Difference between revisions of "Compensation"
m |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Compensation | + | == What is Compensation? == |
| + | '''Compensation''' refers to the total monetary and non-monetary pay provided to an employee by an employer in return for work performed as required. Essentially, it is a tool used by management for a variety of purposes to further the company's existence. Compensation may include hourly wages or an annual salary, plus bonus programs, benefits, stock option grants, and other incentive plans. | ||
| − | |||
| + | [[File:Compensation.png|600px|Types of Compensation]] | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| − | == | + | == Role and Purpose of Compensation == |
| + | The primary role of compensation in an organization is to attract, retain, and motivate employees. Effective compensation strategies ensure that the organization can compete for the best talent in its industry and maintain a motivated workforce. The purposes of compensation include: | ||
| + | *Attracting Talent: Competitive compensation packages help attract the best candidates to an organization. | ||
| + | *Retaining Employees: Adequate and fair compensation is critical in retaining top performers and reducing turnover. | ||
| + | *Enhancing Motivation: Well-structured compensation, including performance-based incentives, can significantly boost employee morale and productivity. | ||
| + | *Ensuring Equity: Compensation systems are designed to ensure fairness and equity in pay structures, often adhering to legal standards and market norms. | ||
| + | *Regulating Expenses: Compensation is a major operational expense, and managing it effectively is crucial for financial stability and profitability. | ||
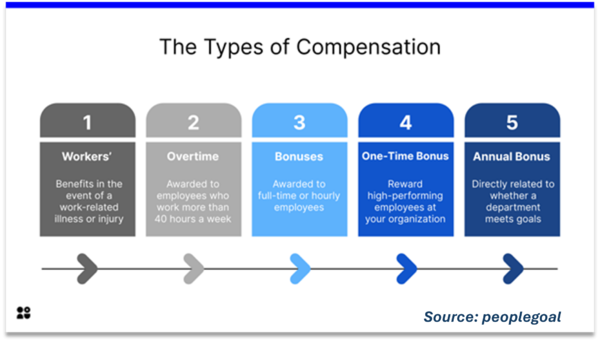
| + | == Components of Compensation == | ||
| + | Compensation typically encompasses several components: | ||
| + | *Base Salary: An employee's core monetary compensation, usually as an hourly wage or salary. | ||
| + | *Bonuses: These can be based on performance, company profit, or other criteria and are designed to reward employees for their contributions to organizational success. | ||
| + | *Equity Compensation: Includes stock options, restricted stock units (RSUs), or other equity-based incentives, which are especially common in startups and publicly traded companies. | ||
| + | *Benefits: Non-wage compensations such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and other perks like gym memberships or commuter assistance. | ||
| + | *Commissions: Often used in sales roles, where employees receive a percentage of the sales they generate. | ||
| + | == Importance of Compensation == | ||
| + | Compensation plays a vital role in the strategic and operational management of an organization because: | ||
| + | *It influences organizational culture and employee satisfaction, key drivers of company performance. | ||
| + | *It impacts the financial and competitive positioning of the company within its industry. | ||
| + | *It helps ensure compliance with employment and wage laws, thereby avoiding legal issues. | ||
| + | == Benefits of Effective Compensation Management == | ||
| + | Effective compensation management can provide several benefits: | ||
| + | *Alignment of Interests: Aligns the employees' interests with the organization's goals, encouraging them to work towards common objectives. | ||
| + | *Competitive Advantage: Organizations offering attractive compensation packages are more likely to attract and retain skilled employees, giving them a competitive edge. | ||
| + | *Operational Efficiency: Motivated employees are typically more productive, directly impacting the efficiency of operations. | ||
| + | *Employee Satisfaction and Loyalty: Fair and transparent compensation practices contribute to higher employee satisfaction and loyalty levels. | ||
| − | ==References== | + | == Examples of Compensation in Practice == |
| + | *Technology Sector: Many tech companies offer a combination of high salaries, bonuses, equity compensation, and exceptional benefits to attract and retain the best talent in a competitive market. | ||
| + | *Retail and Hospitality Industries: These sectors might use a combination of hourly wages, tips, and performance bonuses to compensate their employees, tailored to the operational demands and profit margins of the industry. | ||
| + | *Non-Profit Sector: Compensation might include lower base salaries but enhanced benefits like extra vacation time or flexible working conditions to attract employees who are motivated by factors beyond just monetary gain. | ||
| + | Compensation is a critical function of human resource management that directly affects the organization's success. Effective compensation strategies ensure compliance with laws and industry standards and support business objectives by fostering a committed and satisfied workforce. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == See Also == | ||
| + | *Salary Structures: Discussing different salary structures and levels, including how organizations design compensation packages based on roles, experience, and market standards. | ||
| + | *Benefits Management: Covering the range of benefits employers offer, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off, complementing direct pay in a compensation package. | ||
| + | *[[Performance Management]]: Explaining how compensation is often linked to performance appraisals, with systems in place to reward employees based on their achievements and contributions to the organization. | ||
| + | *Job Evaluation: Discussing the process of job evaluation used to determine the relative value of a job in an organization, which directly influences compensation levels. | ||
| + | *Payroll Management: Covering the systems and processes of paying employees, including managing deductions, taxes, and compliance with employment laws. | ||
| + | *[[Labor Law]]: Explaining the legal aspects of compensation, including minimum wage laws, overtime pay, and other statutory requirements that affect how compensation is structured and distributed. | ||
| + | *[[Incentives]]: Discuss various types of incentive programs, such as bonuses, stock options, and profit-sharing plans, which are used to motivate employees and align their goals with those of the organization. | ||
| + | *[[Human Resource Management (HRM)]]: Explaining the role of HRM in developing and managing compensation strategies that support organizational goals and employee satisfaction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 23:51, 15 May 2024
What is Compensation?
