Logistics
Logistics is the overall management of the way resources are obtained, stored and moved to the locations where they are required. Logistics management entails identifying potential suppliers and distributors; evaluating how accessible and effective they are and establishing relationships and signing contracts with the companies who offer the best combination of price and service. A company might also choose to handle its own logistics if it is cost-effective to do so. "Logistics" was initially a military-based term used in reference to how military personnel obtained, stored, and moved equipment and supplies. The term is now used widely in the business sector, particularly by companies in the manufacturing sectors, to refer to how resources are handled and moved along the supply chain.[1]
source: Gingerman
Categories of Logistics[2]
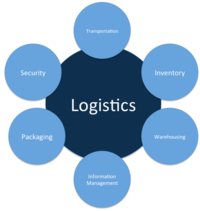
Logistics is widely known as the process of coordinating and moving resources such as equipment, food, liquids, inventory, materials and people from one location to the storage of the desired destination. It was originally a military-based term that was used to describe how the military force obtained, stored and moved equipment and supplies. In the supply chain and business sense, logistics is the management of the flow of things between the point of origin and consumption, so to fulfil the requirements of consumers or corporations. The logistics of the aforementioned resources involve the integration of production, packaging, warehousing, transportation, security, materials handling and information flow. The different categories of logistics are:
- Third Party Logistics (3PL)
- Fourth Party Logistics (4PL)
- Inbound Logistics
- Outbound Logistics
- Reverse Logistics
- Green Logistics
- Construction Logistics
- Digital Logistics
- Military Logistics
Objectives of Logistics[3]
Logistics has the following objectives:
- Reduction of inventory: Inventory is one of the key factors, which can affect the profit of an enterprise to a great extent. In the traditional system, firms had to carry lot of inventoryfor satisfying the customer and toensure excellent customer service. But, when funds areblocked in inventory, they cannot be used for other productive purposes. These costs willdrain the enterprise’s profit. Logistics helps in maintaining inventory at the lowest level, andthus achieving the customer goal. This is done through small, but frequent supplies.
- Economy of freight: Freight is a major source of cost in logistics. This can be reduced byfollowing measures like selecting the proper mode of transport, consolidation of freight,route planning, long distance shipments etc.
- Reliability and consistency in delivery performance: Material required by the customer must be delivered on time, not ahead of the schedule or behind the schedule. Proper planning of the transportation modes, with availability of inventory will ensure this.
- Minimum damage to products: Sometimes products may be damaged due to improper packing, frequent handling of consignment, and other reasons. This damage adds to thelogistics cost. The use of proper logistical packaging, mechanized material handlingequipment, etc will reduce this damage.
- Quicker and faster response: A firm must have the capability to extend service to thecustomer in the shortest time frame. By utilizing the latest technologies in processinginformation and communication will improve the decision making, and thus enable theenterprise to be flexible enough so that the firm can fulfill customer requirements, in theshortest possible time frame
- ↑ Defining Logistics Investopedia
- ↑ Categories of logistics Dovetail
- ↑ Objectives of logistics CII Institute
