining the approach to continuously improve service quality and efficiency in the ITIL framework.
- Capacity Management: Discussing the process of ensuring that IT resources are adequate to meet current and future service level requirements in a cost-effective manner.
- Incident Management: Covering the process for managing IT service disruptions and restoring services within agreed service levels.
- Problem Management: Explaining the process aimed at identifying and managing the root causes of incidents to prevent future recurrences.
- Availability Management: Discussing the discipline focused on ensuring that IT services meet agreed-upon availability requirements.