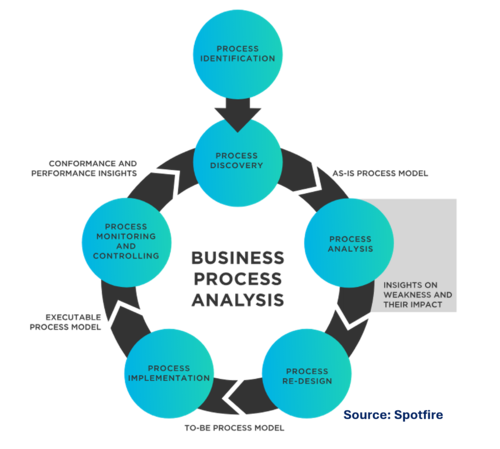
Business Process Analysis
What is Business Process Analysis?
Business Process Analysis (BPA) is a methodical approach to examining the efficiency and effectiveness of a business's workflows and processes. It aims to identify areas where improvements can be made to streamline operations, enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve overall organizational performance. BPA involves understanding the current processes, identifying inefficiencies, and proposing solutions to optimize business operations.
Role and Purpose of Business Process Analysis
The primary role of business process analysis is to provide a clear, detailed understanding of how an organization operates from a process perspective. Its purposes include:
- Identifying Inefficiencies: Detecting bottlenecks, redundancies, and unnecessary complexities within business processes.
- Enhancing Productivity: Proposing changes that make processes more efficient, reducing time and resource wastage.
- Improving Quality: Ensuring processes are aligned with quality standards and can produce the desired outcomes.
- Supporting Strategy Implementation: Aligning processes with strategic goals ensures the organization can effectively meet its objectives.
Usage of Business Process Analysis
Business process analysis is used in various organizational contexts:
- Operational Improvement: Streamlining operational processes to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- Technology Integration: Analyzing processes before implementing new technology to ensure that technology adds value and integrates smoothly.
- Change Management: Supporting change management by clearly understanding current processes and how proposed changes might impact them.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Ensuring processes comply with legal and regulatory requirements and identifying risk factors within processes.
Importance of Business Process Analysis
Business process analysis is crucial because it:
- Drives Continuous Improvement: Helps organizations continuously evolve and improve their processes to maintain competitiveness.
- Enhances Decision Making: Provides data-driven insights that can inform management decisions.
- Supports Organizational Agility: Allows organizations to quickly adapt to new challenges, market conditions, and technological advancements by understanding and modifying their processes.
Benefits of Business Process Analysis
The benefits of conducting a thorough business process analysis include:
- Cost Efficiency: Identifying cost-saving opportunities by eliminating waste and redundancies.
- Customer Satisfaction: Improving the customer experience by optimizing processes that directly impact service delivery.
- Employee Satisfaction: Reducing frustration and increasing productivity by streamlining tasks and removing unnecessary workload.
- Strategic Alignment: Ensuring that every process supports the organization's overarching goals, leading to more focused and effective operations.
Examples of Business Process Analysis in Practice
- Manufacturing Sector: Analyzing the production process to identify stages where inefficiencies cause delays or quality issues and then proposing changes to enhance throughput and reduce waste.
- Healthcare Facilities: Examining patient admission and discharge processes to reduce wait times and improve patient flow and satisfaction.
- Financial Services: Reviewing loan processing workflows to identify delays and automate steps where possible, improving speed and reducing errors.
Business process analysis is a critical tool for any organization looking to optimize performance and maintain competitiveness in its industry. By systematically reviewing and improving processes, companies can achieve higher operational efficiency, better-quality products and services, and increased satisfaction among customers and employees.
See Also
- Business Process Management (BPM): Discussing the broader field of BPM, which encompasses the design, execution, monitoring, and optimization of business processes. BPA is often a critical component within BPM for identifying improvement opportunities.
- Process Model: Covers techniques and tools used to map out business processes, including flowcharts and Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN), which are essential for analyzing and understanding process flows.
- Lean Management: Explaining Lean principles and how they apply to process improvement, focusing on reducing waste and increasing efficiency, which are common goals of BPA.
- Six Sigma: Method used to improve business processes by using statistical analysis to identify and remove the causes of defects and variability.
- Change Management: Discuss strategies for managing organizational changes, including implementing new processes and systems identified through BPA.
- Information Technology Systems: Linking to how IT systems support business processes and how BPA often involves the analysis of these systems to ensure they are effectively meeting business needs.
- Workflow Automation: Explaining how automation can streamline business processes, often identified as a recommendation through BPA to improve efficiency and reduce manual errors.
- Data Analytics: Covering how data analysis techniques can be applied within BPA to quantify process performance and identify areas of improvement.
- Quality Management: Discusses quality management frameworks, such as Total Quality Management (TQM), which overlap with BPA in their focus on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- Risk Management: Explains how BPA helps in identifying and mitigating risks associated with business processes, contributing to more robust and resilient operations.