Service Portfolio Management
Definition - What is ITIL Service Portfolio Management
ITIL Service Portfolio Management is the governance processes of the service portfolio. The process is one by which a service provider can manage their investments across the service lifecycle by taking into account every service in terms of the business value provided by it. A service provider makes use of service portfolio management to control the entry of any service into the service portfolio by tracking any investment in services through its entire lifecycle starting from the development till the delivery and retired stages.[1]
Service Portfolio Management (SPM) enables Managers to assess the quality requirements and associated costs. The primary goal of Service Portfolio Management is to realize maximum value whilst managing accompanying risks and costs. Five basic questions that need to be answered for Service Portfolio Management to help decide what services clients require:
- Why should a client buy these services?
- Why should a client buy these services from our organization?
- What are the price and charge back models?
- What are our strengths and weakness, priorities and risks?
- How should our resources and capabilities be allocated?
Product Managers play a key role in Service Portfolio Management. Their main responsibility is to manage services as products during their entire lifecycle. Other roles include the co-ordination and focus of the organization as well as owning the Service Catalogue.[2]
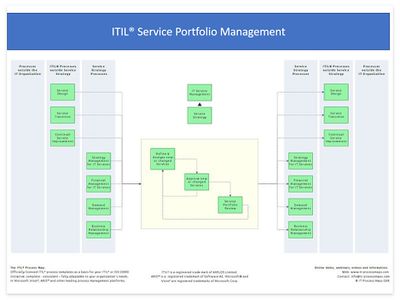
Process Overview of Service Portfolio Management [3]
ITIL V3 introduces the process for managing the Service Portfolio at the strategic level. Following the introduction of the Strategy Management for IT Services process in ITIL 2011, Service Portfolio Management has been re-focused to cover activities more closely associated with managing the Service Portfolio. The process overview of Service Portfolio Management shows the key information flows (see figure below). ITIL 4 refers to Service Portfolio Management as a general management practice, and has renamed the practice to "Portfolio management".
Sub Processes of Service Portfolio Management
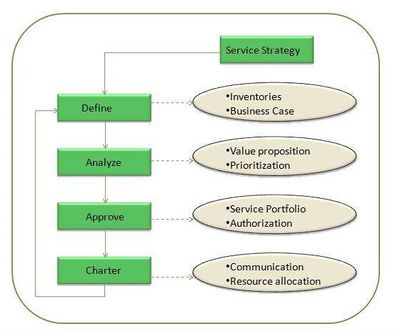
Think of Service Portfolio Management as a dynamic and ongoing process set which includes 4 work methods:
- Define: inventory services, ensure business cases and validated portfolio data.
- Analyze: maximize portfolio value, align and prioritize and balance supply and demand
- Approve: finalize proposed portfolio, authorize services and resources.
- Charter: communicate decisions, allocate resources and charter services.[4]
These four methods or sub processes of service portfolio management are shown in the following diagram:
source: Tutorials Point
Objective of Service Portfolio Management[5]
The purpose of Service Portfolio Management is to create, manage and improve a service portfolio containing a detailed design package for each IT service. Service Portfolio Management contributes to an integrated Service Management approach by achieving the following goals:
- Every service planned and operated by the provider is documented.
- Every new service runs through a set of standardized activities and procedures to ensure that essential management-relevant information, for service delivery and support, are documented and provided to the relevant management processes.
- Every service and their design packages are reviewed at regular intervals.
- Every service is reviewed within the Continual Service Improvement Process
- Through the service portfolio, an information base for a service catalog is provided.
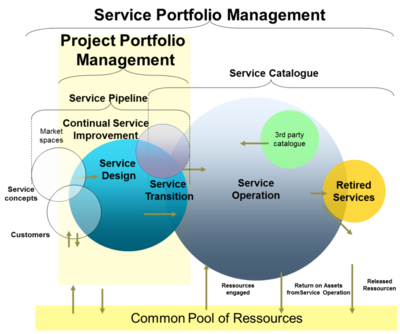
Project Portfolio Management Vs. Service Portfolio Management[6]
It can be argued that while Project Portfolio Management is still the key IT Governance player in most IT organizations, it is absolutely important to extend this by a predominant Service Portfolio Management in order to be a successful IT Service Provider, delivering value to the business.
If we compare Project and Service Portfolio Management, they have obviously many things in common. First of all they both share the same technique and same goal of general Portfolio Management: Making right decisions about investments (by the way, interestingly enough this is not different from classical Financial Portfolio Management, which is completely non-IT):
Project and Service Portfolio Management compared
source: ITIL.ORG
- For Service Portfolio Management this means that each new service or change to an existing service needs to have a clear business case, showing the value to the business (part of the service pipeline). This portfolio technique is continued by tracking the investment of services throughout their lifecyle service design, transition and operation), thus enabling the company to evaluate its strategy, as well as its ability to execute according to their strategy.
- On the other hand, Project Portfolio Management does the same for the lifecycle of projects. It ensures you do the right projects the right way. Since new services or changes to existing services are typically managed as projects, the Project Portfolio Management is obviously very much part of the Service Portfolio Management (and not the other way around).
The Benefits of Service Portfolio Management[7]
Employing service portfolio management may involve a radical re-do for all business units involved, but its benefits are measurable:
- Customers understand exactly what you, as a service provider, will deliver
- There’s cradle-to-grave transparency into value, costs, and risks
- Services in the pipeline can be monitored as well as operational services
- It helps to justify proposed services and major changes to existing services
Ultimately, tracking the value, cost, and risk of every service your service organization provides also helps to position it as indispensable to your customers, because you know – quickly – how valuable a service is.
See Also
- IT Service Management (ITSM): Service Portfolio Management is a key component of ITSM, focusing on the management of IT services.
- Service Catalog: A subset of the service portfolio which lists live services or those ready for deployment.
- ITIL Service Lifecycle: Describes the stages a service goes through from inception to retirement. Service Portfolio Management is an integral part of managing the service lifecycle.
- ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library): A set of practices for IT service management (ITSM) that includes guidance on service portfolio management.
- Demand Management: Understanding and managing customer demand is crucial for effective service portfolio management.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA): An agreement between a service provider and a customer. Service Portfolio Management ensures that services align with these agreements.
- ITIL Service Design: Service Portfolio Management might heavily influence service design decisions.
- Service Strategy: Lays out the strategy for the service lifecycle and is intricately connected with service portfolio management.
- Project Portfolio Management (PPM): Similar to Service Portfolio Management but focuses on projects. Both ensure alignment of activities with organizational objectives.
- Business IT Alignment: Service Portfolio Management is one way IT ensures its services align with business goals and strategies.
References
- ↑ What Does Service Portfolio Management Mean? Invensis
- ↑ What is the primary goal of Service Portfolio Management? ITIL news
- ↑ The Process Overview of Service Portfolio Management IT-Processmaps Wiki
- ↑ The four work methods of Service Portfolio Management Sunview Software
- ↑ What is the Objective of Service Portfolio Management? mITSM
- ↑ Comparing Project Portfolio Management to Service Portfolio Management ITIL Blog
- ↑ What are the Benefits of Service Portfolio Management? ITSM tools