Difference between revisions of "Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (AMOLED)"
(AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) is a display technology used in smartwatches, mobile devices, laptops, and televisions.) |
m (The LinkTitles extension automatically added links to existing pages (https://github.com/bovender/LinkTitles).) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) is a display technology used in smartwatches, mobile devices, laptops, and televisions. OLED describes a specific type of thin-film-display technology in which organic compounds form the electroluminescent material, and active matrix refers to the technology behind the addressing of pixels.<ref>Definition of Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (AMOLED)? [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AMOLED Wikipedia]</ref> | AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) is a display technology used in smartwatches, mobile devices, laptops, and televisions. OLED describes a specific type of thin-film-display technology in which organic compounds form the electroluminescent material, and active matrix refers to the technology behind the addressing of pixels.<ref>Definition of Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (AMOLED)? [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AMOLED Wikipedia]</ref> | ||
| − | Active matrix organic light-emitting diodes (AMOLEDs) consist of pixels of electroluminescent organic compounds “printed” in a matrix onto a base layer. This base layer is currently glass and will be further developed to use flexible polymers in the future. Unlike liquid crystal displays, OLED displays do not require a backlight and consume very little power, making them suitable for battery-powered devices. AMOLEDs use a thin film transistor (TFT) to control the pixels.<ref>What is Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (AMOLED)? [http://www.gartner.com/it-glossary/amoled-active-matrix-organic-light-emitting-diode-oled/ Gartner]</ref> | + | Active matrix organic light-emitting diodes (AMOLEDs) consist of pixels of electroluminescent organic compounds “printed” in a matrix onto a base layer. This base layer is currently glass and will be further developed to use flexible polymers in the future. Unlike liquid crystal displays, OLED displays do not require a backlight and consume very little [[power]], making them suitable for battery-powered devices. AMOLEDs use a thin film transistor (TFT) to [[control]] the pixels.<ref>What is Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (AMOLED)? [http://www.gartner.com/it-glossary/amoled-active-matrix-organic-light-emitting-diode-oled/ Gartner]</ref> |
'''Comparison of Screen technologies''' <ref>Comparing AMOLED with Other Screen Technologies [http://www.radio-electronics.com/info/data/semicond/leds-light-emitting-diodes/amoled-active-matrix-organic.php Radio Electronics]</ref><br /> | '''Comparison of Screen technologies''' <ref>Comparing AMOLED with Other Screen Technologies [http://www.radio-electronics.com/info/data/semicond/leds-light-emitting-diodes/amoled-active-matrix-organic.php Radio Electronics]</ref><br /> | ||
| − | There are a number of contenders for screen technology within the television, computer monitor and other related areas. Although cathode ray tubes are now well out of the picture, developers of equipment have a choice of technologies of which the AMOLED is one. (See figure below) | + | There are a number of contenders for screen technology within the television, [[computer]] monitor and other related areas. Although cathode ray tubes are now well out of the picture, developers of equipment have a choice of technologies of which the AMOLED is one. (See figure below) |
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
'''Advantages'''<br /> | '''Advantages'''<br /> | ||
*One advantage of AMOLED display is thinness. A typical AMOLED display has an organic plastic layer that is about 100 to 500 nanometres thick. This is about 200 times thinner than the strand of human hair, thus making it thinner, lighter, and more flexible than the crystalline layers of LED or LCD display. This thinness also produces brighter luminescence compared to LED. | *One advantage of AMOLED display is thinness. A typical AMOLED display has an organic plastic layer that is about 100 to 500 nanometres thick. This is about 200 times thinner than the strand of human hair, thus making it thinner, lighter, and more flexible than the crystalline layers of LED or LCD display. This thinness also produces brighter luminescence compared to LED. | ||
| − | *Energy efficiency is another advantage of AMOLED display. It is more energy efficiency than LED and LCD, as well as fluorescent lamps for numerous reasons. Because they emit light without generating too much heat, energy loss due to heat transfer is lesser. | + | *Energy [[efficiency]] is another advantage of AMOLED display. It is more energy efficiency than LED and LCD, as well as fluorescent lamps for numerous reasons. Because they emit light without generating too much heat, energy loss due to heat transfer is lesser. |
*An AMOLED display also does not require backlighting unlike LCD because each pixel of organic material generates light itself. Within the same display, power consumption is uneven, focusing mostly on active pixels as represented by on-screen image. Blacks do not consume power because the underlying pixels are actually turned off. | *An AMOLED display also does not require backlighting unlike LCD because each pixel of organic material generates light itself. Within the same display, power consumption is uneven, focusing mostly on active pixels as represented by on-screen image. Blacks do not consume power because the underlying pixels are actually turned off. | ||
*Thus, an AMOLED screen display consumes less power, making it more appropriate for use in portable consumer electronic devices in which battery life is of critical importance. Furthermore, because of this energy efficiency, eco-friendliness is another advantage of AMOLED over its counterparts. | *Thus, an AMOLED screen display consumes less power, making it more appropriate for use in portable consumer electronic devices in which battery life is of critical importance. Furthermore, because of this energy efficiency, eco-friendliness is another advantage of AMOLED over its counterparts. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
'''Disadvantages'''<br /> | '''Disadvantages'''<br /> | ||
