Enterprise Data Integration (EDI)
What is Enterprise Data Integration (EDI)?
Enterprise Data integration (EDI) is the broad set of technologies that help combine, or integrate two or more data sets. EDI typically involves merging data from disparate systems and delivering that combined data in such a way that it can be manipulated and analyzed to support information management activities, such as business intelligence or reporting.[1]
Enterprise data integration can be performed in many ways. One common method is to build a central corporate data warehouse and then funnel in information from various points within the network or from other business operations. For instance, data could enter the data warehouse through a set of middleware applications or through human data entry. Staffers might take data from mailing lists or written customer surveys and integrate them into the data warehouse. Moreover, data may come in automatically through software setups, for instance, from a customer's mobile phone or from a call center environment. One of the issues with enterprise data integration is that companies tend to have different kinds of data in radically different formats. Part of enterprise data integration and enterprise data management is handling sets of unequal data. Different kinds of data include structured data, formatted in easy database table designs, and unstructured data, which is often composed of raw text or raw data sets that are not formatted for database use. An enterprise data integration plan often provides solutions on not only how to integrate all of this data, but also how to make it readable and useful for the business. New technologies accommodate more handling and manipulation of relatively unstructured data sets.[2]
The Value of Enterprise Data Integration[3]
Almost every business initiative calls upon your IT organization to access, integrate, and deliver data. Given that data is everywhere — on-premise, in the cloud, in multiple disparate systems, and in many different formats — accessing data alone is no easy trick. It then has to be cleansed, aggregated, and validated and put into a form that is meaningful to the applications and users who need it. Enterprise data integration empowers your IT organization to access all your fragmented data, create an accurate and consistent view of core information assets, and easily leverage these assets across the enterprise to drive business decisions and operations. Unlike application integration, which focuses on transaction management and process integration, data integration resolves the complex issues that arise out of data fragmentation. In today’s stringent regulatory environment, data needs to be governed properly. Companies must track and document where their data came from, how it has changed, and who has changed it to meet audit requirements. And the security of data must be ensured throughout the whole process. IT organizations are using data integration in many different ways to drive business value. They’re implementing real-time reporting and analysis to optimize minute-by-minute operational, as well as strategic, decisions. They’re migrating data into new applications or implementing master data management. Data integration is also used for big data analytics to gain customer insights and competitive advantages.
A Unified Approach to Enterprise Data Integration (See Figure 1.)[4]
To effectively manage data integration across the enterprise, organizations need to look at the process holistically, considering not only technology but also architecture and the organizational approach to data integration.
- Technology: Enterprise Data Integration Platform: To support multiple projects with consistency and maximum reuse, to interoperate within dynamic IT environments, and to ensure robust data governance, organizations need a single, unified enterprise data integration platform that offers:
- Broad access to all enterprise data, regardless of type, structure, or source — from mainframe and midrange systems to XML documents and spreadsheets
- An open, platform-neutral architecture designed for ever-changing, heterogeneous IT environments
- A single, unified architecture to simplify and accelerate development, deployment, and maintenance
- Enterprise-class security, scalability, reliability, and availability
- A shared services approach based on metadata and open standards for transparency, interoperability, and flexibility
- Architecture: Service-Oriented Architecture
Many IT organizations are adopting service-oriented architecture (SOA), and data integration has an important role to play in that architecture. To increase business agility through loose coupling and reusability of data assets, applications, and processes must be able to access business-relevant data — wherever it resides, in whatever form required, whenever it’s needed — consistently and accurately. To support SOA, organizations need a data integration platform that delivers shared data services, defined by metadata, via open standards to allow easy interoperation with the rest of the IT architecture.
- Approach: Integration Competency Center
Integration Competency Centers (ICCs) have emerged as a best practice for enterprise data integration. ICCs are an organizational approach designed to increase agility and reduce implementation costs by promoting reuse, sharing best practices and resources, and establishing common processes and standards for integration. ICCs facilitate cross-enterprise collaboration and coordination for global IT teams, including both internal and external resources such as systems integrators and outsourcers. While many organizations are migrating to an enterprise-wide approach to data integration, almost no one can afford a high-risk, “big bang” implementation. It is critical that data integration evolves over time, with an incremental rollout focused on delivering urgent business requirements now while laying the foundation for an enterprise-wide data integration infrastructure for the long term.
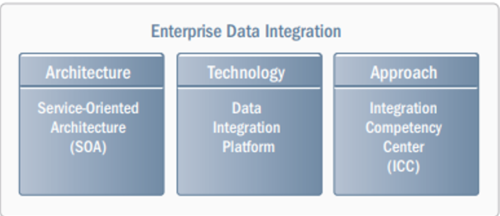
Figure 1. source:Intel
Enterprise Data Integration (EDI) Initiatives[5]
- B2B integration: IT departments are challenged with providing business-to-business integration (B2Bi) solutions to meet their company’s needs. Replacing a ‘spaghetti infrastructure’ with modern enterprise B2B integration reduces complexity, increases flexibility, and drives reliable, efficient business exchanges.
- Cloud integration: Smart use of cloud computing can be a way to increase your competitiveness and control your IT spend. Cloud integration supports your critical B2B integration processes in the cloud, as well as collaboration with mobility, file distribution, and document sharing.
- Big data integration: Using an enterprise integration platform with integrated big data movement solutions, organizations can seamlessly flow an ever-growing volume of information to a wide variety of big data applications, ensuring reliability, business value, and service continuity.
- Application integration: Companies must enable future initiatives via a sustainable application integration architecture. This foundation will help drive operational efficiency and customer satisfaction, while also lowering the total cost of ownership.
See Also
References
Further Readin =
- A Roadmap to Enterprise Data Integration IBM
- Enterprise Data Integration Guide Pitney Bowes
