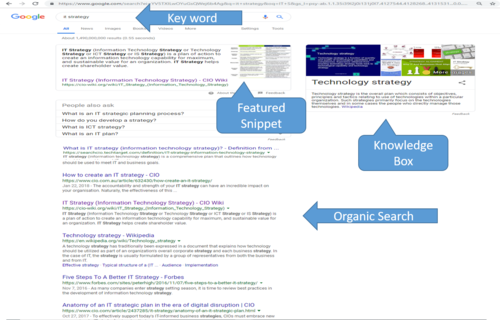
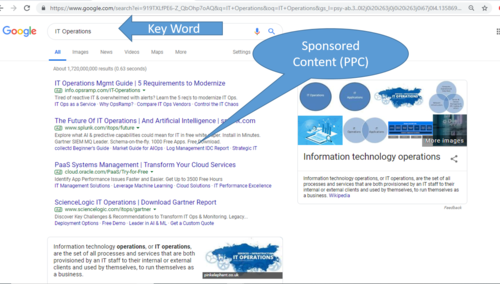
SERP (Search Engine Results Page)
SERPS, or Search engine results page, is a web page that displays a list of results returned by a search engine based on a particular search query that a user has entered. For example, if you type the search query, “dog training tips” into a search engine, such as Google, Bing or Yahoo, the page that you are taken to after submitting your query is called the search engine results page. More on SERPs can be read on our blog. he SERPS will list a title, including your search query as a link, a short description of the web page, and the actual url of the web page underneath the description. The page usually includes about 10 results per page, with links on the bottom to skip to the next page. Most often, browsers will never click on the next page, because the first page displays the most relevant links based on their search query, with result number 1 being the most relevant, accurate choice.[1]
How SERP Works[2]
SERPs are the results a user sees when using a search engine. These web pages are ranked based on their keywords and link profiles or they can be listed at the top of the page if they are ads. The user will type in a search query, or specific keywords, and the search engine will pull the top pages that apply most to the topic.
Keep in mind that each SERP is uniquely its own. That’s because search engines want their users to have a one of a kind experience and will tailor the SERP to each individual depending on their location, search history, and other factors. That means two people can use the same search engine, type in the same exact keyword, and still get different results.
SERP pages have also evolved in appearance throughout the years to stay up to date with the newest technology. Search engines have adapted their SERPs to give the user an easy and informative interface to browse and search. The visual aspect of the SERP may change periodically to stay technologically relevant depending on the search engine used.
Components of SERP[3]
The organic search results, query, and advertisements are the three main components of the SERP, However, the SERP of major search engines, like Google, Yahoo!, and Bing, may include many different types of enhanced results (organic search, and sponsored) such as rich snippets, images, maps, definitions, answer boxes, videos or suggested search refinements. A recent study revealed that 97% of queries in Google returned at least one rich feature. The major search engines visually differentiate specific content types such as images, news, and blogs. Many content types have specialized SERP templates and visual enhancements on the first search results page.
- Search query
Also known as 'user search string', this is the word or set of words that are typed by the user in the search bar of the search engine. The search box is located on all major search engines like Google, Yahoo, and Bing. Users indicate the topic desired based on the keywords they enter into the search box in the search engine. In the competition between search engines to draw the attention of more users and advertisers, consumer satisfaction has been a driving force in the evolution of the search algorithm applied to better filter the results by relevancy. Search queries are no longer successful based upon merely finding words that match purely by spelling. Intent and expectations have to be derived to determine whether the appropriate result is a match based upon the broader meanings drawn from context. And that sense of context has grown from simple matching of words, and then of phrases, to the matching of ideas. And the meanings of those ideas change over time and context. Successful matching can be crowd sourced, what are others currently searching for and clicking on, when one enters keywords related to those other searches. And the crowd sourcing may be focused based upon one's own social networking. With the advent of portable devices, smartphones, and wearable devices, watches and various sensors, these provide ever more contextual dimensions for consumer and advertiser to refine and maximize relevancy using such additional factors that may be gleaned like: a person's relative health, wealth, and various other status, time of day, personal habits, mobility, location, weather, and nearby services and opportunities, whether urban or suburban, like events, food, recreation, and business. Social context and crowd sourcing influences can also be pertinent factors. The move away from keyboard input and the search box to voice access, aside from convenience, also makes other factors available to varying degrees of accuracy and pertinence, like: a person's character, intonation, mood, accent, ethnicity, and even elements overheard from nearby people and the background environment. Searching is changing from explicit keywords: on TV show w, did x marry y or z, or election results for candidate x in county y for this date z, or final scores for team x in game y for this date z to vocalizing from a particular time and location: hey, so who won. And getting the results that one expects.
