Difference between revisions of "Consumer Confidence"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
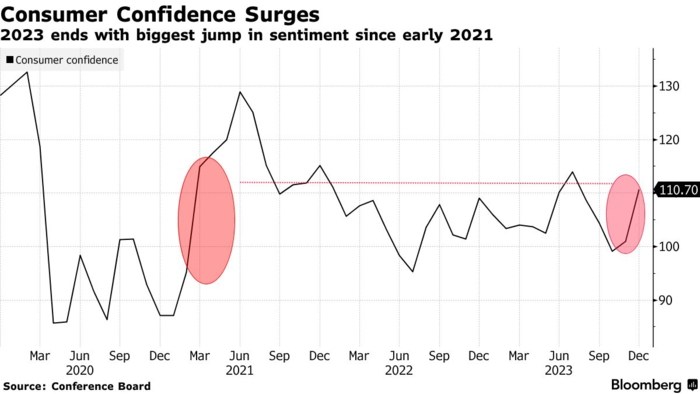
| − | [[File:Consumer Confidence.png|700px|Consumer Confidence]] | + | [[File:Consumer Confidence.png|700px|Consumer Confidence]]<be /> |
| + | Source: Bloomberg | ||
Revision as of 16:31, 8 May 2024
What is Consumer Confidence? Consumer confidence refers to the degree of optimism consumers feel about the overall state of the economy and their personal financial situation. It measures how confident people are about their ability to find and retain good jobs, their perception of their financial situation, and their readiness to make significant purchases. High consumer confidence indicates that consumers feel positive about their financial security and are more likely to spend money, which fuels economic growth.
Role and Purpose of Consumer Confidence
The role of consumer confidence is to serve as an economic indicator that provides insights into the general economic health of a country. It is used to:
- Predict Consumer Spending: Consumer confidence is often a reliable indicator of future consumer spending and economic activity.
- Guide Economic Policy: Governments and central banks use changes in consumer confidence to help decide on fiscal and monetary policies.
- Inform Business Decisions: Businesses use consumer confidence data to make strategic decisions about investments, hiring, and inventory management.
Usage of Consumer Confidence
Various stakeholders widely use consumer confidence data:
- Economic Analysts and Policymakers: To gauge the likely future of the economy and adjust economic policies accordingly.
- Investors and Financial Analysts: To make informed decisions about investments in stock markets, real estate, and other sectors.
- Business Leaders: To plan product launches, marketing strategies, and expansions based on expected consumer spending patterns.
Importance of Consumer Confidence
Consumer confidence is important because it:
- Drives Economic Activity: As a leading indicator, it can predict the expansion or contraction of the economy based on consumer spending, which constitutes a significant part of economic activity in many countries.
- Signals Economic Recoveries or Recessions: Significant changes in consumer confidence can precede economic recoveries or downturns, making it a crucial measure for economic forecasting.
- Impacts Market Sentiment: Fluctuations in consumer confidence can affect stock markets and investment climates, influencing the financial decisions of businesses and investors.
Benefits of Monitoring Consumer Confidence
Monitoring consumer confidence offers several benefits:
- Proactive Policy Making: Allows governments and monetary authorities to implement preemptive measures to avert economic downturns or overheating situations.
- Strategic Business Planning: Helps businesses more effectively plan their growth strategies, budget allocations, and marketing efforts.
- Consumer Insights: Provides deep insights into consumer behavior and trends, which are crucial for tailoring products and services to meet market demands.
Examples of Consumer Confidence Measures
- Consumer Confidence Index (CCI): A measure provided by The Conference Board in the United States, which assesses consumers' optimism on the state of the economy through their saving and spending activities.
- University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index: Another major index in the U.S. that measures consumer sentiment, based on surveys that ask Americans about their personal financial situations and the short-term/long-term state of the economy.
- GfK Consumer Confidence Barometer: Used in the United Kingdom to gauge personal financial expectations and general economic outlook among British consumers.
Consumer confidence is a vital economic indicator that helps in understanding the economic outlook from a consumer perspective. It influences a wide range of economic policies and business strategies. Consumer confidence reflects the overall health of the economy as perceived through the lens of consumer sentiment and behavior.
See Also
- Economic Indicators: Explaining other key metrics that measure economic health, such as GDP, unemployment rates, and inflation, and how they interrelate with consumer confidence.
- Business Cycle: Discussing the phases of economic expansion and contraction and how consumer confidence can be both a predictor and a result of these phases.
- Consumer Spending: Detailing how consumer confidence directly influences consumer spending habits, which in turn affects economic growth.
- Recession: Explaining the economic condition of a recession, its causes and effects, and the role consumer confidence plays in deepening or alleviating it.
- Inflation: Covering how inflation impacts consumer purchasing power and their confidence in the economy.
- Monetary Policy: Discussing how central banks use monetary policy to manage economic stability and growth and how this influences consumer confidence.
- Market Research: Explaining how surveys and other market research tools measure consumer confidence and predict future economic conditions.
- Retail Economics: Linking to how changes in consumer confidence can affect the retail sector, influencing everything from stock levels to pricing strategies.
- Consumer Behavior: Discussing the psychological factors that influence consumer confidence and decision-making in economic contexts.
- Financial Market: Detailing how consumer confidence can influence financial markets, affecting everything from stock prices to investment strategies.