Digital Trust
What is Digital Trust?
Digital Trust is the confidence that users have in the ability of people, technology, and processes to create a secure digital world. Digital trust helps build reliability and confidence between companies and users. It assures safety, privacy, security, reliability, and data ethics with online programs or devices. Users are more likely to choose a company that is trustworthy than one that is unreliable. Companies focus on winning digital trust from their customers in order to create greater confidence in security and reliability among customers.
In the context of information technology and the business use of consumer data, digital trust is the confidence placed in an organization to collect, store and use the digital information of others in a manner that benefits and protects those to whom the information pertains. Digital trust is the currency of today and will be central to defining the high performers of tomorrow.[1]
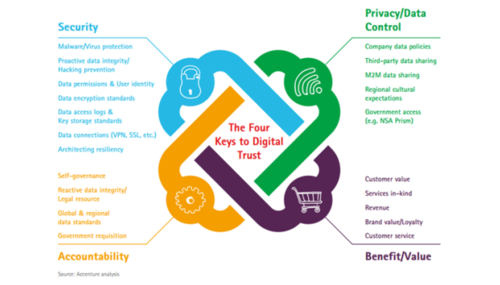
Accenture has defined four keys to digital trust from a consumer perspective. Each dimension must be satisfied to establish consumer trust in a specific brand:
Security—Protecting information against theft or unauthorized use.
Privacy/Data control— Controlling who gains legal access to personal information, when they get access, and what they can do with it.
Benefit/Value— Offering reciprocal benefits that are directly relevant to the data businesses are collecting and storing. This means that the data being collected is clearly necessary for providing the service.
Accountability—Taking responsibility for the misuse and incorrect information and ensuring corrective action.[2]
The Digital Trust Model
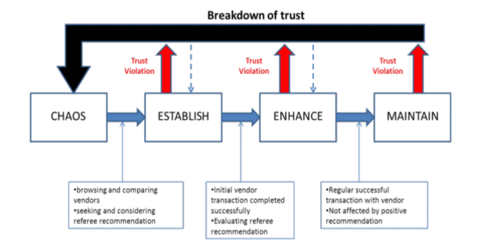
The determinants of an individual's degree of trust are a function of one’s perception of risk, which stems from various contextual factors (the social environment through norms, values, and conventions), the quality and quantity of information available, and one’s natural disposition to trust. In general, while context and disposition to trust are stable over time, the quantity and quality of information, which establish whether the individual believes that s/he is in a risky or uncertain situation, vary over time. Trust is therefore a dynamic process marked by various phases of trust development. The Online Trust Building Model (figure below) proposed by Head and Hassanein, identifies four phases in this process
This model shows consumer behavior at each phase, as well as the consumer's interactions with two other transaction partners: the vendor, obviously, and a third party. This third party provides sources of external information to the consumer: it could be a friend, a consumer website, an advertisement, or even a public certification. Therefore each phase is marked by a distinct mechanism for building and structuring consumer trust. At each phase, the consumer must decide whether or not to engage in a transaction, and at each phase, he must evaluate whether or not to continue this relationship. In sum, he accumulates experience and information that will gradually reduce his ignorance as he moves from the initial phase to the final phase.
The four phases are as follows:
The chaos phase: this is the initial phase of the model where the consumer is in a situation of radical uncertainty.
The trust establishment phase: Having issued the desire to consume a product or service, the consumer will seek to reduce his ignorance. He will seek signals showing that the vendor merits his trust. This is the phase in which the consumer compares vendors and/or products and, in particular, will seek the advice of third parties.
The enhancement phase: The consumer has successfully completed his first transaction. He is therefore able to evaluate the consequences of this decision with a bit more precision. This first experience is determinant, and conditions the continuity of the relationship with the vendor. Starting with this phase, the consumer is able to judge the quality of the advice from the third party, and he is no longer in a situation of radical uncertainty.
The maintenance phase: At this point, the consumer has conducted several successful transactions. His ignorance has been significantly reduced, and he has broad experience on the subject: previous interactions with the vendor drive this trust. Because of this, the third party no longer has any real impact on the consumer's decision-making process, and there is a strong chance that he will engage in a long-term relationship with the vendor.[3]
How can Businesses Establish Digital Trust
- Understand the major trust factors
- Societal Trust: The level of trust that exists between individuals, organizations, institutions, and governments in a given economy.
