Difference between revisions of "ITIL Service Lifecycle"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
| + | == ITIL Service Lifecycle Stages<ref>The Goals, Processess and Functions of the ITIL Service Lifecycle Stages [https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-ITIL-service-lifecycle-6-The-processes-and-functions-proposed-by-the-ITILR-V3-2011_fig8_305953563/download Carolina Ferreira, Andrea Nery,Placido Rogerio Pinheiroa]</ref> == | ||
The ITIL version 3 proposes the concept of service life cycle containing stages, each with different goals, as follows: | The ITIL version 3 proposes the concept of service life cycle containing stages, each with different goals, as follows: | ||
*Service Strategy - SS: to understand the company's strategy and define how IT services will meet the strategic objectives of the organization; | *Service Strategy - SS: to understand the company's strategy and define how IT services will meet the strategic objectives of the organization; | ||
| Line 48: | Line 49: | ||
**Application Management Function | **Application Management Function | ||
*Continual Improvement of Service | *Continual Improvement of Service | ||
| − | **Seven Steps to the Improvement Process | + | **Seven Steps to the Improvement Process |
| + | |||
| + | == How to Revive the Service LifeCycle<ref>How to revive the Service Lifecycle [https://blog.itil.org/2012/05/dont-forget-the-service-lifecycle/ Blog.ITIL.Org]</ref> == | ||
When the Service Lifecycle concept was introduced to the ITIL framework some years ago, the IT Service Management community took a big step forward: ITIL Best Practice turned from a rather isolated process-driven view (ITIL V2) into a more holistic, service lifecycle-oriented approach (ITIL V3), something that didn’t fundamentally change in the 2011 edition. In a nutshell, it’s simple as that: IT services, delivering value to clients, pass through a lifecycle from service structuring, design, transition, operations (where the service is delivered to the client) and finally continual optimization. The role of ITSM processes is to support the Service Lifecycle. Just to give you a practical example: Change Management, which supports mainly the Service Transition Lifecycle, makes sure that Changes to Services are introduced into Operations in a controlled manner and with minimal risk. | When the Service Lifecycle concept was introduced to the ITIL framework some years ago, the IT Service Management community took a big step forward: ITIL Best Practice turned from a rather isolated process-driven view (ITIL V2) into a more holistic, service lifecycle-oriented approach (ITIL V3), something that didn’t fundamentally change in the 2011 edition. In a nutshell, it’s simple as that: IT services, delivering value to clients, pass through a lifecycle from service structuring, design, transition, operations (where the service is delivered to the client) and finally continual optimization. The role of ITSM processes is to support the Service Lifecycle. Just to give you a practical example: Change Management, which supports mainly the Service Transition Lifecycle, makes sure that Changes to Services are introduced into Operations in a controlled manner and with minimal risk. | ||
| − | '''The Service Portfolio is the “backbone” of the Service Lifecycle''' | + | '''The Service Portfolio is the “backbone” of the Service Lifecycle'''<br /> |
[[File:Service_portfolio.jpg|300px|Service Portfolio]]<br /> | [[File:Service_portfolio.jpg|300px|Service Portfolio]]<br /> | ||
| − | + | ||
[[Service Portfolio Management]] and later on [[Service Catalog Management]] are excellent methods to govern your services throughout the Service Lifecycle. The [[IT Service Portfolio|Service Portfolio]] ensures that you as an [[Service Provider|IT Service Provider Organization]] have the right mix of services to meet required business outcomes at an appropriate level of investment. Once these services are in the transition and service operation phase (visible to the client), they are maintained as part of the service catalogue, containing detailed service information. One really useful thing to remember is that whatever [[IT Service Management (ITSM)|ITSM]] process you are discussing in your organization, you always can refer back to the service portfolio and catalog to make sure, that you are still oriented towards the IT services that has to be delivered to your client. | [[Service Portfolio Management]] and later on [[Service Catalog Management]] are excellent methods to govern your services throughout the Service Lifecycle. The [[IT Service Portfolio|Service Portfolio]] ensures that you as an [[Service Provider|IT Service Provider Organization]] have the right mix of services to meet required business outcomes at an appropriate level of investment. Once these services are in the transition and service operation phase (visible to the client), they are maintained as part of the service catalogue, containing detailed service information. One really useful thing to remember is that whatever [[IT Service Management (ITSM)|ITSM]] process you are discussing in your organization, you always can refer back to the service portfolio and catalog to make sure, that you are still oriented towards the IT services that has to be delivered to your client. