Difference between revisions of "3C's Model"
m |
m |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The 3C's | + | == What is Kenichi Ohmae's 3C's Model? == |
| + | '''The 3C's Model''', also known as '''Strategic Triangle''', is a business model which offers a strategic look at the factors needed for success. It was developed by business and corporate strategist Kenichi Ohmae. Only by integrating these three a sustained competitive advantage can exist. Ohmae refers to these key factors as the three C’s or strategic triangle.<ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3C%27s_model Defining 3C's Model]</ref> | ||
| − | The 3C’s model points out that a strategist should focus on three key factors for success. In the construction of a | + | The 3C’s model points out that a strategist should focus on three key factors for success. In the construction of a [[Business Strategy]], three main players must be taken into account: |
| − | ''' | + | #'''The Customer''' - The customers are the basis for any corporation, according to Kenichi Ohmae. Without a doubt, a corporation’s foremost objective ought to be the interests of its customers rather than those of its stockholders or other parties. What is important are needs, requirements, demands, problem areas, buying motives, value components, decision-makers, etc. Segmentation of objectives (use of products) and customers (geography, age, social interests ), and the market (potential customers, competitors) are important for constructing and adopting a strategy. |
| + | #'''The Competitors''' - According to Kenichi Ohmae, these strategies can be constructed by looking at possible differentiation in purchasing, design, engineering, sales, and maintenance functions. An image is one of the most important factors providing the necessary power. Sony and Honda, for example, sell more than their competitors because they invest more in public relations and advertising. Smaller corporations and organizations can use franchise concepts or low margins and make service investments. | ||
| + | #'''The Corporation''' - The Corporation needs to maximize its strengths. As a result, the corporation can influence the functional areas of the competition that are critical to achieving success within a certain industry. Focusing on a key functional area may create a decisive improvement in other competition functions. (for example, quality improvement). Functional areas are meant, for example, culture, image, products, services, technology, etc. It is also important for a corporation to make informed decisions about subcontracting (capacity, cost structure, significant strategic advantages) and how effectively this can be realized for cost reduction (selective purchasing, stock management, choice of commodities, use of automation).<ref>[http://www.toolshero.com/strategy/3c-model-ohmae/ 3C model by Kenichi Ohmae]</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| − | ' | + | [[File:3C's_Model.jpg|300px|3C's Model]]<br /> |
| + | source: mba skool | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | == See Also == | ||
| + | *[[Competitive Advantage]] | ||
| + | *[[Five Forces Model]] | ||
| − | + | == References == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
| − | + | === Further Reading === | |
| − | * | + | *[http://www.valuebasedmanagement.net/methods_3C's.html Summary of the Strategic Triangle by Ohmae-Abstract] |
| − | + | *[https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/situation-analysis-using-3cs-model-hector-hernandez Situation Analysis Using 3C's Model] | |
| − | + | *[http://www.profitguide.com/manage-grow/strategy-operations/the-3-cs-of-a-great-b2b-marketing-strategy-30480 The 3C's of a great B2B marketing strategy] | |
| − | * | + | *[http://www.slideshare.net/sarthak8/ohmaes-3-cs-model Introduction to Ohmae's Business Model] |
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
Latest revision as of 12:20, 2 September 2023
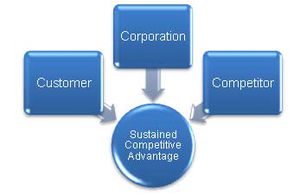
What is Kenichi Ohmae's 3C's Model?
The 3C's Model, also known as Strategic Triangle, is a business model which offers a strategic look at the factors needed for success. It was developed by business and corporate strategist Kenichi Ohmae. Only by integrating these three a sustained competitive advantage can exist. Ohmae refers to these key factors as the three C’s or strategic triangle.[1]
The 3C’s model points out that a strategist should focus on three key factors for success. In the construction of a Business Strategy, three main players must be taken into account:
- The Customer - The customers are the basis for any corporation, according to Kenichi Ohmae. Without a doubt, a corporation’s foremost objective ought to be the interests of its customers rather than those of its stockholders or other parties. What is important are needs, requirements, demands, problem areas, buying motives, value components, decision-makers, etc. Segmentation of objectives (use of products) and customers (geography, age, social interests ), and the market (potential customers, competitors) are important for constructing and adopting a strategy.
- The Competitors - According to Kenichi Ohmae, these strategies can be constructed by looking at possible differentiation in purchasing, design, engineering, sales, and maintenance functions. An image is one of the most important factors providing the necessary power. Sony and Honda, for example, sell more than their competitors because they invest more in public relations and advertising. Smaller corporations and organizations can use franchise concepts or low margins and make service investments.
- The Corporation - The Corporation needs to maximize its strengths. As a result, the corporation can influence the functional areas of the competition that are critical to achieving success within a certain industry. Focusing on a key functional area may create a decisive improvement in other competition functions. (for example, quality improvement). Functional areas are meant, for example, culture, image, products, services, technology, etc. It is also important for a corporation to make informed decisions about subcontracting (capacity, cost structure, significant strategic advantages) and how effectively this can be realized for cost reduction (selective purchasing, stock management, choice of commodities, use of automation).[2]
See Also
References