Business Objective
What is a Business Objective?
A Business Objective, in short, is what a company wants to achieve throughout the year. Instead of focusing on what you're currently doing in your business, an objective is something you want to achieve going forward. Many times, business objectives are spelled out in a business plan and used as part of the strategic planning process of a company going forward. After all, without objectives, how do you know what to do to get there? Business objectives function as a way for business owners to make plans, track their progress, and work toward a particular goal. The thing about objectives is that they're measurable, specific, and tactical. They aren't general statements like We want to be the most recognizable bookstore in the region. Instead, they are focused, such as the objective, We want to open 10 new locations in the coming year.[1]
The Aim of Business Objectives [2]
Business objectives are a vital part of any business owner's business plan. They are the life's blood of the business plan. They are the most important thing a business owner can share with the company. They are a statement of specific, realistic, measurable goals with a time component put on them that a company tries to adhere to. They serve to aim the company towards the goals they are shooting for and hopefully let them attain them.
- Goals: A business is lost without goals, which is what business objectives are. They are a statement of goals. It is important for business owners to sit down and write out their intentions. These objectives need to be listed somewhere that not only the business owner can refer to but also the company as a whole. By writing down goals, business objectives are a vital item in a company's arsenal.
- Direction: Business objectives give a company direction. Stating the company's goals in specific, measurable ways gives direction to the company's efforts and allows every person in the company the chance to work towards those goals. It is the main function of the business objectives to provide direction to the company to guide them towards whatever goal has been specified for whatever time period has been listed in the objective. Business objectives are like an arrow pointing towards a goal.
- Focus: By composing some decent business objectives, it gives a company the focus it needs to do business. It allows a company to know what it is focusing on. It lets them know whether they focus on sales or customer service, product placement, or marketing. Business objectives allow everyone to know what the main thrust of the company's efforts is going to be and state it in explicit terms that everyone can understand and follow.
- Cohesion: Business objectives allow everyone to be a cohesive unit and be on the same page. Sometimes the goals that are on the business owner's mind are not what is on the minds of the rest of the employees. If the business objectives are written out clearly, then everyone will know what the goals are and be able to pursue them to the greatest extent. Business objectives are a great tool for communication with the company and a way to make sure everyone is working together. Composing business objectives is not a hard task if care and effort are taken to complete them. It is really an easy task to complete when so many great benefits come from it. It is helpful for goals to be explicit even when one is working alone so that those goals can become a reality. Nothing beats writing down the things that are in your mind to get them done. Business objectives are a way of getting business goals accomplished, and that's why they are so important.
Types of Business Objectives [3]
Business objectives can be broadly split into quantitative and qualitative, and it’s important you find the right blend based on your context and requirements.
- Quantitative objectives: Probably the most frequently used type of objective, quantitative objectives are those that can be tracked and evidenced by data. They are designed to satisfy our need for certainty and measurability and are the easiest form to tabulate or represent graphically (both popular obsessions at the management level!). So, what are the pros and cons?
- Pros:
- Easy to measure and report on
- Easy to cascade into subsets of contributing objectives for individual targets
- Easy to show variance from target or to compare one team or period to another
- Cons:
- Can be overly simplistic and tend to lack the depth of a qualitative objective
- Can be misleading if taken in isolation
- Require support of a more detailed narrative to explain what figures mean
- Pros:
- Qualitative objectives: Less prevalent due to the relative complexity typical of this form, qualitative objectives are more common in the service business, especially those with a high degree of creativity.
- Pros:
- Tend to present a richer picture and encourage a deeper understanding of the performance being measured
- Tend to enable more detailed discussion about performance and improvement actions
- Cons:
- Can be overly complex
- Can be opinion-based or subjective
- Typically more difficult to measure
- Hard to represent or report on
- Often needs to be underpinned by several quantitative measures
- Pros:
Classification of Business Objectives (Figure 1.) [4]
It is generally believed that a business has a single objective. That is, to make a profit. But it cannot be the only objective of a business. While pursuing the objective of earning a profit, business units do keep the interest of their owners in view. However, any business unit cannot ignore the interests of its employees, customers, the community, as well as the interests of society as a whole. For instance, no business can prosper in the long run unless fair wages are paid to the employees and customer satisfaction is given due importance. Again a business unit can prosper only if it enjoys the support and goodwill of people in general. Business objectives also need to be aimed at contributing to national goals and aspirations as well as to international well-being. Thus, the objectives of business may be classified as
- A. Economic Objectives: Economic objectives of business refer to the objective of earning profit and other objectives that must be pursued to achieve the profit objective, which includes the creation of customers, regular innovations, and the best possible use of available resources.
