Strategic Information Systems Planning (SISP)
What is Strategic Information Systems Planning (SISP)?
Strategic Information Systems Planning or SISP at the most basic can be defined as “the process of determining an organization’s portfolio of computer-based applications that will help it achieve its business objectives.” (Newkirk & Lederer, 2007, p. 34).
The definition of strategic information system planning has many variations. For example Lederer and Sethi (1988) state that “(SISP) is the process of deciding the objectives for organizational computing and identifying potential computer application which the organization should implement” (p.445). Hevner, Bernt, and Studnicki (2000) state that “(SISP) is the process of aligning an organization’s business strategy with effective computer-based information systems to achieve critical business objectives” (p. 1). Doherty et al. (1999) offer a composite definition from different sources and state that SISP is “the process of identifying a portfolio of computer-based applications to be implemented, which is both highly aligned with corporate strategy and has the ability to create an advantage over competitors” (p. 265). Each of these definitions states that there is a process to strategic information system planning.
SISP is needed in order to align IT with the strategic goals of an organization in order to identify new opportunities, and that organizations miss opportunities and fail to implement new business strategies without SISP (Kearns, 2006, p. 237; Lederer & Sethi, 1988, p. 445). The general consensus is that:
(a) there is an ongoing need for strategic information systems planning (Henderson & Sifonis, 1988), and
(b) that SISP has a direct impact in an organizations ability to execute its strategic business strategy, maximize its performance, and leverage IT investments for competitive advantage (Johnson & Lederer, 2010).
Strategic information systems planning is based on two core arguments:
- The first is that, at a minimum, a firm’s information systems investments should be aligned with the overall business strategy, and in some cases may even become an emerging source of competitive advantage. While no one disagrees with this, operations management researchers are just starting to study how this alignment takes place and what the measurable benefits are.
- The second core argument behind SISP is that companies can best achieve IS-based alignment or competitive advantage by following a proactive, formal and comprehensive process that includes the development of broad organizational information requirements. This is in contrast to a “reactive” strategy, in which the IS group sits back and responds to other areas of the business only when a need arises.[1]
What SISP is Not[2]
- SISP is unlikely to lead to fundamental changes in strategy. Situations rarely call for dramatic shifts in course. SISP should not lead to change for the sake of change, nor is it a rubber-stamp for current directions, past actions, or preconceived notions of how things should be.
- SISP is not the final written document, a detailed implementation plan, or a budgeting exercise. It is a learning process that should result in an improved, shared vision of the IS/IT function among senior managers and identification of a select group of potential business initiatives which, after further review, may afford opportunities for high returns on investment.
- SISP is not something that can be contracted out to external consultants. The strategic plan must be “owned” company executives, critical stakeholders, senior managers, and senior IT staff. A consultant’s report should be (and often is) rejected by company executives and critical stakeholders. Although consultants may provide useful assistance at various points in the planning process, extreme care must be exercised lest the result be theirs and not yours.
- SISP is not a technical exercise to create a unified data architecture or extensive, explicit models of all business processes.
SISP Phases[3]
While much has been written about SISP, the important aspect that has been underemphasized is the planning process or how planning is accomplished. SISP planners have to consider the preparatory steps that ensure that business, organizational and information strategies are aligned in a complementary fashion. The overall role of technology and information systems within the organization must be determined, and the internal and external assessments need to be addressed. The most important point to remember is that the SISP process must be part of the overall organization plan. SISP has been described in terms of phases and the specific tasks within them. The phases and tasks represent the components of the planning process, with each having its own objectives, participants, preconditions, products, and techniques. The phases and tasks can be used to describe an organization’s attempts to be comprehensive in its strategic planning process. SISP unfolds in five phases (summarized graphically in figure below)
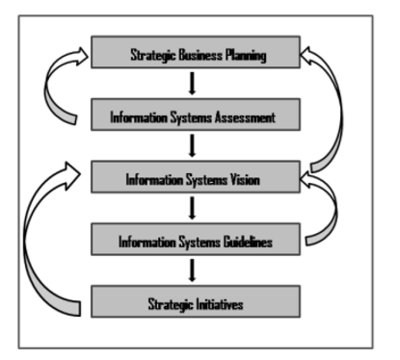
source: Arwa A. Altameem et al.
The overall five phase breakdown is as follows:
- Strategic Business Planning: Prerequisite to systems planning:
- It outlines an organization’s overall direction, philosophy, and purpose.
- It examines its current status in terms of its strengths, weakness, opportunities, and threats.