- Digital Trust: The level of trust people have in digital services such as websites, applications, and platforms used for financial transactions or other sensitive information exchanges.
- Relationship Between Societal and Digital Trust: How well societal trust translates into digital trust; how effective it is at ensuring the safety of personal data online or preventing frauds/scams from occurring on digital platforms?
- Factors That Can Affect Digital Trust: These include issues such as privacy policies not being clearly outlined or understood by users, lack of transparency around data collection practices by companies/organizations/institutions, etc., cyber attacks on websites resulting in data breaches or stolen identities, etc., lack of legal frameworks to protect consumer rights online, etc.
- Build a strategy for building digital trust
- Understand the rapid developments that take place in the digital environment.
- Reduce misunderstandings and embrace better technology to establish digital trust with customers.
- Ensure that customers are satisfied with entrusting their data to you by taking steps towards building a future that is digitally trusted by everyone involved in your business model.
- Dedicate time and effort to understanding cybersecurity measures that will help build digital trust between consumers and service providers alike, starting today!
- Implement C3 metrics
- Implementing C3 metrics can help establish digital trust by providing a comprehensive view of the website's credibility, transparency, and consistency.
- By identifying areas for improvement and creating an action plan based on this information, website owners can increase their trust score and improve the quality of their content. This will help build trust with visitors as they are able to see that the website is taking steps to provide accurate information and follow best practices for digital content creation.
- Leverage Best Practices for TLS/SSL certificates
- Understand the purpose of TLS/SSL certificates: TLS/SSL certificates provide secure encryption and identification for websites, emails, and other digital services.
- Consider your needs: Before deciding on a certificate type, consider your business needs and what level of security is required for your website or email service.
- Evaluate providers: Review the latest Best Practices Guide for TLS/SSL Certificate Providers to ensure that you are choosing a reputable provider that follows industry standards and best practices in security and trustworthiness.
- Select an appropriate certificate type: Based on your needs, choose an appropriate certificate type from DigiCert’s wide range of options such as single domain certificates, wildcard certificates, multi-domain certificates, post-quantum certs, PSD2 certs, code signing certs, s/mime certs for email, etc.
- Purchase the certificate: After reviewing all available options with the provider of choice, purchase a suitable certificate from them.
- Develop an identity management strategy based on 3 types of authentication
- Identify the types of authentication that should be used for your identity management strategy. These should include Trusted & Secure Identities, Trusted & Secure Email (S/MIME), Trusted & Secure Network Devices, Trusted & Secure Network Access (VPNs), and Trusted & Secure Smart Cards.
- Ensure that all services are based on Privacy By Design principles to give users total control over their digital identity data and make it easy for them to access it in an intuitive way no matter what device or ecosystem they are using.
- Make sure all solutions are interoperable so they work seamlessly no matter where someone is located globally and can be applied across multiple use cases with open industry standards such as blockchain technology if necessary for scalability purposes
- Prepare for PSD2 compliance
- Understand the requirements of PSD2: Read up on the regulations set out by PSD2 to understand what your business needs to do in order to comply with the new legislation.
- Identify your data providers: Decide which third-party providers you rely on for data, such as payment processors or cloud storage services, and ensure that they are PSD2 compliant before connecting them to your systems.
- Create a compliance plan: Develop a detailed plan outlining how your business will meet all of its compliance obligations under PSD2, including how you will manage third-party access rights, and monitor transactions for fraud risk and breach notification requirements.
- Implement security measures: Ensure that all systems handling customer data are securely encrypted end-to-end and that any third parties granted access also have appropriate security measures in place to protect customer information at all times per the GDPR ruleset (if applicable).
- Test systems regularly: Conduct regular tests of both internal and external procedures related to PSD2 compliance so that any issues can be identified quickly before they become an issue for customers or regulators.
- Manage emerging technologies such as IoT, OT, blockchain, and 5G securely
- Understand the risks and threats associated with emerging technologies such as IoT, OT, blockchain, and 5G.
- Implement security measures such as encryption techniques, secure data transmission methods, and strong passwords to protect your data from unauthorized access or exploitation.
- Set up threat detection systems that monitor networks for suspicious activities or anomalies that could indicate a potential breach in security measures or vulnerability in the system being used by the business.