- (i) Profit Earning: Profit is the lifeblood of business, without which no business can survive in a competitive market. In fact, profit-making is the primary objective for which a business unit is brought into existence. Profits must be earned to ensure the survival of the business, its growth, and its expansion over time. Profits help businessmen not only to earn their living but also to expand their business activities by reinvesting a part of the profits. In order to achieve this primary objective, certain other objectives are also necessary to be pursued by the business, which are as follows:
- (a) Creation of customers: A business unit cannot survive unless there are customers to buy the products and services. Again a businessman can earn profits only when he/she provides quality goods and services at a reasonable price. For this, it must attract more customers for its existing and new products. This is achieved with the help of various marketing activities.
- (b) Regular innovations: Innovation means changes, which bring about improvement in products, the process of production, and the distribution of goods. Business units, through innovation, are able to reduce costs by adopting better methods of production and also increase their sales by attracting more customers because of improved products. Reduction in cost and increase in sales gives more profit to the businessmen. The use of power looms in place of handlooms, the use of tractors in place of hand implements in farms, etc., are all the results of innovation.
- (c) Best possible use of resources: As we all know, to run any business, we must have sufficient capital or funds. The amount of capital may be used to buy machinery, and raw materials, employ men and have the cash to meet day-to-day expenses. Thus, business activities require resources like men, materials, money, and machines. The availability of these resources is usually limited. Thus, every business should try to make the best possible use of these resources. Employing efficient workers. Making full use of machines and minimizing the wastage of raw materials can achieve this objective.
- (i) Profit Earning: Profit is the lifeblood of business, without which no business can survive in a competitive market. In fact, profit-making is the primary objective for which a business unit is brought into existence. Profits must be earned to ensure the survival of the business, its growth, and its expansion over time. Profits help businessmen not only to earn their living but also to expand their business activities by reinvesting a part of the profits. In order to achieve this primary objective, certain other objectives are also necessary to be pursued by the business, which are as follows:
- B. Social Objectives: Social objectives are those objectives of the business which are desired to be achieved for the benefit of society. Since business operates in a society by utilizing its scarce resources, the society expects something in return for its welfare. No activity of the business should be aimed at giving any kind of trouble to society. If business activities lead to socially harmful effects, there is bound to be a public reaction against the business sooner or later. Social objectives of business include the production and supply of quality goods and services, adoption of fair trade practices and contribution to the general welfare of society, and provision of welfare amenities.
- (i) Production and Supply of Quality Goods and Services: Since the business utilizes the various resources of the society, the society expects to get quality goods and services from the business; the objective of the business should be to produce better quality goods and supply them at the right time and at a right price. It is not desirable on the part of the businessman to supply adulterated or inferior goods which cause injuries to the customers. They should charge the price according to the quality of e goods and services provided to society. Again, the customers also expect a timely supply of all their requirements. So it is important for every business to supply those goods and services on a regular basis.
- (ii) Adoption of Fair Trade Practices: In every society, activities such as hoarding, black-marketing, and over-charging are considered undesirable. Besides, misleading advertisements often give a false impression about the quality of products. Such advertisements deceive customers, and businessmen use them for the sake of making large profits. This is an unfair trade practice. The business unit must not create artificial scarcity of essential goods or raise prices for the sake of earning more profits. All these activities earn a bad name and sometimes make the businessmen liable for penalties and even imprisonment under the law. Therefore, the objective of business should be to adopt fair trade practices for the welfare of the consumers and society.
- (iii) Contribution to the General Welfare of the Society: Business units should work for the general welfare and upliftment of society. This is possible through the running of schools and colleges, better education, opening of vocational training centers to train the people to earn their livelihood, establishing hospitals for medical facilities, and providing recreational facilities for the general public like parks, sports complexes, etc.
- C. Human Objectives: Human objectives refer to the objectives aimed at the well-being as well as fulfillment of expectations of employees as also of people who are disabled, handicapped, and deprived of proper education and training. The human objectives of business may thus include the economic well-being of the employees, social and psychological satisfaction of employees, and the development of human resources.
- (i) Economic Well-being of the Employees: In business, employees must be provided with tan remuneration and incentive for performance benefits of provident fund, pension and other amenities like medical facilities, housing facilities, etc. Through this, they feel more satisfied and contribute more to the business.