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Look at ITSM processes from a Service Lifecycle perspective'''<br /> | ||
| + | ITSM processes support the Service Lifecycle. This means that you should always bring an ITSM process into the context of the Service Lifecycle. For Example: The purpose of Event Management, as described in the books, is to detect events, make sense of them and determine the appropriate control actions. This first looks like a pure Service Operation issue (this is also the way it is described in the Service Operations book). However, if you think about it from a lifecycle view, suddenly service design comes into play, because event rule sets first need to be designed in order to enable the detection of events in a meaningful way and these rule sets need to be orientated towards the services you deliver – which makes the connection to the service catalog mentioned earlier. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''ITSM processes are not limited to one Service LifeCycle''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ITSM Processes.png|300px|ITSM processes in the context of the Service Lifecycle]]<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | With the example mentioned earlier it also becomes clear that an ITSM process usually does not belong only to one Service Lifecycle as commonly understood. Probably the reason for this misunderstanding is due to the way the human brains works (knowledge needs to be hierarchical) and the fact that each of the processes is described in one of the Service Lifecycle books (everything else would have been difficult). The graph shown above illustrates the connection between processes and lifecycle very well. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Implement Continual Service Improvement'''<br /> | ||
| + | One additional way to revive the Service Lifecycle view is to implement Continual Service Improvement (CSI) in your IT Service Provider Organization. CSI as a discipline spans over all other Service Lifecycles and makes sure that Services are aligned and realigned towards changed business requirements by implementing improvement actions. CSI reviews and analyzes each lifecycle and makes recommendations to either improve the service quality or to increase the cost efficiency. | ||
Revision as of 21:06, 5 January 2021
ITIL Service Lifecycle is a framework consisting of processes for effectively managing the service lifecycle of any product or service offered by an organization. Although it is an approach for IT Service Management (ITSM), it can be used by any organization irrespective of its size to manage the full lifecycle of not only the IT services but any service that it offers. Service lifecycle helps to improve the service management technique by using five processes to achieve better business performance.[1]
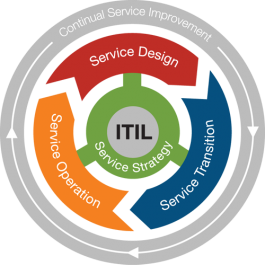
ITIL Service Lifecycle Stages[2]
The ITIL version 3 proposes the concept of service life cycle containing stages, each with different goals, as follows:
- Service Strategy - SS: to understand the company's strategy and define how IT services will meet the strategic objectives of the organization;
- Service Design - SD: to guide the design of IT services to ensure service quality, customer satisfaction and the cost-benefit relationship of the services provided;
- Service Transition - ST: to guide the development of resources for the creation of new services or services in IT operations and ensure that they meet the business needs according to the "strategy" and "design" of the services;
- Service Operation - SO: to provide guidance on how to achieve effectiveness and efficiency in the delivery and support of services, to ensure the value expected by the customer and meet the strategic goals of the company;
- Continual Service Improvement - CSI: to identify results and advise on the improvement of services by joining forces with the Strategy, Design, Transition and Operation Services phases in order to create and maintain the value of services.
