Difference between revisions of "Web Application"
(Created page with "A '''Web Application''' aka web-based application is any program that is accessed over a network connection using HTTP, rath...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A '''Web Application''' aka web-based application is any program that is accessed over a [[Network|network]] connection using [[Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)|HTTP]], rather than existing within a [[Device|device’s]] memory. Web-based applications often run inside a [[Web Browser|web browser]]. However, web-based applications also may be client-based, where a small part of the [[Computer Program|program]] is downloaded to a user’s [[Desktop|desktop]], but processing is done over the [[Internet|internet]] on an external [[Server|server]]. Web-based applications are also known as web apps.<ref>Definition - What is a Web Application [https://www.techopedia.com/definition/26002/web-based-application Techopedia]</ref> | A '''Web Application''' aka web-based application is any program that is accessed over a [[Network|network]] connection using [[Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)|HTTP]], rather than existing within a [[Device|device’s]] memory. Web-based applications often run inside a [[Web Browser|web browser]]. However, web-based applications also may be client-based, where a small part of the [[Computer Program|program]] is downloaded to a user’s [[Desktop|desktop]], but processing is done over the [[Internet|internet]] on an external [[Server|server]]. Web-based applications are also known as web apps.<ref>Definition - What is a Web Application [https://www.techopedia.com/definition/26002/web-based-application Techopedia]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == The Need for a Web Application<ref>Why you need a Web Application? [https://www.guru99.com/difference-web-application-website.html Guru99]</ref> == | ||
| + | Web applications are more popular because of the following reasons: | ||
| + | *Compared to desktop applications, web applications are easier to maintain by as they use the same code in the entire application. There are no compatibility issues. | ||
| + | *Web applications can be used on any platform: Windows, Linux, Mac… as they all support modern browsers. | ||
| + | *Mobile App store approval not required in web applications. | ||
| + | *Released any time and in any form. No need to remind users to update their applications. | ||
| + | *Web applications can be accessed 24 hours of the day and 365 days a year from any PC. | ||
| + | *Both computer and mobile devices can be used to access the required data. | ||
| + | *Web applications are a cost-effective option for any organization. Seat Licenses for Desktop software are expensive where SasS, are generally, pay as you go. | ||
| + | *Web-Based Apps are Internet-enabled apps that are accessed through the mobile's web browser. Therefore, you don't require to download or install them. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == How a Web Application Works<ref>How do Web Applications Work? [https://blog.stackpath.com/web-application/ Stackpath]</ref> == | ||
| + | Web applications are usually coded in browser-supported language such as JavaScript and HTML as these languages rely on the browser to render the program executable. Some of the applications are dynamic, requiring server-side processing. Others are completely static with no processing required at the server. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The web application requires a web server to manage requests from the client, an application server to perform the tasks requested, and, sometimes, a database to store the information. Application server technology ranges from ASP.NET, ASP and ColdFusion, to PHP and JSP. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here's what a typical web application flow looks like: | ||
| + | *User triggers a request to the web server over the Internet, either through a web browser or the application’s user interface | ||
| + | *Web server forwards this request to the appropriate web application server | ||
| + | *Web application server performs the requested task – such as querying the database or processing the data – then generates the results of the requested data | ||
| + | *Web application server sends results to the web server with the requested information or processed data | ||
| + | *Web server responds back to the client with the requested information that then appears on the user’s display | ||
| Line 19: | Line 44: | ||
Above all, mobile apps and web apps are designed and built very differently. To further differentiate between the two, it helps to understand how each is developed. | Above all, mobile apps and web apps are designed and built very differently. To further differentiate between the two, it helps to understand how each is developed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == The Evolution of Web Applications<ref>How Have Web Applications Evolved? [https://www.lifewire.com/what-is-a-web-application-3486637 Lifewire]</ref> == | ||
| + | Most web applications are based on the client-server architecture where the client enters information while the server stores and retrieves information. Internet mail is an example of this, with companies like Google's Gmail and Microsoft's Outlook offering web-based email clients. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Over the past several years, there's been a big push for web applications to be developed for functions that do not normally need a server to store the information. Your word processor, for example, stores documents on your computer, and doesn't need a server. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Web applications can provide the same functionality and gain the benefit of working across multiple platforms. For example, a web application can act as a word processor, storing information in the cloud and allowing you to 'download' the document onto your personal hard drive. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you've been using the web long enough to witness how popular web applications like Gmail or Yahoo mail clients have changed over the years, you have seen how sophisticated web applications have become. Much of that sophistication is because of AJAX, which is a programming model for creating more responsive web applications. | ||
| + | |||
| + | G Suite (formerly Google Apps) and Microsoft Office 365 are other examples of the newest generation of web applications. Mobile applications that connect to the internet (such as your Facebook app, your Dropbox app or your online banking app) are also examples of how web applications have been designed for the ever increasingly popular use of the mobile web. | ||
Revision as of 17:34, 17 January 2020
A Web Application aka web-based application is any program that is accessed over a network connection using HTTP, rather than existing within a device’s memory. Web-based applications often run inside a web browser. However, web-based applications also may be client-based, where a small part of the program is downloaded to a user’s desktop, but processing is done over the internet on an external server. Web-based applications are also known as web apps.[1]
The Need for a Web Application[2]
Web applications are more popular because of the following reasons:
- Compared to desktop applications, web applications are easier to maintain by as they use the same code in the entire application. There are no compatibility issues.
