Difference between revisions of "Innovation Economics"
(Created page with "'''Content Coming Soon'''") |
m |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ''' | + | == What is Innovation Economics? == |
| + | Innovation Economics is a branch of economics that focuses on how innovations, technological changes, and knowledge-based factors contribute to economic growth. This field integrates aspects of industrial organization, development economics, and economic growth theory to explain how new technologies and innovations drive productivity and economic expansion. Unlike traditional economic theories that prioritize factors like labor and capital, Innovation Economics significantly emphasizes the role of ideas, innovation, and intangible assets in economic performance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
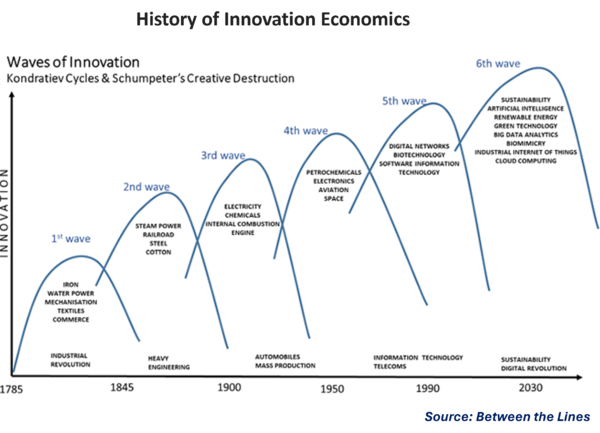
| + | [[File:Innovation Economics.png|600px|History of Innovation Economics]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Role and Purpose of Innovation Economics == | ||
| + | The primary role of Innovation Economics is to understand and predict how technological changes and innovations affect economic dynamics. Its purposes include: | ||
| + | *Driving Economic Growth: Examining how innovations contribute to increased productivity and economic growth. | ||
| + | *Informing Policy: Providing insights for policy-makers on how to support innovation through investments in research and development, education, and infrastructure. | ||
| + | *Enhancing Competitiveness: Analyzing how businesses and nations can leverage innovation to enhance their competitive edge in the global market. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Usage of Innovation Economics == | ||
| + | Innovation Economics is used across various sectors and by multiple stakeholders: | ||
| + | *Government Policy Making: Governments use insights from Innovation Economics to craft policies that encourage research and development, technology adoption, and skill development. | ||
| + | *Corporate Strategy: Businesses apply principles of Innovation Economics to strategize on innovation, research and development investment, and technology management to stay competitive. | ||
| + | *Academic Research: Scholars in economics and business study the impact of technological innovation on economic metrics like productivity, employment, and wealth distribution. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Importance of Innovation Economics == | ||
| + | Innovation Economics is crucial because it: | ||
| + | *Focuses on Sustainable Growth: Emphasizes creating and applying new knowledge and technologies as central to sustainable economic growth. | ||
| + | *Addresses Modern Economic Challenges: Helps understand and solve contemporary economic issues related to technology, globalization, and environmental concerns. | ||
| + | *Shapes Future Economies: Guides the development of future-oriented economies that are resilient, adaptive, and capable of continuous innovation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Benefits of Innovation Economics == | ||
| + | Adopting the principles of Innovation Economics offers several benefits: | ||
| + | *Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency: Promotes developing and diffusing new technologies that improve productivity and operational efficiency. | ||
| + | *Economic Diversification: Encourages economic diversification by developing new industries and sectors centered around innovative technologies and services. | ||
| + | *Job Creation: Stimulates the creation of new job opportunities, particularly in high-tech and knowledge-intensive sectors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Examples of Innovation Economics in Practice == | ||
| + | *Silicon Valley: The region's growth as a global tech hub can be primarily attributed to policies and economic practices derived from Innovation Economics, emphasizing innovation, entrepreneurship, and knowledge sharing. | ||
| + | *South Korea's Economic Development: South Korea's transformation into a high-tech economy was significantly influenced by strategic investments in education and technology, guided by innovative economic principles. | ||
| + | *Renewable Energy Sector: The rapid development and adoption of renewable energy technologies are supported by economic policies incentivizing innovation in green technology and sustainable practices. | ||
| + | Innovation Economics provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the vital role that innovation and technology play in modern economies. It offers strategic insights crucial for policy-makers, businesses, and academics to foster environments that prioritize innovation, ensuring sustained economic growth and development. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==See Also== | ||
| + | *[[Information Technology Enabled Services (ITeS)]] | ||
| + | *Technology Transfer: Explaining the process of transferring skills, knowledge, technologies, methods of manufacturing, samples of manufacturing, and facilities among governments or universities and other institutions to ensure that scientific and technological developments are accessible to a wider range of users. | ||
| + | *Entrepreneurship: Covering the role of entrepreneurs in innovation economics, including how they act as agents of change by transforming inventions into economically viable goods or services. | ||
| + | *[[Intellectual Property]]: Discusses the importance of intellectual property rights in protecting innovations and their impact on promoting economic growth through incentivizing creativity and investment in research and development. | ||
| + | *[[Research and Development (R&D)]]: Detailing how R&D activities contribute to innovation and economic development and the role of both private and public sectors in supporting R&D. | ||
| + | *Cluster Theory: Exploring the geographical clusters of businesses and industries, which is significant in innovation economics for fostering collaboration, knowledge sharing, and innovation. | ||
| + | *Knowledge Economy: Discusses the knowledge economy, where wealth is created through the economic exploitation of understanding, and how policies can support its development. | ||
| + | *[[Globalization]]: Linking to how globalization affects innovation economics, including the opportunities and challenges it presents for innovation across different countries and industries. | ||
| + | *Innovation Policy: Explains government policies that can stimulate or hinder innovation, such as subsidies, tax incentives, and regulations, and their critical role in shaping the innovation landscape. | ||
| + | *[[Human Capital]]: Covers the importance of education and skills development in fostering an innovative workforce that can drive economic development. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:34, 9 May 2024
What is Innovation Economics?
