Business Life Cycle
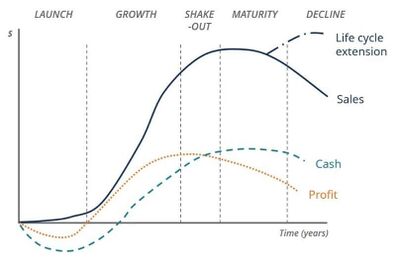
The business life cycle is the progression of a business and its phases over time and is most commonly divided into five stages: launch, growth, shake-out, maturity, and decline. The cycle is shown on a graph with the horizontal axis as time, and the vertical axis as dollars or various financial metrics.
source: Corporate Finance Institute
- Phase One: Launch: Each company begins its operations as a business and usually by launching new products or services. During the launch phase, sales are low but slowly (and hopefully steadily) increasing. Businesses focus on marketing to their target consumer segments by advertising their comparative advantages and value propositions. However, as revenue is low and initial startup costs are high, businesses are prone to incur losses in this phase. In fact, throughout the entire business life cycle, the profit cycle lags behind the sales cycle and creates a time delay between sales growth and profit growth. This lag is important as it relates to the funding life cycle, which is explained in the latter part of this article. Finally, the cash flow during the launch phase is also negative but dips even lower than the profit. This is due to the capitalization of initial startup costs that may not be reflected in the business’ profit but that are certainly reflected in its cash flow.
- Phase Two: Growth: In the growth phase, companies experience rapid sales growth. As sales increase rapidly, businesses start seeing profit once they pass the break-even point. However, as the profit cycle still lags behind the sales cycle, the profit level is not as high as sales. Finally, the cash flow during the growth phase becomes positive, representing an excess cash inflow.
- Phase Three: Shake-out: During the shake-out phase, sales continue to increase, but at a slower rate, usually due to either approaching market saturation or the entry of new competitors in the market. Sales peak during the shake-out phase. Although sales continue to increase, profit starts to decrease in the shake-out phase. This growth in sales and decline in profit represents a significant increase in costs. Lastly, cash flow increases and exceeds profit.
- Phase Four: Maturity: When the business matures, sales begin to decrease slowly. Profit margins get thinner, while cash flow stays relatively stagnant. As firms approach maturity, major capital spending is largely behind the business, and therefore cash generation is higher than the profit on the income statement. However, it’s important to note that many businesses extend their business life cycle during this phase by reinventing themselves and investing in new technologies and emerging markets. This allows companies to reposition themselves in their dynamic industries and refresh their growth in the marketplace.
- Phase Five: Decline: In the final stage of the business life cycle, sales, profit, and cash flow all decline. During this phase, companies accept their failure to extend their business life cycle by adapting to the changing business environment. Firms lose their competitive advantage and finally exit the market.[1]
The Purpose of the Business Life Cycle[2]
Although all businesses are inherently unique, they often follow a similar trajectory. In fact, if you plot a business’ journey from conception to present on a timeline, you’ll usually see five distinct phases. It’s similar to how people grow and mature; the business life cycle shows businesses maturing from infancy through adolescence to adulthood and eventually, old age.
According to the Startup Genome Report, 90 percent of small businesses fail. To be clear, almost all businesses start as small businesses before processing through the stages of business growth. And when a business does fail, it doesn’t usually happen right away.
Though it varies by industry, about 20 percent of businesses fail within one year of launch. Of the 80 percent that remains, 30 percent fail within the second year. Then 50 percent of the remaining businesses fail by the fifth year, and between years five and ten, 70 percent of the remaining businesses fail.
Why? It often boils down to poor planning, preparation, and decision making.
The business life cycle may have originated as an analytics tool, but it’s increasingly used as a business blueprint. Since it outlines the trajectory of a business, entrepreneurs can use the business life cycle to build stronger, healthier businesses.
Navigating The Business Lifecycle[3]
Not all businesses will experience every stage of the business lifecycle, and those that do may not necessarily experience them in chronological order. For example, some businesses may see astronomical growth right after startup, and the founders may decide to cash out right away, jumping straight to that “exit” stage.
For many companies, though, there will be some sort of resemblance to the stages defined above, and awareness may help you anticipate what is coming next and how you can best prepare yourself and your team to maximize your chance of success. Making the right decisions at each stage is another thing altogether, however, and that will require your usual mix of gut instinct and practical business sense.
See Also
The Business Life Cycle is a concept that outlines the stages of growth and development through which a typical business progresses. Understanding the business life cycle is crucial for entrepreneurs, managers, and investors as it helps in strategic planning, decision-making, and resource allocation tailored to each phase of the business.
- Business Planning: Discussing the process of writing a business plan, which is especially crucial in the Seed and Development stage.
- Market Research: Covering the process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market, necessary for understanding potential customers and competitors.
- Capital Raising: Explaining different methods and sources of raising business capital, vital for the Startup and Growth stages.
- Marketing Strategy: Discussing various strategies to promote products or services, critical for building brand awareness in the Startup and Growth stages.
- Scale-up Strategies: Covering methods to scale business operations, important for businesses in the Growth and Expansion stages.
- Innovation Management: Discussing the process of managing innovations in a business, crucial for sustaining growth or addressing the Decline stage.
- Restructuring and Turnaround Management: Covering strategies to reorganize and revive a business, applicable to the Decline stage.
- Exit Strategies: Discussing options for business owners to exit their business, relevant to the Exit or Renewal stage.
- Succession Planning: Explaining the process for identifying and developing new leaders who can replace old leaders when they leave, retire, or die, important for the Exit or Renewal stage.
- Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A): Covering the aspects of corporate strategy, corporate finance, and management dealing with buying, selling, dividing, and combining companies, relevant to the Exit or Renewal stage.