| − | *Tenured users of Samsung Galaxy S and Galaxy Note line of smartphones could attest to the fact that the quality of their screen display had degraded overtime. This is one of the major disadvantages of AMOLED display. Organic materials have limited lifespan, far shorter than the lifespan of LED or LCD. | + | *Tenured users of Samsung Galaxy S and Galaxy Note line of smartphones could attest to the fact that the [[quality]] of their screen display had degraded overtime. This is one of the major disadvantages of AMOLED display. Organic materials have limited lifespan, far shorter than the lifespan of LED or LCD. |
*In addition, lifespans of each color-specific organic material varies. Red and green OLED films have longer lifespans compared to blue OLED films. This variation results in colour shifts as a particular pixel fades faster than the other pixels. | *In addition, lifespans of each color-specific organic material varies. Red and green OLED films have longer lifespans compared to blue OLED films. This variation results in colour shifts as a particular pixel fades faster than the other pixels. | ||
*Because of overall shorter lifespan and variations in the lifespan of color-specific organic materials, AMOLED displays are very prone to screen burn-in, which leaves a permanent imprint of overused colors represented by overused images. | *Because of overall shorter lifespan and variations in the lifespan of color-specific organic materials, AMOLED displays are very prone to screen burn-in, which leaves a permanent imprint of overused colors represented by overused images. | ||
| − | *Organic compounds are also highly susceptible to water damages unlike light diodes or inorganic crystalline. Submerging an AMOLED display in water would result in immediate loss of some colors represented by burn-in or dead pixels. This susceptibility makes sealing processes an important consideration in fabrication and manufacturing. | + | *Organic compounds are also highly susceptible to water damages unlike light diodes or inorganic crystalline. Submerging an AMOLED display in water would result in immediate loss of some colors represented by burn-in or dead pixels. This susceptibility makes sealing processes an important consideration in fabrication and [[manufacturing]]. |
*Compared with an LCD, an AMOLED display is difficult to view in direct sunlight due to reduced maximum brightness and lack of backlighting. There have been several workarounds to this problem including reducing the size of gaps between the layers of screen to reduce reflectivity. | *Compared with an LCD, an AMOLED display is difficult to view in direct sunlight due to reduced maximum brightness and lack of backlighting. There have been several workarounds to this problem including reducing the size of gaps between the layers of screen to reduce reflectivity. | ||
*Another disadvantage of AMOLED display is cost. Manufacturing this display technology can be costly due to the complexity in fabricating substrates. The individual parts of the same display can also be costly and assembling them together remains much more expensive than LCD manufacturing. | *Another disadvantage of AMOLED display is cost. Manufacturing this display technology can be costly due to the complexity in fabricating substrates. The individual parts of the same display can also be costly and assembling them together remains much more expensive than LCD manufacturing. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
*Low-Voltage, Low-Power, Organic Light-Emitting Transistors for Active Matrix Displays [http://science.sciencemag.org/content/332/6029/570 M. A. McCarthy, B. Liu et. al] | *Low-Voltage, Low-Power, Organic Light-Emitting Transistors for Active Matrix Displays [http://science.sciencemag.org/content/332/6029/570 M. A. McCarthy, B. Liu et. al] | ||
*Reliability of Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting-Diode Arrays With Amorphous Silicon Thin-Film Transistor Backplanes on Clear Plastic [https://www.princeton.edu/sturm/publications/journal-articles/JP.170.pdf Bahman Hekmatshoar, Student Member, IEEE, Alex Z. Kattamis et al.] | *Reliability of Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting-Diode Arrays With Amorphous Silicon Thin-Film Transistor Backplanes on Clear Plastic [https://www.princeton.edu/sturm/publications/journal-articles/JP.170.pdf Bahman Hekmatshoar, Student Member, IEEE, Alex Z. Kattamis et al.] | ||
| − | *Active matrix organic light emitting diode (amoled) display pixel structure and data load/illuminate circuit therefor US 5952789 A [https://www.google.com/patents/US5952789 Patents] | + | *Active matrix organic light emitting diode (amoled) display pixel structure and [[data]] load/illuminate circuit therefor US 5952789 A [https://www.google.com/patents/US5952789 Patents] |
Revision as of 13:32, 6 February 2021
AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) is a display technology used in smartwatches, mobile devices, laptops, and televisions. OLED describes a specific type of thin-film-display technology in which organic compounds form the electroluminescent material, and active matrix refers to the technology behind the addressing of pixels.[1]
Active matrix organic light-emitting diodes (AMOLEDs) consist of pixels of electroluminescent organic compounds “printed” in a matrix onto a base layer. This base layer is currently glass and will be further developed to use flexible polymers in the future. Unlike liquid crystal displays, OLED displays do not require a backlight and consume very little power, making them suitable for battery-powered devices. AMOLEDs use a thin film transistor (TFT) to control the pixels.[2]
Comparison of Screen technologies [3]
There are a number of contenders for screen technology within the television, computer monitor and other related areas. Although cathode ray tubes are now well out of the picture, developers of equipment have a choice of technologies of which the AMOLED is one. (See figure below)
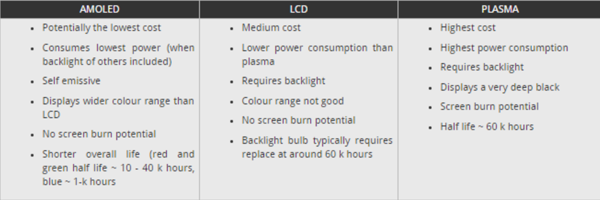
source: Radio Electronics
Advantages and DisAdvantages of AMOLED[4]
Advantages
- One advantage of AMOLED display is thinness. A typical AMOLED display has an organic plastic layer that is about 100 to 500 nanometres thick. This is about 200 times thinner than the strand of human hair, thus making it thinner, lighter, and more flexible than the crystalline layers of LED or LCD display. This thinness also produces brighter luminescence compared to LED.