- Web applications can be used on any platform: Windows, Linux, Mac… as they all support modern browsers.
- Mobile App store approval not required in web applications.
- Released any time and in any form. No need to remind users to update their applications.
- Web applications can be accessed 24 hours of the day and 365 days a year from any PC.
- Both computer and mobile devices can be used to access the required data.
- Web applications are a cost-effective option for any organization. Seat Licenses for Desktop software are expensive where SasS, are generally, pay as you go.
- Web-Based Apps are Internet-enabled apps that are accessed through the mobile's web browser. Therefore, you don't require to download or install them.
How a Web Application Works[3]
Web applications are usually coded in browser-supported language such as JavaScript and HTML as these languages rely on the browser to render the program executable. Some of the applications are dynamic, requiring server-side processing. Others are completely static with no processing required at the server.
The web application requires a web server to manage requests from the client, an application server to perform the tasks requested, and, sometimes, a database to store the information. Application server technology ranges from ASP.NET, ASP and ColdFusion, to PHP and JSP.
Here's what a typical web application flow looks like:
- User triggers a request to the web server over the Internet, either through a web browser or the application’s user interface
- Web server forwards this request to the appropriate web application server
- Web application server performs the requested task – such as querying the database or processing the data – then generates the results of the requested data
- Web application server sends results to the web server with the requested information or processed data
- Web server responds back to the client with the requested information that then appears on the user’s display
Mobile Apps Vs. Web Apps[4]
Native mobile apps are built for a specific platform, such as iOS for the Apple iPhone or Android for a Samsung device. They are downloaded and installed via an app store and have access to system resources, such as GPS and the camera function. Mobile apps live and run on the device itself. Snapchat, Instagram, Google Maps and Facebook Messenger are some examples of popular mobile apps.
Web apps, on the other hand, are accessed via the internet browser and will adapt to whichever device you’re viewing them on. They are not native to a particular system, and don’t need to be downloaded or installed. Due to their responsive nature, they do indeed look and function a lot like mobile apps — and this is where the confusion arises.
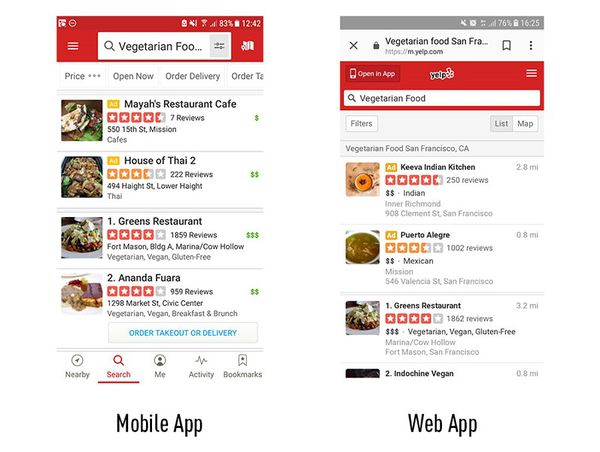
Let’s consider the Yelp native app vs. the Yelp.com web app. If you install the Yelp app on your mobile and then access Yelp.com via the browser on your phone, you’ll notice that the web app has been made to look and feel like the native mobile app: it turns your browser bar red, and when you scroll down, locks the search bar in place.
While the designs are similar and follow the same fonts and colour scheme, these are essentially two different products.
Web apps need an active internet connection in order to run, whereas mobile apps may work offline. Mobile apps have the advantage of being faster and more efficient, but they do require the user to regularly download updates. Web apps will update themselves.
Above all, mobile apps and web apps are designed and built very differently. To further differentiate between the two, it helps to understand how each is developed.
The Evolution of Web Applications[5]
Most web applications are based on the client-server architecture where the client enters information while the server stores and retrieves information. Internet mail is an example of this, with companies like Google's Gmail and Microsoft's Outlook offering web-based email clients.
Over the past several years, there's been a big push for web applications to be developed for functions that do not normally need a server to store the information. Your word processor, for example, stores documents on your computer, and doesn't need a server.
Web applications can provide the same functionality and gain the benefit of working across multiple platforms. For example, a web application can act as a word processor, storing information in the cloud and allowing you to 'download' the document onto your personal hard drive.
If you've been using the web long enough to witness how popular web applications like Gmail or Yahoo mail clients have changed over the years, you have seen how sophisticated web applications have become. Much of that sophistication is because of AJAX, which is a programming model for creating more responsive web applications.
G Suite (formerly Google Apps) and Microsoft Office 365 are other examples of the newest generation of web applications. Mobile applications that connect to the internet (such as your Facebook app, your Dropbox app or your online banking app) are also examples of how web applications have been designed for the ever increasingly popular use of the mobile web.
- ↑ Definition - What is a Web Application Techopedia
- ↑ Why you need a Web Application? Guru99
- ↑ How do Web Applications Work? Stackpath
- ↑ Mobile Apps Vs. Web Apps Career Foundry
- ↑ How Have Web Applications Evolved? Lifewire