- (ii) Social and Psychological Satisfaction of Employees: It is the duty of business units to provide social and psychological satisfaction to their employees. This is possible by making the job interesting and challenging, putting the right person in the right job, and reducing the monotony of work Opportunities for promotion and advancement in career should also be provided to the employees. Further, employees' grievances should be given prompt attention, and their suggestions should be considered seriously when decisions are made. If employees are happy and satisfied they can put their best efforts into work.
- (iii) Development of Human Resources: Employees, as human beings, always want to grow. Their growth requires proper training as well as development. Businesses can prosper if the people employed can improve their skills and develop their abilities and competencies over time. Thus, it is important that businesses should arrange training and development programs for their employees.
- (iv) Well-being of Socially and Economically Backward People: Business units being inseparable parts of society, should help backward classes and also people who are physically and mentally challenged. This can be done in many ways. For instance, vocational training programs may be arranged to improve the earning capacity of backward people in the community. While recruiting its staff, businesses should prefer physically and mentally challenged persons. Business units can also help and encourage meritorious students by awarding scholarships for higher studies.
- D. National Objectives: Being an important part of the country, every business must have the objective of fulfilling national goals and aspirations. The goal of the country may be to provide employment opportunities to its citizen, earn revenue for its exchequer, become self-sufficient in the production of goods and services, promote social justice, etc. Business activities should be conducted keeping these goals of the country in mind, which may be called the national objectives of the business. The following are the national objectives of the business.
- (i)Creation of Employment: One of the important national objectives of the business is to create opportunities for the gainful employment of people. This can be achieved by establishing new business units, expanding markets, widening distribution channels, etc.
- (ii) Promotion of Social Justice: As a responsible citizen, a businessman is expected to provide equal opportunities to all persons with whom he/she deals. He/ She is also expected to provide equal opportunities to all the employees to work and progress. Towards these objectives, special attention must be paid to weaker and backward sections of society.
- (iii) Production According to National Priority: Business units should produce and supply goods in accordance with the priorities laid down in the plans and policies of the government. One of the national objectives of the business in our country should be to increase the production and supply of essential goods at reasonable prices.
- (iv) Contribute to the Revenue of the Country: The business owners should pay their taxes and dues honestly and regularly. This will increase the revenue of the government, which can be used for the development of the nation.
- (v) Self-sufficiency and Export Promotion: To help the country to become self-reliant, business units have the added responsibility of restricting the import of goods. Besides, every business unit should aim at increasing exports and adding to the foreign exchange reserves of the country.
- E. Global Objectives: Previously, India had very restricted business relationships with other nations. There was a very rigid policy for the import and export of goods and services. But, nowadays, due to liberal economic and export-import policies, restrictions on foreign investments have been largely abolished, and duties on imported goods have been substantially reduced. This change has brought about an increase in competition in the market. Today because of globalization, the entire world has become a big market. Goods produced in one country are readily available in other countries. So, to face the competition in the global market every business has certain objectives, which may be called global objectives. Let us learn about them.
- (i) Raise General Standard of Living: Growth of business activities across national borders makes quality goods available at reasonable prices worldwide. The people of one country get to use similar types of goods that people in other countries are using. This improves the standard of living of people.
- (ii) Reduce Disparities among Nations: Businesses should help to reduce disparities between the rich and poor nations of the world by expanding its operation. By way of capital investment in developing and underdeveloped countries, it can foster their industrial and economic growth.
- (iii) Make Available Globally Competitive Goods and Services: Businesses should produce goods and services which are globally competitive and have huge demand in foreign markets. This will improve the image of the exporting country and also earn more foreign exchange for the country.
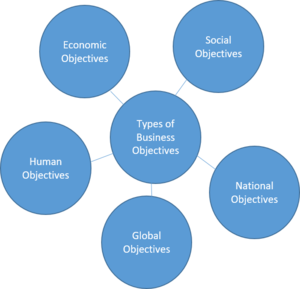
Figure 1, source: CIO Index
Examples of Business Objectives [5]
- Example objective #1: Percentage change
For this year's summer swimwear line, we will increase sales by 15% over last year's line through customer relationship marketing. We will execute distinct email campaigns by segmenting last year's summer swimwear customers and this year's spring casualwear customers and offering season-long discount codes.
- Example objective #2: Goal number
Our SaaS product implementation team will grow to five during the next fiscal year. This will require us to submit a budget proposal by the end of the quarter and look into restructured growth tracks, new job posting templates, and revised role descriptions by the start of the next fiscal year.