The processes and functions proposed by the ITIL® V3 2011 edition for each stage of the service lifecycle, as shown in figure above, are:
- Service Strategy
- Strategy Management Process for IT Services
- Financial Management Process for IT Services
- Service Portfolio Management Process
- Demand Management Process and
- Management of the Relationship with the Business Process
- Service Design
- Design Coordination Process
- Service Catalog Management Process
- Service Level Management Process
- Capacity Management Process
- Availability Management Process
- Management of IT
- Service Continuity Process
- Supplier Management Process
- Service Transition
- Planning and Transition Support Process
- Change Management Process
- Configuration and Service Asset Management Process
- Knowledge Management Process
- Release and Deployment Management Process
- Validation and Service Testing Process
- Changes Evaluation Process
- Service Operation
- Event Management Process
- Incident Management Process
- Request Fulfillment Process
- Access Management Process
- Problem Management Process
- Service Desk Function
- Technical Management Function
- IT Operations Management Function
- Application Management Function
- Continual Improvement of Service
- Seven Steps to the Improvement Process
How to Revive the Service LifeCycle[3]
When the Service Lifecycle concept was introduced to the ITIL framework some years ago, the IT Service Management community took a big step forward: ITIL Best Practice turned from a rather isolated process-driven view (ITIL V2) into a more holistic, service lifecycle-oriented approach (ITIL V3), something that didn’t fundamentally change in the 2011 edition. In a nutshell, it’s simple as that: IT services, delivering value to clients, pass through a lifecycle from service structuring, design, transition, operations (where the service is delivered to the client) and finally continual optimization. The role of ITSM processes is to support the Service Lifecycle. Just to give you a practical example: Change Management, which supports mainly the Service Transition Lifecycle, makes sure that Changes to Services are introduced into Operations in a controlled manner and with minimal risk.
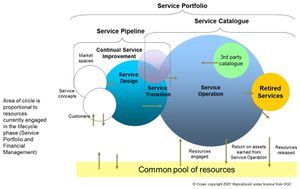
The Service Portfolio is the “backbone” of the Service Lifecycle
Service Portfolio Management and later on Service Catalog Management are excellent methods to govern your services throughout the Service Lifecycle. The Service Portfolio ensures that you as an IT Service Provider Organization have the right mix of services to meet required business outcomes at an appropriate level of investment. Once these services are in the transition and service operation phase (visible to the client), they are maintained as part of the service catalogue, containing detailed service information. One really useful thing to remember is that whatever ITSM process you are discussing in your organization, you always can refer back to the service portfolio and catalog to make sure, that you are still oriented towards the IT services that has to be delivered to your client.
Look at ITSM processes from a Service Lifecycle perspective
ITSM processes support the Service Lifecycle. This means that you should always bring an ITSM process into the context of the Service Lifecycle. For Example: The purpose of Event Management, as described in the books, is to detect events, make sense of them and determine the appropriate control actions. This first looks like a pure Service Operation issue (this is also the way it is described in the Service Operations book). However, if you think about it from a lifecycle view, suddenly service design comes into play, because event rule sets first need to be designed in order to enable the detection of events in a meaningful way and these rule sets need to be orientated towards the services you deliver – which makes the connection to the service catalog mentioned earlier.
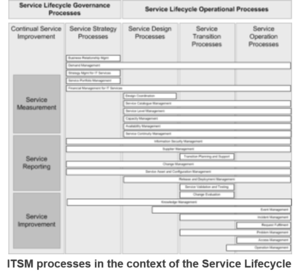
ITSM processes are not limited to one Service LifeCycle
With the example mentioned earlier it also becomes clear that an ITSM process usually does not belong only to one Service Lifecycle as commonly understood. Probably the reason for this misunderstanding is due to the way the human brains works (knowledge needs to be hierarchical) and the fact that each of the processes is described in one of the Service Lifecycle books (everything else would have been difficult). The graph shown above illustrates the connection between processes and lifecycle very well.
Implement Continual Service Improvement
One additional way to revive the Service Lifecycle view is to implement Continual Service Improvement (CSI) in your IT Service Provider Organization. CSI as a discipline spans over all other Service Lifecycles and makes sure that Services are aligned and realigned towards changed business requirements by implementing improvement actions. CSI reviews and analyzes each lifecycle and makes recommendations to either improve the service quality or to increase the cost efficiency.
- ↑ Definition - What Does ITIL service Library Mean? EduCBA
- ↑ The Goals, Processess and Functions of the ITIL Service Lifecycle Stages Carolina Ferreira, Andrea Nery,Placido Rogerio Pinheiroa
- ↑ How to revive the Service Lifecycle Blog.ITIL.Org