- Ensure that all employees are trained on best practices when it comes to handling sensitive information so they can avoid accidentally leaking it via emails or other types of communication channels they use with clients and partners etc.
- Deploy firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), antivirus software, malware protection software etcetera to safeguard against cyber-attacks from hackers who may try to exploit vulnerabilities in your network’s security architecture.
- Optimize website performance with metaverse and web3 technology
- Optimizing website performance with metaverse and web3 technology can help establish digital trust by improving the user experience. By reducing page load times, optimizing web accessibility, and providing secure payment options, website owners can build trust with their customers.
- By implementing these types of digital trust optimizations, site visitors will feel more confident about visiting a site. They will be more likely to engage with it and make purchases if they feel secure in their transactions or interactions with a website owner.
Benefits of Having Digital Trust
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Having digital trust increases customer satisfaction by providing customers with the convenience of being able to do business from anywhere and at any time. By offering a secure and reliable platform, businesses can build customer trust which in turn leads to increased conversions and increased customer satisfaction.
- Increased Efficiency: Having digital trust allows businesses to build relationships with their customers. This builds trust, increases customer loyalty, and encourages them to make more purchases. This leads to an increase in efficiency as businesses can gain insight into customer preferences and tailor their offerings accordingly. It also helps them coordinate with customer financial data seamlessly for a better user experience.
- Improved Security: Having digital trust improves security because it encourages companies to be more aware of cyber risks and take the necessary steps to protect their customers' data. Promoting trust in online platforms helps to ensure that customer's data is safe and secure, reducing the likelihood of security breaches.
- Increased Profits: Having digital trust can increase profits because it builds customer trust, increases conversions, and helps you offer your services at an affordable price. By building customer trust, you will be able to increase your sales as customers feel more comfortable doing business with you. Additionally, by offering the service at an affordable price, more people will be able to take advantage of it which will lead to increased profits in the long run.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation: Having digital trust can enhance brand reputation by providing a platform for e-SMEs to build trust and engage with customers. Building trust through social media can help increase consumer patronage, drive sales, and create long-term success for enterprises that rely on e-commerce. It also enables greater transparency, consumer empowerment, and online activism which can lead to positive effects if used correctly.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: Having digital trust can increase customer loyalty by providing customers with the peace of mind that their data is safe and secure. This trust can be established through strong cybersecurity measures and a track record of maintaining high standards when it comes to data protection. By building digital trust, companies are able to build stronger relationships with their customers which will lead to increased loyalty. Customers who feel confident in the security of their personal information are more likely to continue doing business with a company they trust than switch over to one that may not be as secure or up-to-date with its cybersecurity measures.
- Greater Collaboration Possibilities: Having digital trust allows enterprises, small and medium businesses, governments, technology alliances, and consortia to easily integrate customer financial data for seamless coordination. This increases the possibilities for collaboration as parties can easily share information without the risk of data breaches or loss of confidentiality.
- Increased Efficiency of Processes: Having digital trust allows businesses to easily integrate customer financial data, assure code integrity, automate software signing workflows, centralize key and permission management, simplify compliance processes, and enforce compliance. This reduces the time and effort needed to manage these processes while ensuring they are carried out correctly. It also increases efficiency by reducing the risk of mistakes or inconsistencies in the process.
- Increased Ability to Adapt to Change: Having digital trust helps to adapt to change because it provides an assurance of security and reliability. This gives users the confidence they need to engage in online transactions without fear of cyber risks or data breaches. By building trust in their digital environments, technology providers can ensure profitable growth while maintaining user loyalty and reducing friction in their services. Additionally, having a trustworthy framework for creating digital relationships encourages innovation and helps companies stay ahead of the competition.
- Improved Data Security and Privacy: Having digital trust improves data security and privacy by ensuring that businesses are up to date with their cybersecurity. Customers are more aware of cyber risks now than ever, which leads them to choose companies they believe can be trusted with their data. Additionally, encryption at the network and data level helps ensure that customers' information remains secure and private.