- Example objective #3: Success range
We will increase customer satisfaction for our mobile app product demonstrably by the end of the year by integrating a new AI chatbot feature. To measure the change in customer satisfaction, we will monitor ratings in the app store, specifically looking for decreases in rates of negative reviews by 5%-10% and increases in overall positive reviews by 5%-10%.
- Example objective #4: Clear change
Each of our water filtration systems will achieve NSF certification ahead of the launch of our rebranding campaign. Our product team will establish a checklist of changes necessary for meeting certification requirements and communicate timelines to the marketing team.
- Example objective #5: Executable action
HR will implement bi-annual performance reviews starting next year. Review timelines will be built into scheduling software, and HR will automate email reminders to managers to communicate with their teams.
Nature Characteristics of Business Objectives (Figure 2.) [6]
The features or characteristics of business objectives are:
- Multiplicity of Objectives: Business objectives are multiple in character. That is, a business does not have only one objective. It has many or multiple objectives. This is because a business has to satisfy different groups, i.e., shareholders, employees, customers, creditors, vendors, society, etc. The business has to fix different objectives for each group.
- Hierarchy of Objectives: Hierarchy means writing down the objectives according to their importance. The most important objective is written first, and the least important objective is written last. All objectives are important. However, some objectives are more important than others. Some objectives need immediate action, while others can be kept aside for some time.
- Periodicity of Objectives: Based on period, business objectives can be classified into two types,
- Short-term objectives: The short-term objectives are made for a short period, i.e., a maximum of one year. Short-term objectives are more specific, and
- Long-term objectives The long-term objectives are made for a long period, i.e., five years or more. Long-term objectives are more general. They are like a Master Plan.
- Flexibility of Objectives: The business is flexible. Therefore, the business objectives must also be flexible. If the objectives are rigid, the business will not survive. This is because the business environment keeps on changing. There are continuous changes in the technical, social, economic, and political environment. The business has to change its objectives according to the changes in the business environment. The hierarchy of objectives must also be changed from time to time.
- Qualitative and Quantitative Objectives: There are two types of objectives,
- Quantitative objectives are easy to measure. It is expressed in numbers. For e.g., in Dollars, Rupees, Percentages, etc. Quantitative objectives are visible, tangible, and countable.
- Qualitative objectives are not easy to measure. It is not expressed in numbers. For e.g., Employee performance, employee satisfaction, etc. These objectives cannot be measured. Qualitative objectives are invisible, intangible, and uncountable. Today modern methods are used to measure qualitative objectives. A business must have both quantitative and qualitative objectives.
- Measurability of Objectives: The objectives must be clear and specific. It must be easy to measure. For e.g., Each salesman must sell 100 units of water purifiers per month. This is a clear and specific objective. It is easy to measure the performance of the salesman. If a salesman sells 200 units of water purifiers in a month then his performance is good. He can be given a bonus and promotion. However, if a salesman sells only 10 units of water purifiers in a month then his performance is bad. He needs more training. Measurable objectives motivate employees to work hard. This is because they know their target clearly. Their performance can also be measured easily.
- Network of Objectives: A network means an interconnection between different objectives. A business has many different objectives, viz., corporate objectives, departmental objectives, sectional objectives, and individual objectives. It also has objectives for shareholders, customers, employees, etc. All these objectives must be interconnected. They must support each other. They must not clash with each other. They must move in the same direction. If not, the business will not survive. Similarly, the objectives of all the departments must support each other. They must not clash or conflict will each other.
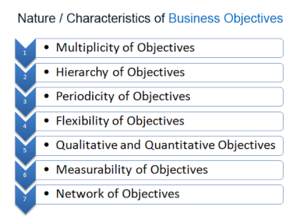
Figure 2. source: KalyanCityLife
Properties of a Business Objective [7]
- Target Date: The date when the Business Objective is to be accomplished.
- Achievement %: An indication of the progress toward accomplishing the Business Targets associated with the Business Objective. You can enter a numeric value representing the percentage.
- Owner: In the Owner property, you specify the Organizational Unit that has specified the objective. It is important to understand who has specified the objective. If you do not know the responsible party for an objective, it might be hard in the future to track down the reason for it, which might lead to the perpetuation of unnecessary objectives. Objectives might have been created because of requirements that have long since become defunct or to temporarily build workarounds in systems that did not fully support business needs. Knowing the owner enables you to challenge the objective to see if it is still necessary. These objectives should be very specific and should state specific measurements of success. Two such objectives might be Increase on-time arrivals by 10 percent by 2002 or Achieve $100 million in sales by 2003.