- Organic results
Organic SERP listings are the natural listings generated by search engines based on a series of metrics that determines their relevance to the searched term. Webpages that score well on a search engine's algorithmic test show in this list. These algorithms are generally based upon factors such as the content of a webpage, the trustworthiness of the website, and external factors such as backlinks, social media, news, advertising, etc. People tend to view the first results on the first page. Each page of search engine results usually contains 10 organic listings (however some results pages may have fewer organic listings). The listings, which are on the first page are the most important ones, because those get 91% of the click through rates (CTR) from a particular search. According to a 2013 study, the CTR's for the first page goes as:
TOP 1: 32.5% TOP 2: 17.6% TOP 3: 11.4% TOP 4: 8.1% TOP 5: 6.1% TOP 6: 4.4% TOP 7: 3.5% TOP 8: 3.1% TOP 9: 2.6% TOP 10: 2.4%
- Sponsored results
Every major search engine with significant market share accepts paid listings. This unique form of search engine advertising guarantees that your site will appear in the top results for the keyword terms you target within a day or less. Paid search listings are also called sponsored listings and/or Pay Per Click (PPC) listings.
- Rich snippets
Rich snippets are displayed by Google in the search results pages when a website contains content in structured data markup. Structured data markup helps the Google algorithm to index and understand the content better. Google supports rich snippets for the following data types:
- Product – Information about a product, including price, availability, and review ratings.
- Recipe – Recipes that can be displayed in web searches and Recipe View.
- Review – A review of an item such as a restaurant, movie, or store.
- Event – An organized event, such as musical concerts or art festivals, that people may attend at a particular time and place.
- SoftwareApplication – Information about a software app, including its URL, review ratings, and price.
- Video – An online video, including a description and thumbnail.
- News article – A news article, including headline, images, and publisher info.
- Science datasets
- Knowledge Graph (or Knoledge Box)
Search engines like Google or Bing have started to expand their data into encyclopedias and other rich sources of information. Google for example calls this sort of information "Knowledge Graph", if a search query matches it will display an additional sub-window on right hand side with information from its sources. Information about product (example Nike), hotels, events, flights, places, businesses, people, books and movies, countries, sport groups, architecture and more can be obtained that way.
Optimizing Important Components of SERP[4]
The following important components of SERP must be thoroughly optimized to ensure organic high rankings.
- Title Of Your Web Page
Your web page’s title should not only be attractive, but it should be intriguing enough to make the user want to click the link to your site. The important thing is to ensure that your page’s title is optimized with the most common keywords used to search for it. So spend some time and do some keyword research before you zero-in down on a title.
- The URL Of Your Web Page
Your webpage’s URL is another excellent target for keyword optimization. Ideally, the URL should contain the root keyword and the key search phrase. In the above example, the URL is “What is SEO”, which allows the Google bots to index the page based on its relevance to the search keywords.
- Your Web Page’s Description
The web page’s description is a line or two of highly-optimized text that appears just below the page title. Google highlights the keywords used to search for the site in this description. Optimize your page’s description in such a way that it dangles a carrot in front of the searcher without revealing too much of the content. You need to word the meta-description in such a way that the right amount of unique content is provided within the space given.
SERP Analysis[5]
SERP analysis is a process of evaluating search results for a particular keyword or a list of keywords you plan to optimize for. It’s an important part of keyword research as it helps to find out whether the keywords are relevant and what’s the possibility to outrank your competitors in order to gain quality organic traffic. Google SERP analysis will help you to:
- Make sure you picked relevant keywords for your niche
- Find out whether you are able to outrank the competitors
See Also
References
- ↑ What is SERP (Search Engine Results Page)? Conversioner
- ↑ How SERP Works Power Digital Marketing
- ↑ Components of SERP Wikipedia
- ↑ Optimizing Important Components of SERP Content4Brands
- ↑ What is SERP analysis? Mangools
Further Reading
- 4 SERP Features Your Business Should Take Advantage Of Upwork
- A Study of First Click Behaviour and User Interaction on the Google SERP Chris Barry, Mark Lardner
- PDF Conversions for SERP Rankings Performics
- 3 Ways to Re-Use Your Content Magnets to Dominate SERPs [https://contentmarketinginstitute.com/2017/03/reuse-content-serps/ CMI)
- The changing SERP: understanding and optimizing above and below the fold Search Engine Watch