Innovation Economics is a branch of economics that focuses on how innovations, technological changes, and knowledge-based factors contribute to economic growth. This field integrates aspects of industrial organization, development economics, and economic growth theory to explain how new technologies and innovations drive productivity and economic expansion. Unlike traditional economic theories that prioritize factors like labor and capital, Innovation Economics significantly emphasizes the role of ideas, innovation, and intangible assets in economic performance.
Role and Purpose of Innovation Economics
The primary role of Innovation Economics is to understand and predict how technological changes and innovations affect economic dynamics. Its purposes include:
- Driving Economic Growth: Examining how innovations contribute to increased productivity and economic growth.
- Informing Policy: Providing insights for policy-makers on how to support innovation through investments in research and development, education, and infrastructure.
- Enhancing Competitiveness: Analyzing how businesses and nations can leverage innovation to enhance their competitive edge in the global market.
Usage of Innovation Economics
Innovation Economics is used across various sectors and by multiple stakeholders:
- Government Policy Making: Governments use insights from Innovation Economics to craft policies that encourage research and development, technology adoption, and skill development.
- Corporate Strategy: Businesses apply principles of Innovation Economics to strategize on innovation, research and development investment, and technology management to stay competitive.
- Academic Research: Scholars in economics and business study the impact of technological innovation on economic metrics like productivity, employment, and wealth distribution.
Importance of Innovation Economics
Innovation Economics is crucial because it:
- Focuses on Sustainable Growth: Emphasizes creating and applying new knowledge and technologies as central to sustainable economic growth.
- Addresses Modern Economic Challenges: Helps understand and solve contemporary economic issues related to technology, globalization, and environmental concerns.
- Shapes Future Economies: Guides the development of future-oriented economies that are resilient, adaptive, and capable of continuous innovation.
Benefits of Innovation Economics
Adopting the principles of Innovation Economics offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency: Promotes developing and diffusing new technologies that improve productivity and operational efficiency.
- Economic Diversification: Encourages economic diversification by developing new industries and sectors centered around innovative technologies and services.
- Job Creation: Stimulates the creation of new job opportunities, particularly in high-tech and knowledge-intensive sectors.
Examples of Innovation Economics in Practice
- Silicon Valley: The region's growth as a global tech hub can be primarily attributed to policies and economic practices derived from Innovation Economics, emphasizing innovation, entrepreneurship, and knowledge sharing.
- South Korea's Economic Development: South Korea's transformation into a high-tech economy was significantly influenced by strategic investments in education and technology, guided by innovative economic principles.
- Renewable Energy Sector: The rapid development and adoption of renewable energy technologies are supported by economic policies incentivizing innovation in green technology and sustainable practices.
Innovation Economics provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the vital role that innovation and technology play in modern economies. It offers strategic insights crucial for policy-makers, businesses, and academics to foster environments that prioritize innovation, ensuring sustained economic growth and development.
See Also
- Information Technology Enabled Services (ITeS)
- Technology Transfer: Explaining the process of transferring skills, knowledge, technologies, methods of manufacturing, samples of manufacturing, and facilities among governments or universities and other institutions to ensure that scientific and technological developments are accessible to a wider range of users.
- Entrepreneurship: Covering the role of entrepreneurs in innovation economics, including how they act as agents of change by transforming inventions into economically viable goods or services.
- Intellectual Property: Discusses the importance of intellectual property rights in protecting innovations and their impact on promoting economic growth through incentivizing creativity and investment in research and development.
- Research and Development (R&D): Detailing how R&D activities contribute to innovation and economic development and the role of both private and public sectors in supporting R&D.
- Cluster Theory: Exploring the geographical clusters of businesses and industries, which is significant in innovation economics for fostering collaboration, knowledge sharing, and innovation.
- Knowledge Economy: Discusses the knowledge economy, where wealth is created through the economic exploitation of understanding, and how policies can support its development.
- Globalization: Linking to how globalization affects innovation economics, including the opportunities and challenges it presents for innovation across different countries and industries.
- Innovation Policy: Explains government policies that can stimulate or hinder innovation, such as subsidies, tax incentives, and regulations, and their critical role in shaping the innovation landscape.
- Human Capital: Covers the importance of education and skills development in fostering an innovative workforce that can drive economic development.