Quality Competitive Index (QCi) Model
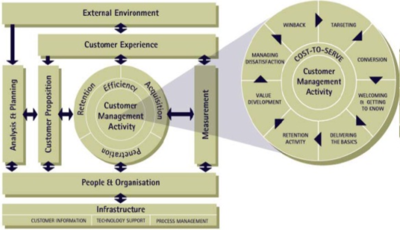
The Quality Competitive Index Model (QCi model) is a customer management model. The QCi model represents the different activities that organizations should perform to acquire and retain customers. This model describes the technology usage in the assisting process performed by people. The QCi model discusses the customer relationships process without the external environment, and that process affects the organisation’s planning activities. Customer experience has an impact on customer proposition, measurement and customer management activity. The focus of the QCi model is the customer, not the CRM process itself. Customer management has three distinct factors; namely, acquisition, retention and penetration, in order to be successful in the CRM implementation strategy (Buttle 2009). The supporting elements are people and organization, while these are affected by customer experience and external environment (Grazdane, 2013).
Described as a customer management model rather than a customer relationship model, the Quality Competitive Index model focuses on three main activities: acquisition, retention, and penetration. The QCI model starts with the customer’s external environment at the top—their pain points, business goals, and other factors will affect whether they are ready to buy or interact with your sales team, which in turn impacts the customer experience. The customer experience then affects customer proposition (what you offer the customer) and customer management activities. As you can see from the magnified version of the inner circle, many activities are involved to acquire and retain customers. The QCI model also considers the people and technology involved with keeping this whole system going. Although QCI has replaced the word “relationship” in CRM, this model still starts and ends with people.[1]
source: Wikimemoire
The model is made up of eight elements:[2]
- Analysis and planning: The process of customer management starts with an analysis of customer behaviour and planning to develop the value of the company. The business can then plan to design customer management activities for engagement. The analysis and planning are based on the REAP of customer management activities, which is Retention, Efficiency, Acquisition, and penetration (Starkey & Woodcock, 2002).
- Proposition: The ‘analysis and planning’ is the base of customers and their needs, leading to effective planning. The next element of the QCI model is coming up with the ‘proposition’. The proposition includes processes that can attract new customers, which depends upon the evaluation of the needs of the customers in the previous step. The segmentation of customer needs to form the base for different propositions. This further helps to derive enhanced customer experience and engagement strategies (Eko, 2014).
- Information and technology (IT): Information and technology is an enabler in managing customers as well as customer-related data. Technology helps deliver critical information related to the customers to the organization and vice-versa. Thus Information and Technology systems need to be updated constantly to effectively manage customers and people, as per the changing needs of both entities. This element includes important sub-processes such as:
- sourcing customer information,
- planning and analyzing information,
- management of quality and review of technology systems for replacement and renewal (Grazdane, 2013).
- People and organization: A business cannot manage customers without a robust team of customer relationship executives. As per the QCI model, the business needs to develop and maintain a responsible team for:
- managing customer requests,
- feedback,
- queries and concerns.
Also, businesses need to establish a system for role identification, task segregation, and conduction of gap analysis for training (Ahmadi, Osmani, Ibrahim, & Nilashi, 2012).
- Process management: Coordinating marketing, sales, and customer support are essential for customer management, as per the QCI model. According to this model, a consistent process which provides continuous management support to customers and identifies shortcomings is important. This is the importance of ‘process management’ element (Shukla & Pattnaik, 2019).
- Customer management activity : This element of the QCI model has three sub-categories of activities, governed by efficiency in all (Hollensen, 2010):
- Acquisition: It includes targeting of customers and getting to know their needs for developing products/ services. The execution of this activity involves effectively putting across the business’s propositions after identifying the customers and their needs.
- Penetration: This sub-activity includes understanding the customers through the collection of information, which can be then processed to understand how to best create a valuable customer base. The activities involve simple messages to welcome customers to the organization, provide an understanding of the business activities and helping customers connect with the business goals.
- Retention: This can be done through value development, as well as through win-back strategy. This strategy serves as a retention process and an acquisition process.
- Measuring the effect: This element involves the assessment of the process to ensure continuous improvement of the customer management process. The measurement also helps understand the level of performance of individuals and teams on their roles and creates benchmarking on customer management success (Srivastava, 2013).
- Customer experience: Addition of customer experience to the customer management mix provides an additional layer of measurement. It bridges gaps in customer perception and customer enhancement processes (Grazdane, 2013). The QCI model provides a detailed process of how to establish a connection with customers, cordially interact with them, and customer management. The model also accepts the role of external environment in impacting customer experience and provides an understanding of how to counteract any negative aspects by making sure the foundation of the CRM processes.
See Also
- Total Quality Management (TQM): An extensive and structured approach to organizational management that seeks to improve the quality of products and services through ongoing refinements in response to continuous feedback.
- Benchmarking: The process of comparing one's business processes and performance metrics to industry bests or best practices from other companies.
- Balanced Scorecard (BSC): A strategic planning and management system used to align business activities to the vision and strategy of the organization, improve internal and external communications, and monitor organizational performance against strategic goals.
- Six Sigma: A set of techniques and tools for process improvement that aims to improve the quality of the output of a process by identifying and removing the causes of defects and minimizing variability in manufacturing and business processes.
- SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats): A framework for identifying and analyzing the internal and external factors that can have an impact on the viability of a project, product, place, or person.
- Porter's Five Forces: A model that identifies and analyzes five competitive forces that shape every industry and helps determine an industry's weaknesses and strengths.
- ISO 9001: Part of the ISO 9000 family of quality management standards, ISO 9001 specifies requirements for a quality management system when an organization needs to demonstrate its ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
References
- ↑ What is the Quality Competitive Index (QCi) Model LucidChart
- ↑ What are the elements of Quality Competitive Index (QCi) Model ProjectGuru
