Difference between revisions of "Object Diagram"
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
|Objects are instances of classes. | |Objects are instances of classes. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Other UML Object Diagram Examples'''<ref>Other UML Object Diagram Examples [https://www.lucidchart.com/pages/uml-object-diagram Lucidchart]</ref><br /> | ||
| + | UML specifications typically don't change when you describe an object diagram in different programming languages. The whole purpose of UML is for developers to plan out software independent of specific platforms. Below are two of the most commonly used types of object diagrams in different programming languages. | ||
| + | *Objective C object diagram: Objective C has become very popular since Apple's release of "Objective C 2.0," and now it's the programming language of choice for Apple marketplace applications. Most people who use Objective C object diagrams are attempting to show instances for an iPhone app. | ||
| + | *Java object diagram: There are object diagrams that can be used in UML to describe instances that would ultimately be programmed in Java, and there are diagrams that describe Java objects that have nothing to do with UML. Whether you are looking for the former or the latter, Lucidchart can help you map the structure you need to create | ||
Revision as of 15:26, 15 February 2022
An Object Diagram can be referred to as a screenshot of the instances in a system and the relationship that exists between them. Since object diagrams depict behavior when objects have been instantiated, we are able to study the behavior of the system at a particular instant. Object diagrams are vital to portray and understand functional requirements of a system. In other words, “An object diagram in the Unified Modeling Language (UML), is a diagram that shows a complete or partial view of the structure of a modeled system at a specific time.”[1]
Overview of Object Diagrams[2]
In the Unified Modeling Language (UML), an object diagram focuses on some particular set of objects and attributes, and the links between these instances. A correlated set of object diagrams provides insight into how an arbitrary view of a system is expected to evolve over time. In early UML specifications the object diagram is described as:
- "An object diagram is a graph of instances, including objects and data values. A static object diagram is an instance of a class diagram; it shows a snapshot of the detailed state of a system at a point in time. The use of object diagrams is fairly limited, namely to show examples of data structure."
The latest UML 2.5 specification does not explicitly define object diagrams, but provides a notation for instances of classifiers.
Object diagrams and class diagrams are closely related and use almost identical notation. Both diagrams are meant to visualize static structure of a system. While class diagrams show classes, object diagrams display instances of classes (objects). Object diagrams are more concrete than class diagrams. They are often used to provide examples or act as test cases for class diagrams. Only aspects of current interest in a model are typically shown on an object diagram.
Purpose of Object Diagrams[3]
The purpose of a diagram should be understood clearly to implement it practically. The purposes of object diagrams are similar to class diagrams.
The difference is that a class diagram represents an abstract model consisting of classes and their relationships. However, an object diagram represents an instance at a particular moment, which is concrete in nature. It means the object diagram is closer to the actual system behavior. The purpose is to capture the static view of a system at a particular moment. The purpose of the object diagram can be summarized as −
- Forward and reverse engineering.
- Object relationships of a system
- Static view of an interaction.
- Understand object behavior and their relationship from practical perspective
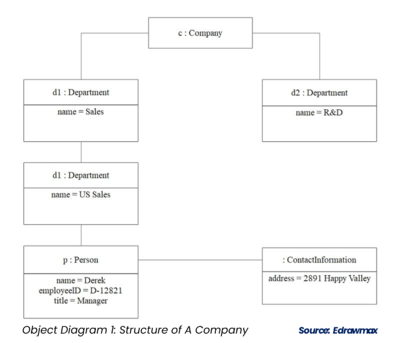
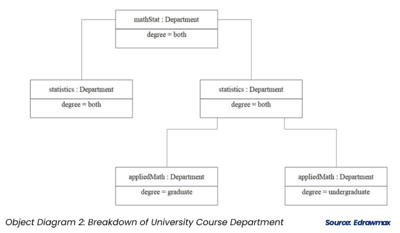
Examples of Object Diagrams[4]
Here is an example of object diagrams illustrating a company's structure, from which there are mainly two departments - The sales department and the R&D department.
The example 2 demonstrate the university course department. For the math statics, it divided by graduate and undergraduate
Class Diagram Vs. Object Diagram[5]
| Serial No. | Class Diagram | Object Diagram |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | It represents static aspects of a system. | It represents the behavior of a system in real time. |
| 2 | It doesn’t include dynamic changes. | It captures runtime changes of a system. |
| 3 | It never includes attributes or data values of an instance. | It includes attributes and data values of any instance. |
| 4 | Class Diagram manipulates the behavior of objects. | Objects are instances of classes. |
Other UML Object Diagram Examples[6]
UML specifications typically don't change when you describe an object diagram in different programming languages. The whole purpose of UML is for developers to plan out software independent of specific platforms. Below are two of the most commonly used types of object diagrams in different programming languages.
- Objective C object diagram: Objective C has become very popular since Apple's release of "Objective C 2.0," and now it's the programming language of choice for Apple marketplace applications. Most people who use Objective C object diagrams are attempting to show instances for an iPhone app.
- Java object diagram: There are object diagrams that can be used in UML to describe instances that would ultimately be programmed in Java, and there are diagrams that describe Java objects that have nothing to do with UML. Whether you are looking for the former or the latter, Lucidchart can help you map the structure you need to create
Applications of Object Diagrams[7]
The following are the application areas where the object diagrams can be used.
- To build a prototype of a system.
- To model complex data structures.
- To perceive the system from a practical perspective.
- Reverse engineering.
References
- ↑ Definition - What does Object Diagram in UML Mean? Geeks for Geeks
- ↑ Overview of Object Diagrams Wikipedia
- ↑ What is the Purpose of Object Diagrams? Tutorials Point
- ↑ The Examples of Object Diagrams Edrawmax
- ↑ Class Diagram Vs. Object Diagram Guru 99
- ↑ Other UML Object Diagram Examples Lucidchart
- ↑ What are the Applications of Object diagrams? Java T Point