Continuous Delivery
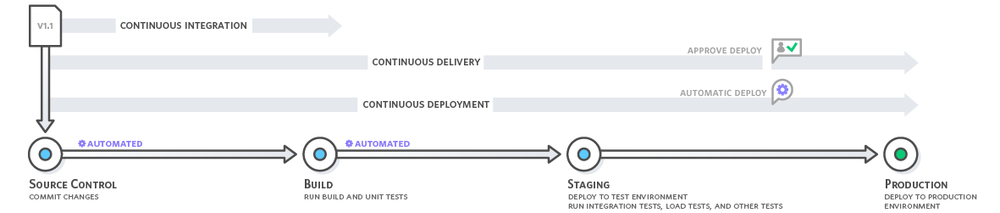
Continuous Delivery (CD) is a software engineering approach in which teams produce software in short cycles, ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time and, when releasing the software, doing so manually. It aims at building, testing, and releasing software with greater speed and frequency. The approach helps reduce the cost, time, and risk of delivering changes by allowing for more incremental updates to applications in production. A straightforward and repeatable deployment process is important for continuous delivery.[1]
Continuous Delivery vs. Continuous Deployment[2]
With continuous delivery, every code change is built, tested, and then pushed to a non-production testing or staging environment. There can be multiple, parallel test stages before a production deployment. The difference between continuous delivery and continuous deployment is the presence of a manual approval to update to production. With continuous deployment, production happens automatically without explicit approval.
Continuous delivery automates the entire software release process. Every revision that is committed triggers an automated flow that builds, tests, and then stages the update. The final decision to deploy to a live production environment is triggered by the developer.
References