Difference between revisions of "Quality Management System (QMS)"
(Created page with "'''Content Coming Soon'''") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ''' | + | A '''Quality Management System (QMS)''' is a collection of [[Business Process|business processes]] focused on consistently meeting [[Customer Needs|customer requirements]] and enhancing their satisfaction. It is aligned with an organization's purpose and strategic direction (ISO9001:2015). It is expressed as the [[Business Goals|organizational goals]] and aspirations, [[Policy|policies]], [[Process|processes]], documented information and resources needed to implement and maintain it. Early quality management systems emphasized predictable outcomes of an industrial product production line, using simple [[Statistics|statistics]] and[[Random Sampling|random sampling]]. By the 20th century, labor inputs were typically the most costly inputs in most industrialized societies, so focus shifted to team cooperation and dynamics, especially the early signaling of problems via a [[Continual Improvement|continual improvement cycle]]. In the 21st century, QMS has tended to converge with sustainability and transparency initiatives, as both investor and customer satisfaction and perceived quality is increasingly tied to these factors. Of QMS regimes, the ISO 9000 family of standards is probably the most widely implemented worldwide – the ISO 19011 audit regime applies to both, and deals with quality and sustainability and their integration. Other QMS, e.g. Natural Step, focus on sustainability issues and assume that other quality problems will be reduced as result of the systematic thinking, transparency, documentation and diagnostic discipline. The term "Quality Management System" and the initialism "QMS" were invented in 1991 by Ken Croucher, a British management consultant working on designing and implementing a generic model of a QMS within the IT industry.<ref>Definition - What is a Quality Management System (QMS)? [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quality_management_system Wikipedia]</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | |||
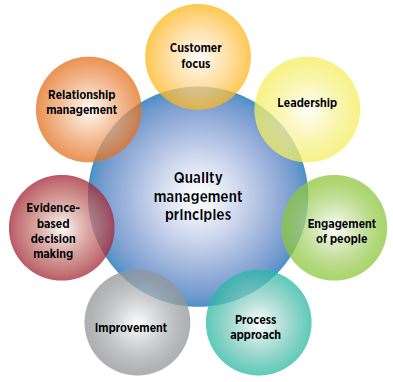
| + | == Elements and Requirements of a QMS<ref>Elements and Requirements of a QMS [https://asq.org/quality-resources/quality-management-system Asq]</ref> == | ||
| + | Each element of a quality management system helps achieve the overall goals of meeting the customers’ and organization’s requirements. Quality management systems should address an [[Business Requirements|organization’s unique needs]]; however, the elements all systems have in common include: | ||
| + | *The organization’s quality policy and quality objectives | ||
| + | *Quality manual | ||
| + | *Procedures, instructions, and records | ||
| + | *Data management | ||
| + | *Internal processes | ||
| + | *Customer satisfaction from product quality | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:QMS Principles.JPG|400px|QMS Principles]]<br /> | ||
| + | source: ASQ | ||
| + | *Improvement opportunities | ||
| + | *Quality analysis | ||
Revision as of 20:32, 8 February 2021
A Quality Management System (QMS) is a collection of business processes focused on consistently meeting customer requirements and enhancing their satisfaction. It is aligned with an organization's purpose and strategic direction (ISO9001:2015). It is expressed as the organizational goals and aspirations, policies, processes, documented information and resources needed to implement and maintain it. Early quality management systems emphasized predictable outcomes of an industrial product production line, using simple statistics andrandom sampling. By the 20th century, labor inputs were typically the most costly inputs in most industrialized societies, so focus shifted to team cooperation and dynamics, especially the early signaling of problems via a continual improvement cycle. In the 21st century, QMS has tended to converge with sustainability and transparency initiatives, as both investor and customer satisfaction and perceived quality is increasingly tied to these factors. Of QMS regimes, the ISO 9000 family of standards is probably the most widely implemented worldwide – the ISO 19011 audit regime applies to both, and deals with quality and sustainability and their integration. Other QMS, e.g. Natural Step, focus on sustainability issues and assume that other quality problems will be reduced as result of the systematic thinking, transparency, documentation and diagnostic discipline. The term "Quality Management System" and the initialism "QMS" were invented in 1991 by Ken Croucher, a British management consultant working on designing and implementing a generic model of a QMS within the IT industry.[1]
Elements and Requirements of a QMS[2]
Each element of a quality management system helps achieve the overall goals of meeting the customers’ and organization’s requirements. Quality management systems should address an organization’s unique needs; however, the elements all systems have in common include:
- The organization’s quality policy and quality objectives
- Quality manual
- Procedures, instructions, and records
- Data management
- Internal processes
- Customer satisfaction from product quality
- Improvement opportunities
- Quality analysis