Difference between revisions of "Infrastructure Reference Model (IRM)"
(The Infrastructure Reference Mode (IRM) categorizes the network/cloud related standards and technologies to support and enable the delivery of voice, data, video, and mobile service components and capabilities.) |
m (The LinkTitles extension automatically added links to existing pages (https://github.com/bovender/LinkTitles).) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The Infrastructure Reference Mode (IRM) categorizes the network/cloud related standards and technologies to support and enable the delivery of voice, data, video, and mobile service components and capabilities.<ref>Infrastructure Reference Model Definition [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Federal_enterprise_architecture Wikipedia]</ref> | + | The Infrastructure Reference Mode (IRM) categorizes the [[network]]/cloud related standards and technologies to support and enable the delivery of voice, [[data]], video, and mobile [[service]] components and capabilities.<ref>Infrastructure Reference [[Model]] Definition [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Federal_enterprise_architecture Wikipedia]</ref> |
| − | The IRM implementation enables sharing and reuse of infrastructure to reduce costs, increase interoperability across the government and its partners, support efficient acquisition and deployment, and enable greater access to information across enterprises. In addition to providing a categorization schema for IT infrastructure assets, the IRM enables analysis of IT infrastructure assets at a Department or Agency level as well as at a Federal Government level. In the Federal context, the IRM is adopted and used to conduct Government-wide analysis of IT infrastructure assets and to identify consolidation initiatives. In the Department or Agency context, the IRM is used to drive good IT infrastructure asset management practices such as identifying end-of-life assets before they affect the mission of an organization and to identify opportunities for sharing and consolidating infrastructure.<ref>Purpose of the Infrastructure Reference Model [https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/assets/egov_docs/fea_v2.pdf OWH]</ref> | + | The IRM implementation enables sharing and reuse of infrastructure to reduce costs, increase [[interoperability]] across the government and its partners, support efficient [[acquisition]] and deployment, and enable greater access to information across enterprises. In addition to providing a categorization schema for IT infrastructure assets, the IRM enables analysis of IT infrastructure assets at a Department or Agency level as well as at a Federal Government level. In the Federal context, the IRM is adopted and used to conduct Government-wide analysis of IT infrastructure assets and to identify consolidation initiatives. In the Department or Agency context, the IRM is used to drive good IT infrastructure [[asset]] [[management]] practices such as identifying end-of-life assets before they affect the [[mission]] of an [[organization]] and to identify opportunities for sharing and consolidating infrastructure.<ref>Purpose of the Infrastructure [[Reference Model]] [https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/assets/egov_docs/fea_v2.pdf OWH]</ref> |
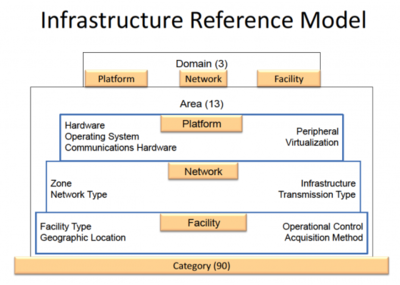
| − | The IRM taxonomy is intended to provide a categorization scheme for physical IT assets, the operating systems and firmware that run them, and the locations or facilities that host the physical IT assets. The IRM is divided into three levels as shown in the figure below. Level 1 of the hierarchy, called “Domain”, consists of three entities, Platform, Network and Facility, | + | The IRM [[taxonomy]] is intended to provide a categorization scheme for physical IT assets, the operating systems and firmware that run them, and the locations or facilities that host the physical IT assets. The IRM is divided into three levels as shown in the figure below. Level 1 of the hierarchy, called “Domain”, consists of three entities, Platform, Network and Facility, |
| − | which are linked and related to each other to enable analysis of IT assets across the three dimensions. Level 2 of the hierarchy, called “Area”, consists of 13 total Areas (for example, “Hardware”) linked to the three Domains in Level 1. Level 3 of the hierarchy, called “Category”, consists of 90 total Categories (for example, “Personal Computer – Laptop”) linked to the 13 Areas in Level 2. The adaptive and loosely coupled approach of the IRM supports multiple levels of executive management, capital planning and architecture stakeholders and their analytical needs.<ref>Structure of the Infrastructure Reference Model[https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/assets/egov_docs/fea_v2.pdf OWH Archives]</ref> | + | which are linked and related to each other to enable analysis of IT assets across the three dimensions. Level 2 of the hierarchy, called “Area”, consists of 13 total Areas (for example, “Hardware”) linked to the three Domains in Level 1. Level 3 of the hierarchy, called “Category”, consists of 90 total Categories (for example, “Personal [[Computer]] – Laptop”) linked to the 13 Areas in Level 2. The adaptive and loosely coupled approach of the IRM supports multiple levels of executive management, [[capital]] planning and [[architecture]] stakeholders and their analytical needs.<ref>Structure of the Infrastructure Reference Model[https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/assets/egov_docs/fea_v2.pdf OWH Archives]</ref> |
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
===Further Reading=== | ===Further Reading=== | ||
| − | Federal Enterprise Architecture Framework Version 2 [https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/assets/egov_docs/fea_v2.pdf OWH] | + | Federal [[Enterprise Architecture]] [[Framework]] Version 2 [https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/assets/egov_docs/fea_v2.pdf OWH] |
Revision as of 16:34, 6 February 2021
The Infrastructure Reference Mode (IRM) categorizes the network/cloud related standards and technologies to support and enable the delivery of voice, data, video, and mobile service components and capabilities.[1]
The IRM implementation enables sharing and reuse of infrastructure to reduce costs, increase interoperability across the government and its partners, support efficient acquisition and deployment, and enable greater access to information across enterprises. In addition to providing a categorization schema for IT infrastructure assets, the IRM enables analysis of IT infrastructure assets at a Department or Agency level as well as at a Federal Government level. In the Federal context, the IRM is adopted and used to conduct Government-wide analysis of IT infrastructure assets and to identify consolidation initiatives. In the Department or Agency context, the IRM is used to drive good IT infrastructure asset management practices such as identifying end-of-life assets before they affect the mission of an organization and to identify opportunities for sharing and consolidating infrastructure.[2]
The IRM taxonomy is intended to provide a categorization scheme for physical IT assets, the operating systems and firmware that run them, and the locations or facilities that host the physical IT assets. The IRM is divided into three levels as shown in the figure below. Level 1 of the hierarchy, called “Domain”, consists of three entities, Platform, Network and Facility,
which are linked and related to each other to enable analysis of IT assets across the three dimensions. Level 2 of the hierarchy, called “Area”, consists of 13 total Areas (for example, “Hardware”) linked to the three Domains in Level 1. Level 3 of the hierarchy, called “Category”, consists of 90 total Categories (for example, “Personal Computer – Laptop”) linked to the 13 Areas in Level 2. The adaptive and loosely coupled approach of the IRM supports multiple levels of executive management, capital planning and architecture stakeholders and their analytical needs.[3]
source: The EA Pad
References
- ↑ Infrastructure Reference Model Definition Wikipedia
- ↑ Purpose of the Infrastructure Reference Model OWH
- ↑ Structure of the Infrastructure Reference ModelOWH Archives
Further Reading
Federal Enterprise Architecture Framework Version 2 OWH
