Product Lifecycle Management
Product lifecycle management, sometimes "product life cycle management", represents an all-encompassing vision for managing all data relating to the design, production, support and ultimate disposal of manufactured goods. PLM concepts were first introduced where safety and control have been extremely important, notably the aerospace, medical device, military and nuclear industries. These industries originated the discipline of configuration management (CM), which evolved into electronic data management systems (EDMS), which then further evolved to product data management (PDM). Over the last ten years, manufacturers of instrumentation, industrial machinery, consumer electronics, packaged goods and other complex engineered products have discovered the benefits of PLM solutions and are adopting efficient PLM software in increasing numbers.[1]
Introduction to PLM Development Process[2]
The core of PLM (product lifecycle management) is in the creation and central management of all product data and the technology used to access this information and knowledge. PLM as a discipline emerged from tools such as CAD, CAM and PDM, but can be viewed as the integration of these tools with methods, people and the processes through all stages of a product’s life. It is not just about software technology but is also a business strategy
For simplicity the stages described are shown in a traditional sequential engineering workflow ( see figure below). The exact order of event and tasks will vary according to the product and industry in question but the main processes are:
- Conceive
- Specification
- Concept design
- Design
- Validation and analysis (simulation)
- Tool design
- Realise
- Plan manufacturing
- Manufacture
- Build/Assemble
- Test (quality control)
- Service
- Sell and deliver
- Use
- Maintain and support
- Dispose
The major key point events are:
- Order
- Idea
- Kickoff
- Design freeze
- Launch
The reality is however more complex, people and departments cannot perform their tasks in isolation and one activity cannot simply finish and the next activity start. Design is an iterative process, often designs need to be modified due to manufacturing constraints or conflicting requirements. Whether a customer order fits into the time line depends on the industry type and whether the products are for example, built to order, engineered to order, or assembled to order.
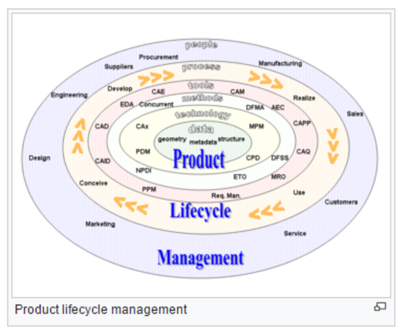
source: |Wikipedia
References
