Customer Data Platform (CDP)
Definition - What is Customer Data Platform (CDP)?[1]
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a software that aggregates and organizes customer data across a variety of touchpoints and is used by other software, systems, and marketing efforts. CDPs collect and structure real-time data into individual, centralized customer profiles. According to the CDP Institute, a vendor-neutral organization dedicated to helping marketers manage customer data, a CDP is defined as “a packaged software that creates a persistent, unified customer database that is accessible to other systems.”
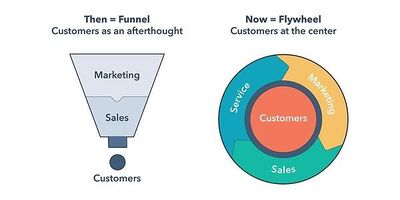
Customer Data Platforms build customer profiles by integrating data from a variety of first-, second-, and third-party sources. This includes your CRM and DMP, transactional systems, web forms, email and social media activity,website and e-commerce behavioral data, and more. CDPs inform people-based marketing — putting the customer at the center of the flywheel of your organization.
What a CDP is Not[2]
While some CDPs may include overlapping functionality, a CDP…
- Is Not a CRM system: CRMs mostly store customer transaction data. They do not have insight into anonymous user behavior (often requiring a form fill or purchase), typically are focused on sales data and only have limited integrations to other systems.
- Is Not a DMP: DMPs are cookie-based, do not create a persistent customer profile and integrations tend to be limited to advertising (not the full customer journey). DMPs are focused on 3rd-party data, with some limited ability to integrate 1st-party data, whereas CDPs have a much heavier focus on 1st-party data.
- Is Not a Personalization tool: While some CDPs have built native execution tools such as website personalization, this is not a core functionality for the category. This takes focus away from solving the underlying data fragmentation problem that companies in the market are experiencing today.
The Purpose of Customer Data Platform (CDP)[3]
A customer data platform serves three purposes.
- Collect and unify all first-party data: Many of the systems—such as email, analytics, CRM, ecommerce, and social sites—that marketers use operate in silos and don’t pass data back and forth. It’s hard to get a complete picture, and even harder to analyze what you’re looking at. The purpose of a customer data platform is to eliminate those issues by connecting all the tools that marketers use and acting as a single source of truth for first-party customer data.
- Customer data management: CDPs manage first-party data and consumer privacy and data rights by controlling the data flows between different marketing systems and managing consent. This is the world of GDPR and data privacy; your business needs to actively manage, and document that management of, consent and data flows.
- Customer data activation: Once you've received permission to collect first-party user data and have unified and structured it into profiles, you can then take action on it. CDPs can create audience segments that can be used across the rest of your marketing platforms and channels.
What Is a CDP’s Greatest Advantage over CRMs and DMPs?
There is often confusion between a customer data platform (CDP) and other marketing and sales technology, specifically other customer databases like CRMs (customer relationship management systems) and DMPs (data management platforms). Before we talk more about CDPs, let’s clear up any confusion.
A Customer Data Platforms (CDP) is a unified customer database that builds rich customer profiles using data collected from systems across the company. It provides these profiles back to these systems to improve customer experiences.
A Data Management Platform (DMP) is a solution used by marketers to improve advertising, retargeting, and media buying. Data collected is primarily anonymous data from cookies, devices, and IP addresses, and it’s only stored for a limited time (typically 90 days). DMP data is often fed into a CDP to improve customer profiles. There are other differences between CDPs and DMPs, summarized in the table that follows.
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a solution for tracking and managing interactions with prospects and customers. It is primarily a sales tool used for contact management and sales management. Marketing activity can be fed into the CRM through predefined connectors. Most data is user generated through sales people entering contact engagement and sales activity manually.
What Is a CDP’s Advantage over DMPs and CRMs? CDP vs. DMP vs. CRM
These solutions sound similar but have very different capabilities and are used for different purposes. The following table explains the CDP vs. DMP question, as well as the CDP vs. CRM issue.
Benefits of Using a Customer Data Platform (CDP)[4]
Automating customer data accuracy and integration through a CDP can provide numerous benefits to marketers and to other functions across the enterprise, though we’re focused on the marketing implications in this report. These include the following:
- Expanded enterprise collaboration. A CDP fosters cooperation among siloed groups because it gathers data from throughout the enterprise and supports customer interactions across many touchpoints. The unification of data allows enterprises to see how strategies for audience, customer experience and execution all fit together – and enables audience portability to ensure a more consistent, informed customer experience.
- Improved data accessibility. A CDP is a centralized hub that collects and houses customer data from every corner of the enterprise. Pieces of data are normalized and stitched together to build unique, unified profiles of each individual customer. The result is a persistent customer database whose main purpose is to gather and share data more easily and efficiently across the organization
- Streamlined systems integration. A CDP unifies data systems across the enterprise, from marketing and customer service, to call centers and payment systems. By creating a single “system of record” for first-party customer data, data redundancies and errors can be minimized, and data can flow more quickly into — and out of — marketing automation platforms, email service providers (ESPs), CRMs and other martech systems.
- Increased marketing efficiency. A CDP unifies individual data with unique IDs that create more robust customer records. Many manual tasks are also automated by the CDP, allowing marketers to focus on the creative and analytical tasks they are trained for. The result is more accurate modeling, targeting and personalization in marketing campaigns, and more relevant customer experiences with the brand across channels.
- Faster marketing velocity. In many cases, CDPs are “owned” by marketing, minimizing the need for IT or developer intervention to collect, analyze and act upon data. With control in marketers’ hands, the time to segment and build audiences, execute campaigns and analyze results significantly decreases. That said, engineers may still be needed to perform deep data analysis and facilitate integrations. This is especially true as CDPs extend beyond marketing and into sales and service functions.
- Stronger regulatory compliance. A CDP creates greater internal control over customer data, streamlining data governance to comply with the many regulations now impacting brands worldwide. Marketers in the healthcare industry must comply with both HIPAA and HITECH regulations. Businesses that handle European data or serve customers in the EU must also comply with GDPR and those dealing with Californians must deal with CCPA
(California Consumer Privacy Act). The majority of CDP vendors are both ISO and SOC certified for best practices in handling personally identifiable information (PII).