Challenges of Establishing Digital Trust
- Lack of Understanding of the Concept of Trust: The lack of understanding of the concept of trust is causing problems for digital trust. Traditional models of trust are not flexible enough to meet the demanding requirements of digital interactions due to the high number of different relationships between entities. Furthermore, traditional models do not take into account factors such as speed and agility that are essential in a digital world. Moreover, it is important for enterprises to establish Digital Trust with consumers, shareholders, partners, vendors, and governing bodies - but this cannot be achieved if all parties do not have an understanding of what constitutes trustworthy behavior in a digital context.
- Lack of Cybersecurity Measures: The challenges of establishing digital trust without cybersecurity measures include:
- Increased risk of data breaches, which can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and other damage.
- Confidence in the company may be diminished if they are known to have had security issues in the past.
- Loss of customers due to a lack of trust in the brand's ability to protect their data and keep it private.
- Slow response time due to a lack of automation that would otherwise help reduce errors caused by human error or negligence.
- Lack of Transparency in Data Collection and Usage Practices: Lack of transparency can affect the establishment of digital trust by making it difficult for consumers to understand how their data is being used. Without transparency, customers may not be aware if their personal information is being shared with third parties or used in ways they do not agree with. This lack of transparency can lead to a loss of trust between companies and their customers, as consumers may feel that their data is being exploited without their knowledge or consent. Without trust, it becomes difficult for companies to build successful relationships with consumers in the digital world.
- Lack of Authentication Methods: The challenges of providing authentication methods for digital trust include:
- Securing the device from malware and other threats.
- Protecting personal, sensitive data shared on the device with encryption.
- Ensuring that the device has a secure connection to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Providing two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA) methods to prevent unauthorized access to accounts.
- Vulnerability to Cyberattacks: Establishing digital trust mitigates vulnerability to cyberattacks by providing customers with confidence in the company and its services. This encourages them to share more personal information online, which increases their vulnerability to cyberattacks. By focusing on managing privacy and cyber risks, companies can reduce their customers' vulnerability to cyberattacks by ensuring that their systems are up-to-date with the latest security measures. Additionally, machines can automate the decision process by calculating the level of confidence in a program or system, further reducing any potential vulnerabilities that may exist.
- Inadequate Data Security Measures: Inadequate data security measures can have serious consequences for establishing digital trust. Data breaches have become increasingly common and costly, resulting in increased identity fraud. This poses a significant risk to individuals, businesses, and governments alike as personal information can be easily accessed by criminals without any trace of its original owner. Furthermore, the cost of repairing damage caused by data breaches can be high as organizations are often held liable for financial losses incurred due to identity theft or fraud. Finally, a lack of trust in digital systems may deter individuals from using online services which rely on personal data such as banking applications or healthcare providers’ websites.
- Complexity of Systems: The complex nature of systems and networks can make it difficult for businesses to keep up with the latest cybersecurity practices. This can lead to vulnerabilities in the system that can be exploited by cybercriminals. As a result, customers may lose their trust in these companies due to security breaches surrounding their data or other cyber risks. This can have a significant impact on customer loyalty and revenue as consumers become more aware of cyber threats and choose companies they believe are capable of securing their data.
- Incomplete or Inaccurate Information: The challenges of establishing digital trust when information is incomplete or inaccurate include:
- Increased risk of data breaches and identity fraud.
- Difficulty in verifying the legitimacy of websites, accounts, and other digital services.
- Inaccurate information makes it difficult to provide personalized customer service or tailored offerings.
- Lack of trust from customers who may have concerns about the accuracy and security of their data.
- Lack of Commitment to Trust-Building Measures: When establishing digital trust, it is important to have a commitment to trust-building measures. Without such commitment, it is difficult to measure and compare digital trust across countries or establish effective regulations that ensure the safety of personal data. Without a commitment to trust-building measures when establishing digital trust, users may be less likely to feel secure about the use of their data and their online activities. This can result in a loss of confidence in companies that handle personal information and an overall decrease in usage rates for digital services. Additionally, without effective regulations around data protection laws or corporate trust-building strategies, there is no guarantee that personal data will be kept safe from cyberattacks or other malicious threats online.
- Unwillingness to Share Information: The challenges of establishing digital trust when information is unwilling to be shared include:
- Lack of transparency in operations and activities of the company.
- Inability for customers to have access to their personal data or control over its use.
- Decrease in customer confidence and trust due to lack of information-sharing practices.
- Reduction in customer satisfaction due to a lack of personalized experiences related to their data usage.
See Also
References