- Targets, by Performance Measure: A reference property that links the Business Objective to its targets. A Business Target definition is keyed to Business Objectives and Performance Measures. The Target Value property of the Business Target is the value to be achieved. The corresponding units of measure are found in the related Performance Measure.
- Initiatives: This property links the Business Objective with those initiatives that are intended to bring about its realization.
- Business Rules: A Business Rule supports the achievement of a Business Objective. You can specify which Business Rules support the achievement of which Business Objectives
- Performance Measures: Targets by Performance Measure is a reference property that links the Business Objective to its targets. A Business Target definition is keyed to Business Objectives and Performance Measures. The Target Value property of the Business Target is the value to be achieved.
- Expectations: The Expectations of Stakeholders can align with certain Business Objectives.
- Influences: You can specify external or internal influences which can bode positively or negatively on a Business Objective. This enables you to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) involved in a project or business venture.
Business Objectives vs. Business Goals(Figure 3.) [8]
A company’s goals and objectives are not the same.
- The goal includes a broad primary outcome. A business objective, on the other hand, is a measurable step people take to achieve that goal.
- Goals are general, while objectives are specific. A business objective is more specific and easier to measure than a goal. All our basic tools that underlie our planning and strategic activities are our objectives. Our objectives serve as the basis for creating policy and gauging performance.
- Business goals are where you aim to be one day. Business Objectives, on the other hand, describe how you plan to get there.
Why Business Objectives Change [9]
The aim of a business can change over time. This can happen in response to internal factors, such as business growth, or in response to external factors, such as an economic recession. A small start-up business may aim to survive in the first year. Once successful, the business sets itself the objective of increasing profits or growing in size. Alternatively, a profitable business hard hit by an economic recession may struggle to maintain the same output level. Faced with declining sales, a business may change its objective from growth or making a profit to simply surviving. The competitive environment might change with the launch of new products from competitors. Technology might change product designs, so sales and production targets might need to change.
See Also
Business Objective refers to specific, measurable outcomes that organizations aim to achieve within a certain timeframe to advance their mission and overall strategy. These objectives are essential for guiding the direction of a company, motivating employees, and measuring progress toward achieving broader business goals.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Quantifiable measures used to evaluate the success of an organization, employee, or process in meeting objectives for performance. KPIs are critical for tracking progress towards business objectives.
- Strategic Planning: The process of defining a company's direction and making decisions on allocating its resources, including its capital and people, to pursue this strategy. Strategic planning sets the foundation for defining business objectives.
- Benchmarking: Comparing business processes and performance metrics to industry bests and best practices from other companies. Benchmarks can help set realistic and competitive business objectives.
- Operational Efficiency: The ability to cost-effectively provide products or services without compromising quality. Enhancing operational efficiency is often a key business objective.
- Market Penetration: The strategy of selling existing products within existing markets to gain a higher market share. This can be a specific objective for businesses looking to grow in familiar markets.
- Product Development: Creating new products or improvements to existing products to meet customer needs and respond to market changes. Product development can be a central business objective for innovation-driven companies.
- Customer Satisfaction: A measure of how a company's products and services meet or surpass customer expectations. Increasing customer satisfaction is a common business objective.
- Corporate Governance: The system of rules, practices, and processes by which a firm is directed and controlled. Strengthening corporate governance can be an objective to ensure compliance, ethical behavior, and sustainable growth.
- Revenue Growth: An increase in a company’s sales over a period. Companies often set specific revenue growth rates as objectives to measure financial success and market expansion.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Efforts to conduct business in a way that is environmentally responsible and beneficial to society. Adopting sustainability initiatives can be an objective for businesses aiming to contribute positively to the world.
These terms illustrate the broad scope of considerations involved in setting and pursuing business objectives. They underscore the importance of aligning these objectives with the company’s strategic vision, operational capabilities, market demands, and societal expectations.
References
- ↑ Definition of Business Objective
- ↑ The Aim of Business Objectives
- ↑ Main Types of Business Objectives
- ↑ Classification of Objectives of Business
- ↑ Business objectives: How to set them (with 5 examples and a template)
- ↑ Characteristics and Features of Business Objectives
- ↑ Properties of a Business Objective
- ↑ Business Objectives vs. Business Goals
- ↑ Why business objectives change

