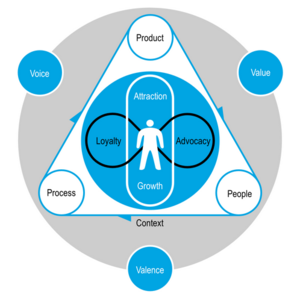
Customer Experience Management (CEM)
Gartner defines Customer Experience Management (CEM) as “the practice of designing and reacting to customer interactions to meet or exceed customer expectations and, thus, increase customer satisfaction, loyalty and advocacy.”[1]
Definition of Customer Experience Management (CEM)[2]
Customer Experience Management or CEM or CXM is a concept that describes how a company takes control of how it interacts with its customers. Typically, each group in an organization will build out customer interactions from its own perspective — that of the various silos. CEM is about viewing and then improving the interactions between your business and your customer entirely from the customers’ perspective — and across the entire journey they have with your business. Why do this? Well, the ultimate aim is two-fold: to build customer loyalty and positive word of mouth; and to reduce customer churn and detractors who speak negatively about your business. In other words: better business results.
The Importance of Customer Experience Management (CEM)[3]
The concept of customer experience may sound idealistic or touchy-feely, but anyone who dismisses it as such is woefully out of touch. In fact, customer experience has become a critical differentiator in today’s hyper-competitive, hyper-connected global marketplace. There’s tangible business value in managing the customer experience effectively. Good customer experience management can:
- Strengthen brand preference through differentiated experiences.
- Boost revenue with incremental sales from existing customers and new sales from word of mouth.
- Improve customer loyalty (and create advocates) through valued and memorable customer interactions.
- Lower costs by reducing customer churn.
Customer Experience Management (CEM) Techniques[4]
Companies rely on business intelligence and customer data analytics tools to learn how to market and sell to customers in a more personalized, one-to-one fashion.
- Personalization strategies include new technologies, such as mobile marketing, location-based services and beacons, which help companies identify where customers are and market to them in real time. In some cases, the data can help companies give consumers pointed information that may or may not be related to a discrete purchase. For example, a stadium might use location-based services to inform consumers about which concession stand is proximal and less-busy.
- Companies also use emotional analytics to gauge whether customers benefit from their interactions with the brand. Emotional analytics software can help analyze the success of a variety of operations that are related -- but potentially tangential to -- customer service, such as inventory management or supply chain management.
- Knowledge Management systems are also important tools for seamless customer service. Agents can use these systems to look up product information and customer interactions with other products. Agents can also combine this information with customer data and inventory information to provide customers with account information, product education and inventory.
- There is more incoming data to process from more sources than ever before, and this data needs to be integrated with existing customer account data. The ability to combine customer relationship management (CRM) system data with financials, ERP and inventory management, as well as real-time data on social platforms, can be challenging.
CRM platforms from vendors such as Salesforce, Microsoft, SAP and Oracle attempt to bridge the gaps between communication channels to make database integration easier. These providers support integrating sales, marketing and service data as well, so customer information isn't siloed.
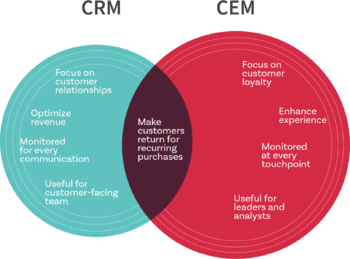
Customer Experience Management Vs. Customer Relationship Management[5]
Business leaders and product managers have often confused Customer Experience Management with Customer Relationship Management and used them interchangeably. However, this isn’t the case. Let’s explore what makes CRM different from CEM.
- The goal of CRM includes customer relationships and optimizing the overall revenue and growth of the company. CEM, on the other hand, focuses on the interaction and the experience customers have with a company. Therefore, CRM captures how a company perceives a customer. CEM is all about what a customer thinks about the company.
- CRM or customer relationship management, mines data and analyzes it to track customer behavior and purchase patterns.How did a customer hear about the product? What prompted them to purchase it? How often do they make a purchase? How do they interact with the brand? These are some questions which any company might have in mind. CRM brings answers to all these questions. Therefore, we can say that customer relationship management focuses on nurturing customer relationships and making it last longer. CEM, on the other hand, shifts attention towards driving customer loyalty, brand advocacy by creating a positive persona about the company in the minds of customers.
- CRM comes into play when there’s a customer interaction happening- like sales-talk, support query, or assistance of any kind. On the contrary, CEM is monitored and measured at every customer touchpoint. CEM is measured with research data, online surveys, observational studies, and the likes.
Challenges of Customer Experience Management[6]
Designing a successful CEM strategy can be a daunting task. Businesses must know their customers, and know them well, in order to get customer experience management right.
- One of the toughest challenges is creating a consistent multi-channel brand experience. Customers interact with your brand online, through customer service, in person, and more. It is crucial that you ensure brand consistency at every point of interaction.