- It sets long-term objectives.
- It formulates short-term tactics to reach them.
- Information Systems Assessment: Evaluation of the system to assess its status (current information systems resources) in terms of original or current expectations and how they are serving the organization.
- Information Systems Vision: Ideal role that should be pursued for use of information systems resources
- Information Systems Guidelines: Set of statements that clarify use of organization’s technical and information systems resources.
- Strategic Initiatives: Three to five year long-term proposals that specify new initiatives for information systems organization.
SISP Methodologies[4]
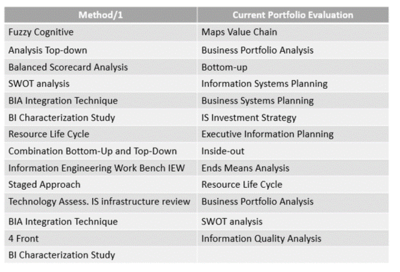
There are a number of SISP methodologies to choose from. Pita et al. (2008) provide a list of a number of SISP methodologies, which is reproduced in the Table below. While this list is by no means exhaustive, it shows the range of methodologies and provide a means for those interested in further study. An attempt to determine the most used methodology does not yield definitive results; however, Pita et al. (2008) list the top methodologies used in Australia and suggest that the most popular methodologies are alignment methodologies (p. 754).
Strategic information systems planning is considered a complex activity with a potential for problems, thus it’s important for the organization to choose the methodology with the best fit (Lederer & Sethi, 1988, p. 448). As noted by Lederer and Sethi (1988) organizations may choose to adopt a specific SISP methodology or modify an existing strategic management planning strategy and incorporate information technology (p. 448). An organization may also choose to combine a number of SISP methodologies into a SISP approach (Doherty et al., 1999, p. 265). According to Pita et al. (2008), “one of the major issues on the IS planning agenda is choosing the right methodology” and that the use of more than one methodology is preferred (p. 752). Additionally, Pita et al. (2008) note that the selection of a wrong SISP methodology can significantly contribute to SISP failure (p. 752).
Benefits of SISP[5]
SISP has been increasingly becoming essential for organizations to enhance their performance. It provides a wide range of benefits to an organization including improvements in terms of business activities and information flow. Furthermore, SISP enhances the organization’s competitive advantages. Essential benefits of SISP have been identified as:
(i) Align information technology with business needs.
(ii) Integrating IT into an organization, and promote organizational competitiveness
(iii) Effectiveness of IT implementation
(iv) Helping to identify strategic applications by information executives and top management
(v) Justify IT investments by addressing the expectation out of such investments
Studies have shown that SISP assists managers in determining the new information systems (IS) and information technology (IT) strategies, allocating resources, positioning suitable applications and gaining competitive advantages. It is essential for an organization as the measurement of organization's success is based on the return on the money invested in IT. Thus, it plays an important role in management functions. Moreover, it can help organizations to use IT more competitively, identify new higher payback applications and better forecast on IT resource requirement. The picture that emerges from previous studies indicates that SISP is a relatively successful management process. For example, there is consistency across the studies and most of IS managements are reported being satisfied with SISP implementation for organization performance. Galliers et al. also found that the perceptions of the management improved as the organization moves from its first SISP exercise into subsequent SISP exercises. Lederer et al. broke down the SISP process into a number of component parts and measured the satisfaction of the IS planners they surveyed with each component part individually. They found considerable differences in satisfaction. Whilst over half were satisfied with the SISP methodology used, this fell to less than one third for SISP implementation.
Finnegan et al. also identified the following benefits from SISP in their study of Irish companies:
- New projects justified to provide a basis for IS budgets in the performance of the IS department can be judged more fairly. A strategy for technology selection is set. Business managers become better informed and more involved in IT Scarce. IT resources are allocated more wisely Emergency IS projects are avoided Business programmers are more assured of IT requirements Both et al. demonstrated that SISP success varies according to SISP approach with the administrative and technological approaches being the least successful and the organizational approach being the most successful.
- Obviously SISP brings about strategic benefits to the organization in such matters as effectiveness of IT implementation. However, the effectiveness implies addressing issues associated with IT implementation at the planning level.
See Also
References
- ↑ What is Strategic Information Systems Planning (SISP) NC State University
- ↑ What SISP is Not Michelle Lombardo et al.
- ↑ SISP Phases Arwa A. Altameem et al.
- ↑ SISP Methodologies Brian Fergerson
- ↑ Benefits of SISP Muneer Alsurori, Juhana Salim