- Energy efficiency is another advantage of AMOLED display. It is more energy efficiency than LED and LCD, as well as fluorescent lamps for numerous reasons. Because they emit light without generating too much heat, energy loss due to heat transfer is lesser.
- An AMOLED display also does not require backlighting unlike LCD because each pixel of organic material generates light itself. Within the same display, power consumption is uneven, focusing mostly on active pixels as represented by on-screen image. Blacks do not consume power because the underlying pixels are actually turned off.
- Thus, an AMOLED screen display consumes less power, making it more appropriate for use in portable consumer electronic devices in which battery life is of critical importance. Furthermore, because of this energy efficiency, eco-friendliness is another advantage of AMOLED over its counterparts.
- The images produced by an AMOLED display are remarkable and incomparable due to its deep blacks and high contrast. This advantage is noticeable when compared to other LOCD display technologies such as in-plane switching display or IPS or twisted nematic or TN display technologies.
- Because each pixel of organic material emit light, the entire display has greater artificial contrast ratio measurable in pure dark conditions and has better viewing angle compared to an LCD. The display is also more responsive due to a higher refresh rate than LCD making moving images more fluid and less straining to the eyes.
Disadvantages
- Tenured users of Samsung Galaxy S and Galaxy Note line of smartphones could attest to the fact that the quality of their screen display had degraded overtime. This is one of the major disadvantages of AMOLED display. Organic materials have limited lifespan, far shorter than the lifespan of LED or LCD.
- In addition, lifespans of each color-specific organic material varies. Red and green OLED films have longer lifespans compared to blue OLED films. This variation results in colour shifts as a particular pixel fades faster than the other pixels.
- Because of overall shorter lifespan and variations in the lifespan of color-specific organic materials, AMOLED displays are very prone to screen burn-in, which leaves a permanent imprint of overused colors represented by overused images.
- Organic compounds are also highly susceptible to water damages unlike light diodes or inorganic crystalline. Submerging an AMOLED display in water would result in immediate loss of some colors represented by burn-in or dead pixels. This susceptibility makes sealing processes an important consideration in fabrication and manufacturing.
- Compared with an LCD, an AMOLED display is difficult to view in direct sunlight due to reduced maximum brightness and lack of backlighting. There have been several workarounds to this problem including reducing the size of gaps between the layers of screen to reduce reflectivity.
- Another disadvantage of AMOLED display is cost. Manufacturing this display technology can be costly due to the complexity in fabricating substrates. The individual parts of the same display can also be costly and assembling them together remains much more expensive than LCD manufacturing.
References
- ↑ Definition of Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (AMOLED)? Wikipedia
- ↑ What is Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (AMOLED)? Gartner
- ↑ Comparing AMOLED with Other Screen Technologies Radio Electronics
- ↑ Advantages and Disadvantages of AMOLED Version Daily
Further Reading
- Transparent Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode Displays Driven by Nanowire Transistor Circuitry Sanghyun Ju, Jianfeng Li et. al
- Low-Voltage, Low-Power, Organic Light-Emitting Transistors for Active Matrix Displays M. A. McCarthy, B. Liu et. al
- Reliability of Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting-Diode Arrays With Amorphous Silicon Thin-Film Transistor Backplanes on Clear Plastic Bahman Hekmatshoar, Student Member, IEEE, Alex Z. Kattamis et al.
- Active matrix organic light emitting diode (amoled) display pixel structure and data load/illuminate circuit therefor US 5952789 A Patents