- Another challenge of customer experience management is getting a single view of the customer. Companies get customer data from a multitude of sources, and the trick is to consolidate all of that data into a single view to gain a 360-degree view of the customer. This becomes especially difficult if the data remains siloed.
- Another challenge of customer experience management is personalization. Customers have expectations and are aware that companies have more information about them today than ever before. That translates to customer demand for personalization, and businesses must remember to personalize every interaction. Businesses can succeed at personalization if they add context to their customer focus so they can offer what the customer wants, when the customer wants it.
Overcoming Challenges of Customer Experience Management[7]
- Create consistent experiences with brands across all channels: While customers may be willing to accept different levels of service from different channels, they expect your brand value proposition to stay consistent. But the proliferation of media makes it difficult to guarantee this consistency across all channels.
- Integration of channel and brand experiences: An integrated channel experience is highly desirable but difficult to achieve. The technology, process, management can all become obstacles.
- Consolidate customer data in one view: Having an overview of the customer through interactions, channels, products and time would facilitate the creation of unified and coordinated customer communications. Departmental silos, fragmented data and inconsistent processes make this challenge insurmountable.
Benefits of Customer Experience Management (CEM)[8]
- CEM can help towards giving everyone in an organisation a single customer view (SCV), the benefits of which include improved customer service, better customer retention, higher conversion rates and hopefully an improved overall customer lifetime value (CLV).
- Providing great customer experiences can help create loyal brand advocates, who are more likely to spread positive word of mouth about your brand.
- Strengthening brand loyalty can then lead to higher spend. Brand advocates will often spend more, purchase more items and return to the business more frequently.
- Ensuring your customers understand why you’re different from your competitors and that you’re a unique entity will help ensure they continue interacting with you.
- CEM can help businesses identify customers who are likely to stray, therefore they can be offered incentives to stay loyal. A freebie here or there is certainly worth it for the promise of repeat custom.
- CEM is much cheaper than standard market research. Market research can be lengthy and costly to develop, particularly as they are often incentivized. CEM surveys however are short and to the point.
See Also
Customer Experience Management (CEM or CXM) designs and reacts to customer interactions to meet or exceed customer expectations, increasing customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy. CEM involves understanding the entire customer journey, from initial awareness and engagement through purchasing and post-purchase support. By focusing on the customer's experience, businesses aim to build a loyal customer base that is more likely to repeat business, share positive word-of-mouth, and have a higher lifetime value. Effective CEM leverages data and insights from various touchpoints across the customer journey to create personalized, seamless experiences.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Discussing the tool used to visualize the complete customer journey, identifying all the touchpoints where customers interact with the brand, which is crucial for effective CEM.
- Voice of the Customer (VOC): Explaining the process of capturing customers' expectations, preferences, and aversions across all touchpoints and phases of the customer lifecycle, a key component of CEM.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Covering the metric used to gauge the loyalty of a company's customer relationships based on their likelihood to recommend the brand to others, often used within CEM to measure success.
- Customer Feedback: Discussing the importance of gathering and analyzing customer feedback to understand their experience and identify areas for improvement.
- Omnichannel Strategy: Explaining the seamless and cohesive customer experience approach, regardless of channel or device. An omnichannel strategy is vital for CEM, ensuring consistent experiences across physical and digital touchpoints.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Covering the strategies and technologies that companies use to manage their interactions with current and potential customers, supporting CEM by centralizing customer data and interactions.
- Customer Loyalty Programs: Discussing programs designed to encourage repeat business by rewarding loyal customers, which can enhance the overall customer experience and contribute to a positive CEM strategy.
- Personalization: Covering the customization of products, services, and communications to the individual needs and preferences of customers, a key tactic in CEM for improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Service Design: Explaining the activity of planning and organizing a company's resources to improve the employee's experience, and thus indirectly, the customer's experience. Service design is a critical aspect of CEM.
- Emotional Connection: Discussing the development of deep, emotional relationships between customers and brands, which can significantly impact customer loyalty and advocacy, a desired outcome of effective CEM.
- Brand Experience: Covering the sensations, emotions, perceptions, and behavioral responses evoked by brand-related stimuli. Brand experience is closely related to CEM, focusing on the holistic perception of the brand by the customer.
- Data Analytics: Discussing the techniques to examine, clean, transform, and model data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making in CEM.
References
- ↑ Defining Customer Experience Management (CEM Gartner
- ↑ Definition - What is of Customer Experience Management (CEM)? Medallia
- ↑ Why customer experience management is important SAS
- ↑ CXM Management Techniques Techtarget
- ↑ Customer Experience Management Vs. Customer Relationship Management Survey Sparrow
- ↑ What are the Challenges of Customer Experience Management? NGData
- ↑ What do marketers need to do to overcome the challenges of customer experience management? Advantage Media
- ↑ What are the Benefits of quality CX and CEM? EConsultancy