Compensation refers to the total monetary and non-monetary pay provided to an employee by an employer in return for work performed as required. Essentially, it is a tool used by management for a variety of purposes to further the company's existence. Compensation may include hourly wages or an annual salary, plus bonus programs, benefits, stock option grants, and other incentive plans.
Role and Purpose of Compensation
The primary role of compensation in an organization is to attract, retain, and motivate employees. Effective compensation strategies ensure that the organization can compete for the best talent in its industry and maintain a motivated workforce. The purposes of compensation include:
- Attracting Talent: Competitive compensation packages help attract the best candidates to an organization.
- Retaining Employees: Adequate and fair compensation is critical in retaining top performers and reducing turnover.
- Enhancing Motivation: Well-structured compensation, including performance-based incentives, can significantly boost employee morale and productivity.
- Ensuring Equity: Compensation systems are designed to ensure fairness and equity in pay structures, often adhering to legal standards and market norms.
- Regulating Expenses: Compensation is a major operational expense, and managing it effectively is crucial for financial stability and profitability.
Components of Compensation
Compensation typically encompasses several components:
- Base Salary: An employee's core monetary compensation, usually as an hourly wage or salary.
- Bonuses: These can be based on performance, company profit, or other criteria and are designed to reward employees for their contributions to organizational success.
- Equity Compensation: Includes stock options, restricted stock units (RSUs), or other equity-based incentives, which are especially common in startups and publicly traded companies.
- Benefits: Non-wage compensations such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and other perks like gym memberships or commuter assistance.
- Commissions: Often used in sales roles, where employees receive a percentage of the sales they generate.
Importance of Compensation
Compensation plays a vital role in the strategic and operational management of an organization because:
- It influences organizational culture and employee satisfaction, key drivers of company performance.
- It impacts the financial and competitive positioning of the company within its industry.
- It helps ensure compliance with employment and wage laws, thereby avoiding legal issues.
Benefits of Effective Compensation Management
Effective compensation management can provide several benefits:
- Alignment of Interests: Aligns the employees' interests with the organization's goals, encouraging them to work towards common objectives.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations offering attractive compensation packages are more likely to attract and retain skilled employees, giving them a competitive edge.
- Operational Efficiency: Motivated employees are typically more productive, directly impacting the efficiency of operations.
- Employee Satisfaction and Loyalty: Fair and transparent compensation practices contribute to higher employee satisfaction and loyalty levels.
Examples of Compensation in Practice
- Technology Sector: Many tech companies offer a combination of high salaries, bonuses, equity compensation, and exceptional benefits to attract and retain the best talent in a competitive market.
- Retail and Hospitality Industries: These sectors might use a combination of hourly wages, tips, and performance bonuses to compensate their employees, tailored to the operational demands and profit margins of the industry.
- Non-Profit Sector: Compensation might include lower base salaries but enhanced benefits like extra vacation time or flexible working conditions to attract employees who are motivated by factors beyond just monetary gain.
Compensation is a critical function of human resource management that directly affects the organization's success. Effective compensation strategies ensure compliance with laws and industry standards and support business objectives by fostering a committed and satisfied workforce.
See Also
- Salary Structures: Discussing different salary structures and levels, including how organizations design compensation packages based on roles, experience, and market standards.
- Benefits Management: Covering the range of benefits employers offer, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off, complementing direct pay in a compensation package.
- Performance Management: Explaining how compensation is often linked to performance appraisals, with systems in place to reward employees based on their achievements and contributions to the organization.
- Job Evaluation: Discussing the process of job evaluation used to determine the relative value of a job in an organization, which directly influences compensation levels.
- Payroll Management: Covering the systems and processes of paying employees, including managing deductions, taxes, and compliance with employment laws.
- Labor Law: Explaining the legal aspects of compensation, including minimum wage laws, overtime pay, and other statutory requirements that affect how compensation is structured and distributed.
- Incentives: Discuss various types of incentive programs, such as bonuses, stock options, and profit-sharing plans, which are used to motivate employees and align their goals with those of the organization.
- Human Resource Management (HRM): Explaining the role of HRM in developing and managing compensation strategies that support organizational goals and employee satisfaction.